Studies have shown that voiding symptoms do not correlate with a high postvoid residual volume. It is important to have clinical tools that help make early and effective decisions during the initial consultation.
ObjectiveTo assess the validity and degree of concordance between the sensation of incomplete voiding and high postvoid residual volume.
Materials and methodsCross-sectional study of patients who underwent uroflowmetry (UFM) and postvoid residual volume (PVR) measurement due to lower urinary tract symptoms, with simultaneous scoring of International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire – Female Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (ICIQ-FLUTS) or Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (ICIQ-MLUTS) during 2014–2015. We analyzed the relationship between these data and the postvoid residual volume.
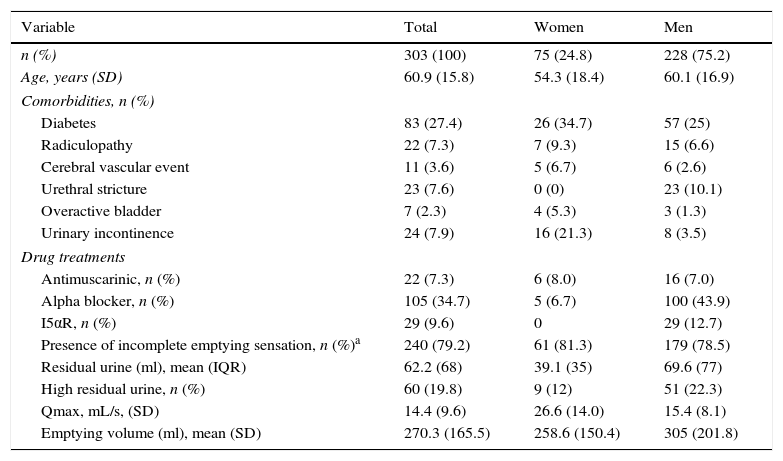
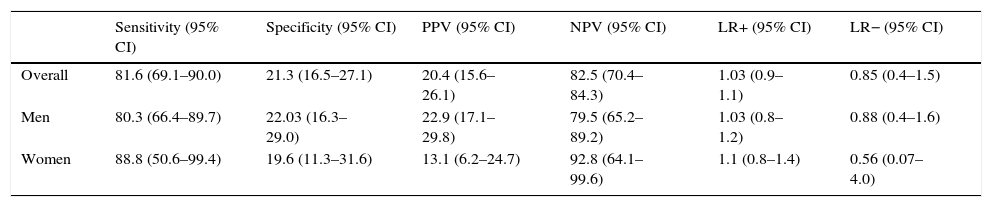
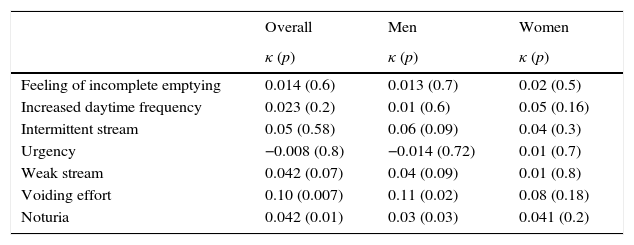
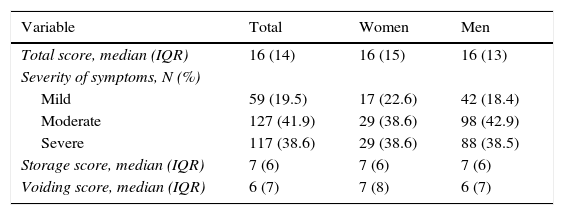
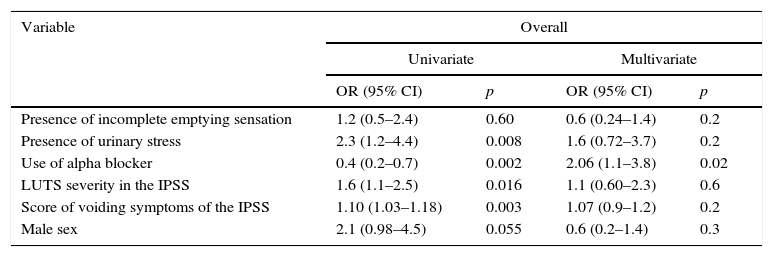
ResultsThe study included 303 patients, 75 (24.8%) of whom were women and 228 (75.2%) of whom were men. The mean age was 60.9 years (SD, 15.8), and the mean Qmax was 14.47mL/s (SD, 9.6). Sixty (19.8%) patients had a high PVR. We detected 240 (79.2%) patients with sensations of incomplete voiding (SIV), but its presence was not associated with a high PVR in the population. For the SIV, the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and positive and negative likelihood ratios were 81.6%, 21.3%, 20.4%, 82.5%, 1.03 and 0.85, respectively. The area under the curve for the frequency of SIV was 0.52 (95% CI, 0.44–0.60, p=0.5). The degree of concordance between SIV and high PVR was 0.014 (p=0.6). In the ICIQ-MLUTS, PVR correlated with intermittence (Rho=0.132, p=0.043) but not with SIV (Rho=0.09, p=0.15). In the ICIQ-FLUTS, the frequency of urinary incontinence was positively correlated with PVR (Rho=0.216, p=0.026).
ConclusionsThe sensation of incomplete voiding is not associated with a high postvoid residual volume. Other variables such as symptom severity, urinary effort and total score for voiding symptoms can be associated with a high residual urine volume.
Algunos estudios han demostrado que los síntomas de vaciado no correlacionan con el residuo posmiccional elevado. Es importante contar con herramientas clínicas que permitan tomar decisiones prontas y efectivas en la primera consulta.
ObjetivoEvaluar la validez y el grado de concordancia entre la sensación de vaciado incompleto y el residuo posmiccional elevado.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal de pacientes a los que se les realizó uroflujometría (UFM) y medición de residuo posmiccional (RP) por síntomas urinarios inferiores con determinación simultánea de IPSS, ICIQ-FLUTS o ICIQ-MLUTS durante los años 2014-2015. Analizamos la relación entre estos datos con el volumen del residuo posmiccional.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 303 pacientes: 75 (24,8%) mujeres y 228 (75,2%) hombres, con una edad media de 60,9años (DE15,8) y un Qmáx medio de 14,47ml/s (DE9,6); 60 (19,8%) presentaron RP elevado. Se detectaron 240 (79,2%) pacientes con sensación de vaciado incompleto (SVI) y su presencia no se asoció a RP elevado en la población. Para la SVI, la sensibilidad, la especificidad, el valor predictivo positivo y negativo, y los cocientes de probabilidad positivos y negativos fueron de 81,6%, 21,3%, 20,4%, 82,5%, 1,03 y 0,85, respectivamente. El área bajo la curva para la frecuencia de SVI fue de 0,52 (IC95%, 0,44-0,60, p=0,5). El grado de concordancia entre SVI y RP elevado fue de 0,014 (p=0,6). En el cuestionario ICIQ-MLUTS correlacionó RP con intermitencia (Rho=0,132, p=0,043) y no con SVI (Rho=0,09, p=0,15). En el ICIQ-FLUTS la frecuencia de incontinencia urinaria correlacionó positivamente con el RP (Rho=0,216, p=0,026).
ConclusionesLa sensación de vaciado incompleto no se asocia a un residuo posmiccional elevado. Otras variables, como severidad de los síntomas, esfuerzo miccional y puntuación total de síntomas de vaciado, pueden asociarse con una orina residual elevada.