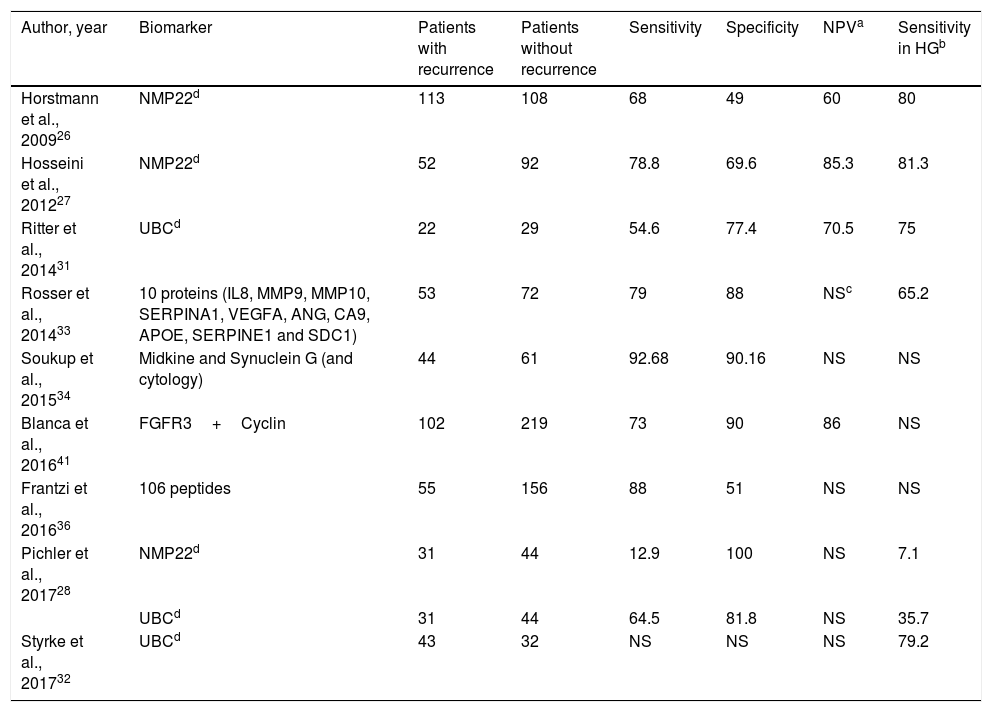
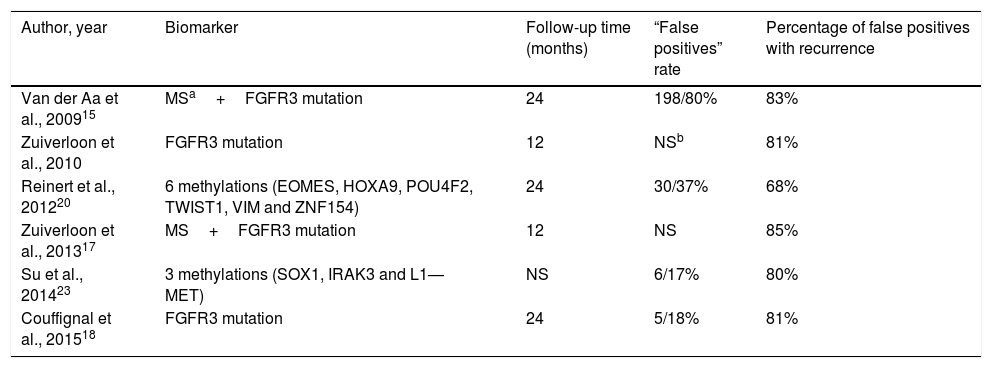
The surveillance of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) is usually performed by cystoscopy and cytology. Until today, no effective urinary biomarker has been used to reduce the morbidity and cost associated with these procedures.
ObjectiveTo describe the performance of urinary biomarkers in the surveillance of NMIBC.
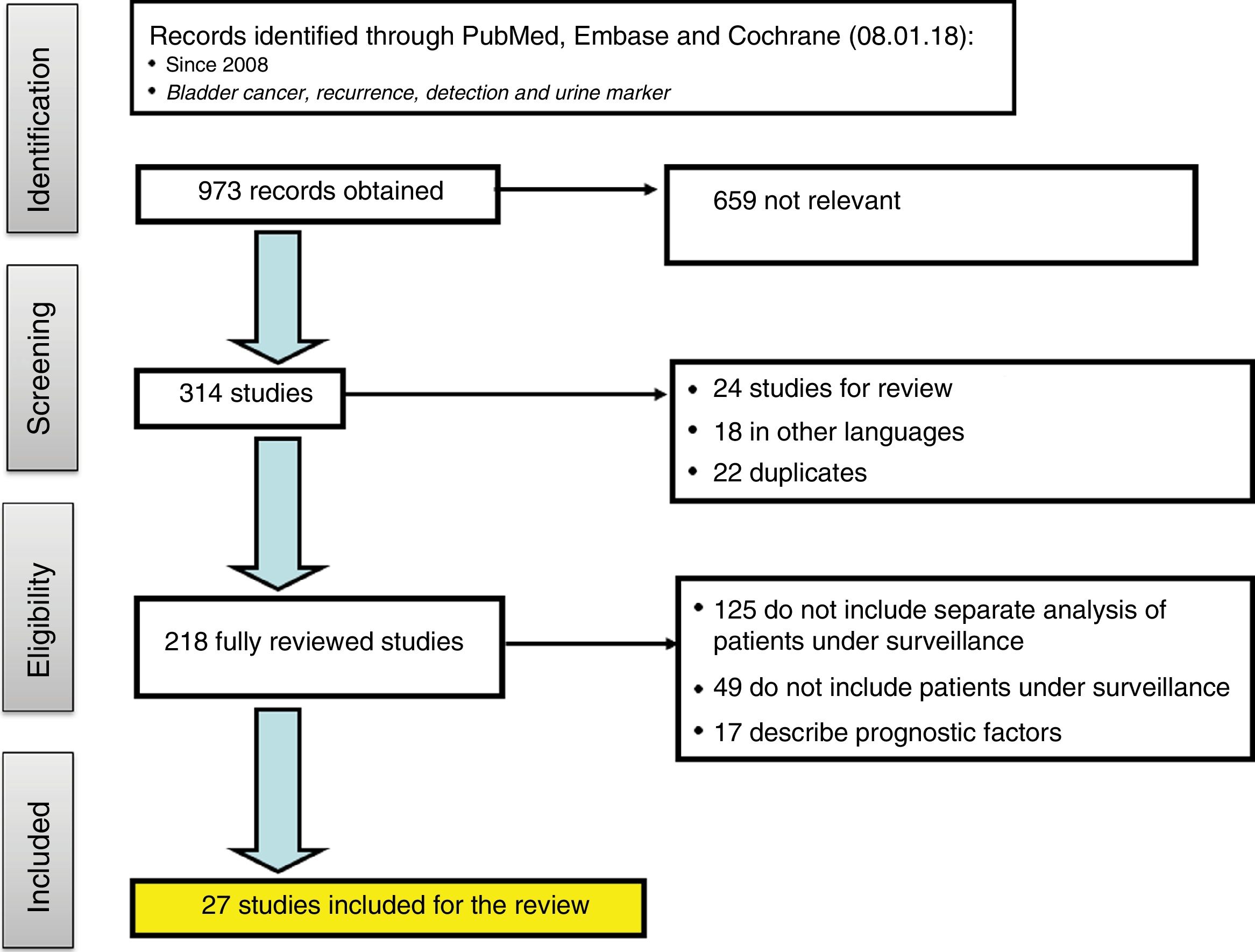
Evidence acquisitionOn August 1, 2018, a bibliographic search was carried out in Pubmed, Embase and Cochrane Library, limited to the last 10 years, with the terms: bladder cancer, recurrence, detection and urine marker. 973 registers were obtained, and 27 publications were selected following the PRISMA recommendations.
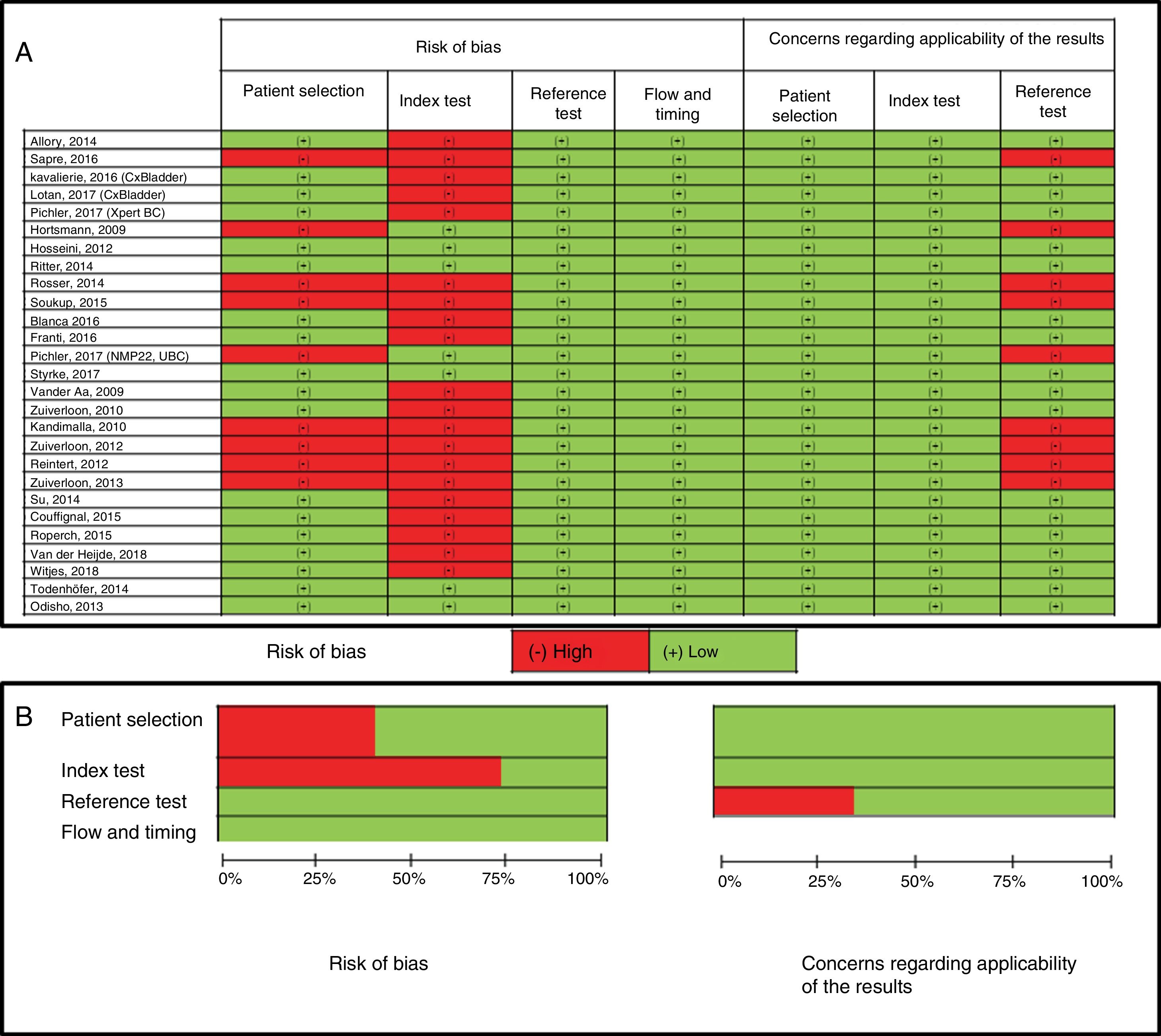
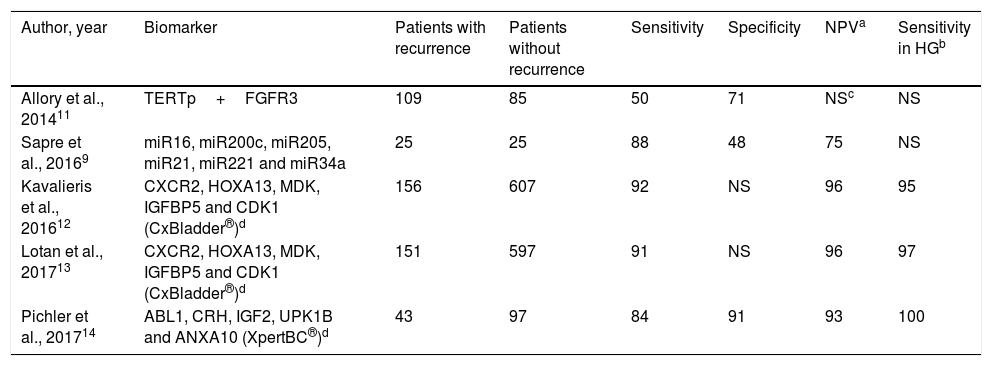
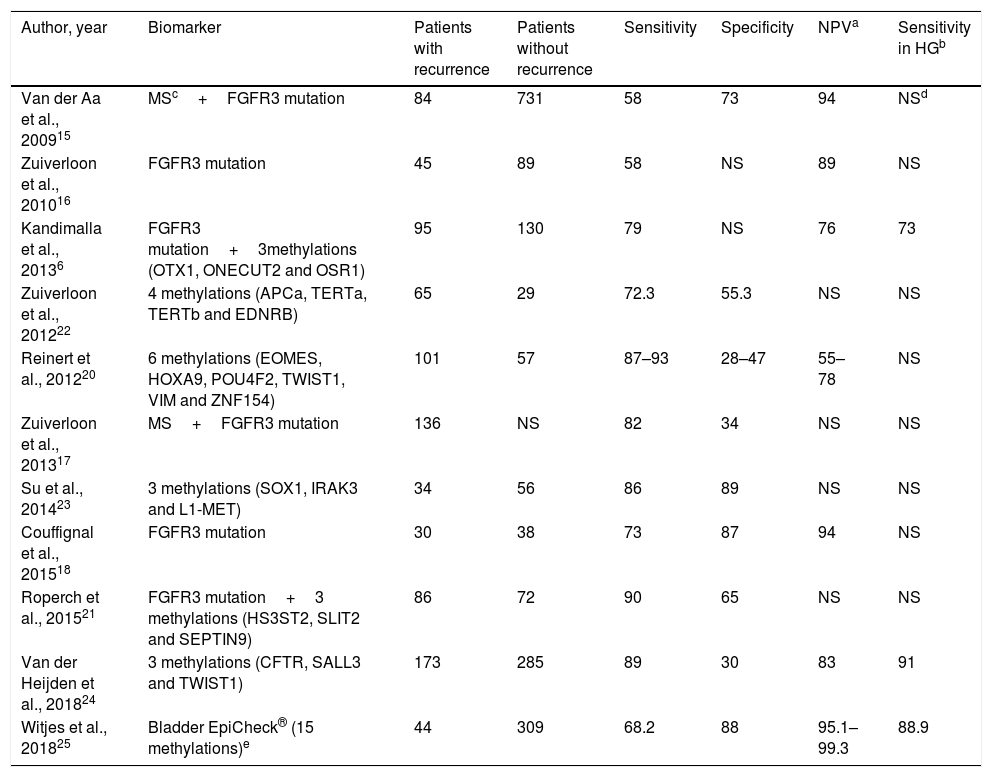
Evidence synthesisThe negative predictive values (NPV) of several assays could reduce the number of cystoscopies in NMIBC surveillance. Six transcription-factor trials had an NPV rate greater than 90%, and one of them can be performed at the control point. Six transcription-factors evaluations describe anticipated diagnosis between 68% and 83% of their “false positives”. Two transcription factors and one protein assays proved reduction between 23% and 35% of surveillance cystoscopies. Nowadays, cell-based assays are restricted to reflex test after doubtful cytologies.
ConclusionThere are few studies analysing the improvement of the NMIBC surveillance protocols. Several transcription factor assays are more precise and allow anticipatory diagnosis. Currently, there are no comparative studies between alternative surveillance protocols and classic ones.
La vigilancia del tumor vesical no músculo infiltrante (TVNMI) se realiza habitualmente mediante cistoscopia y citologías urinarias seriadas. Hoy, no se utiliza ningún marcador urinario, suficientemente eficaz, para reducir la morbilidad y coste de este seguimiento.
ObjetivoDescribir el rendimiento de los marcadores urinarios en la vigilancia del TVNMI.
Adquisición de la evidenciaEl 1 de agosto de 2018 se realizó búsqueda bibliográfica en Pubmed, Embase y librería Cochrane, acotada a los últimos 10 años, con los términos: bladder cancer, recurrence, detection y urine marker. Se obtuvieron 973 registros y siguiendo las recomendaciones PRISMA se seleccionaron 27 publicaciones.
Síntesis de la evidenciaLos valores predictivos negativos de varios ensayos permitirían reducir el número de cistoscopias en la vigilancia del TVNMI. Seis ensayos de factores de transcripción tuvieron un valor predictivo negativo superior al 90% y uno de ellos se puede realizar en el punto de control. Seis ensayos de factores de transcripción describen diagnóstico anticipado entre el 68% y 83% de sus «falsos positivos». Dos ensayos de factores de transcripción y uno de proteínas demuestran reducir entre el 23% y el 35% de las cistoscopias de vigilancia. Los ensayos celulares se restringen a pruebas reflejo ante citologías urinarias dudosas.
ConclusiónExisten pocas publicaciones que permitan analizar la mejoría del protocolo de vigilancia del TVNMI. Los ensayos de factores de transcripción tienen la mejor precisión diagnóstica y algunos permiten diagnóstico anticipado. Hoy en día no hay análisis que comparen entre protocolos alternativos de vigilancia y el convencional.