Different degrees of testicular torsion result in varying degrees of testicular damage, which influences treatment options and outcomes. Therefore, establishing a testicular torsion model with different degrees is necessary for clinical diagnosis.
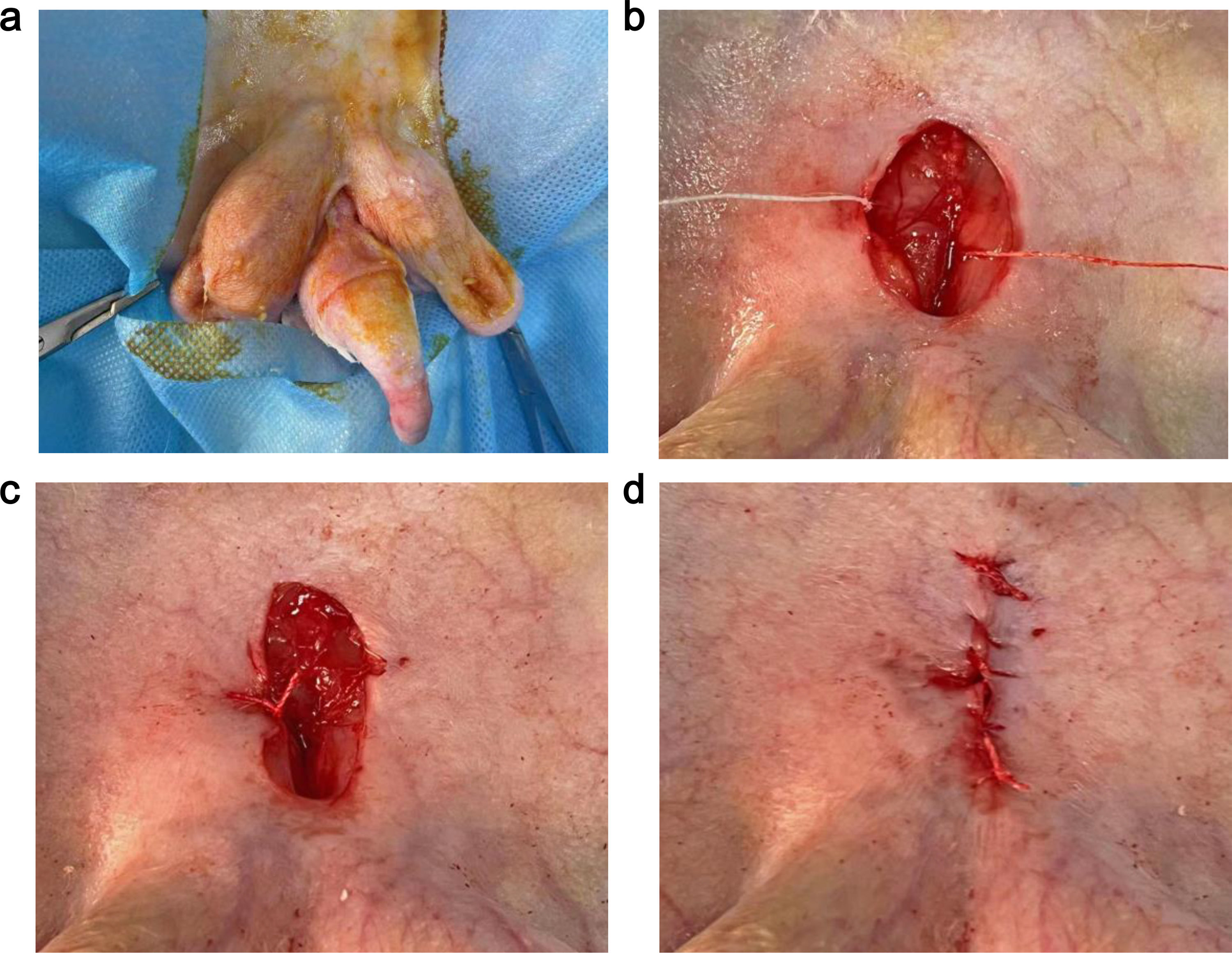
Materials and methodsRabbits were randomly divided into four groups and their spermatic cords were twisted at 0 °, 180 °, 360 °, and 720 °, respectively. Color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI) were performed to evaluate the blood supply in testicles. The twisted testicles were surgically removed at six hours post-operation and were evaluated by morphological observation and Hematoxylin and Eosin staining.
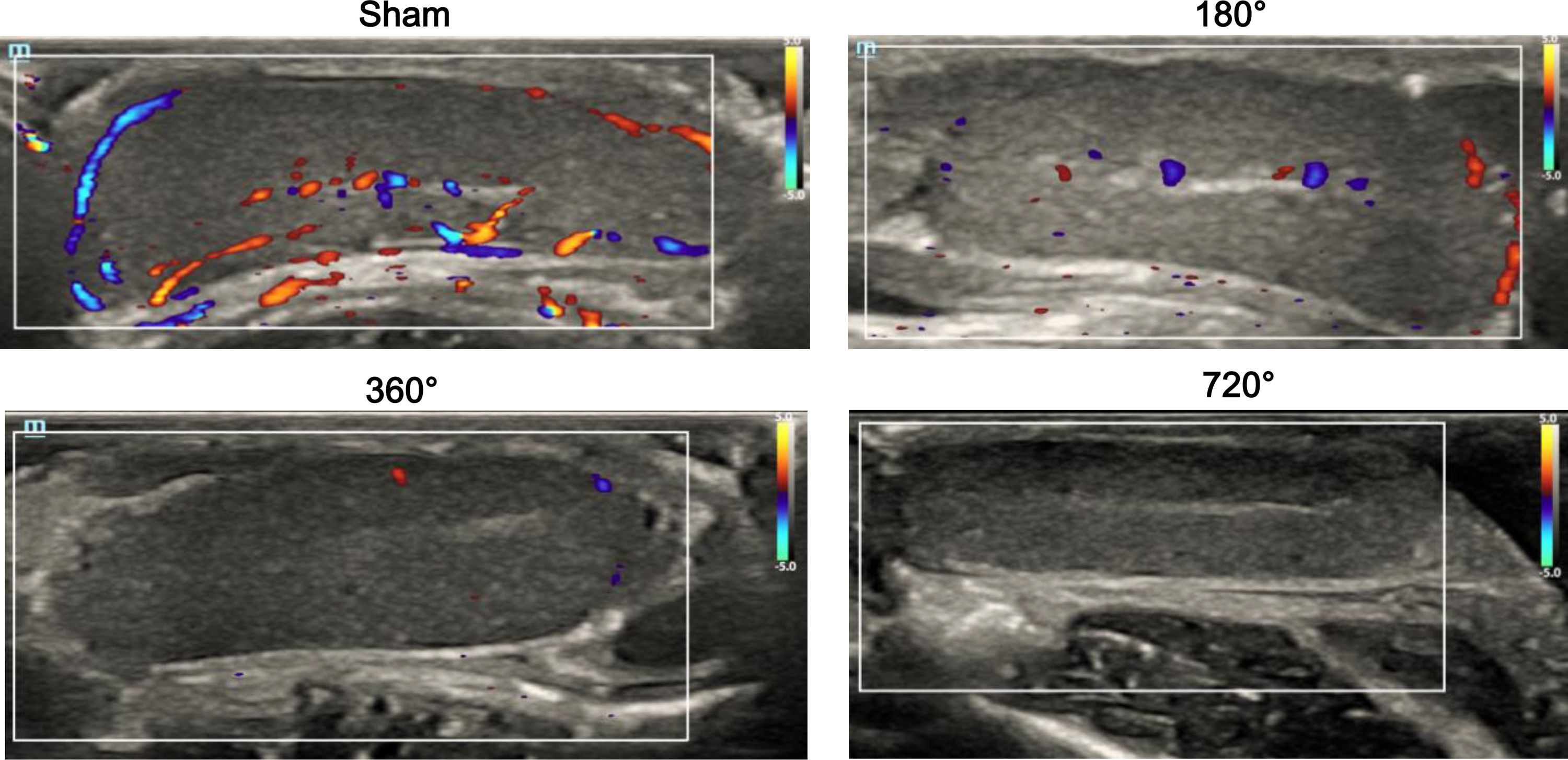
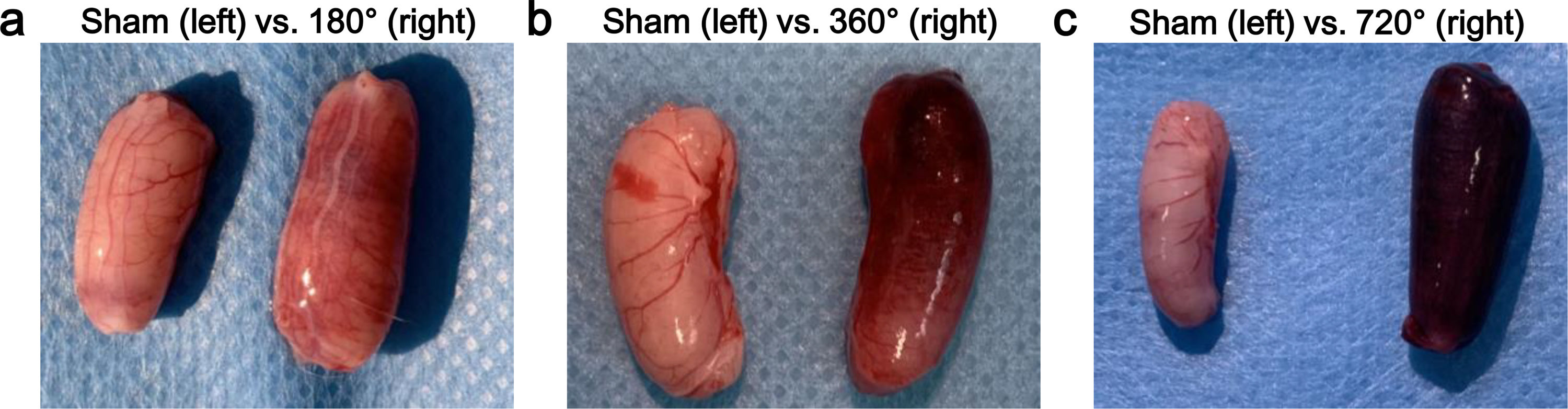
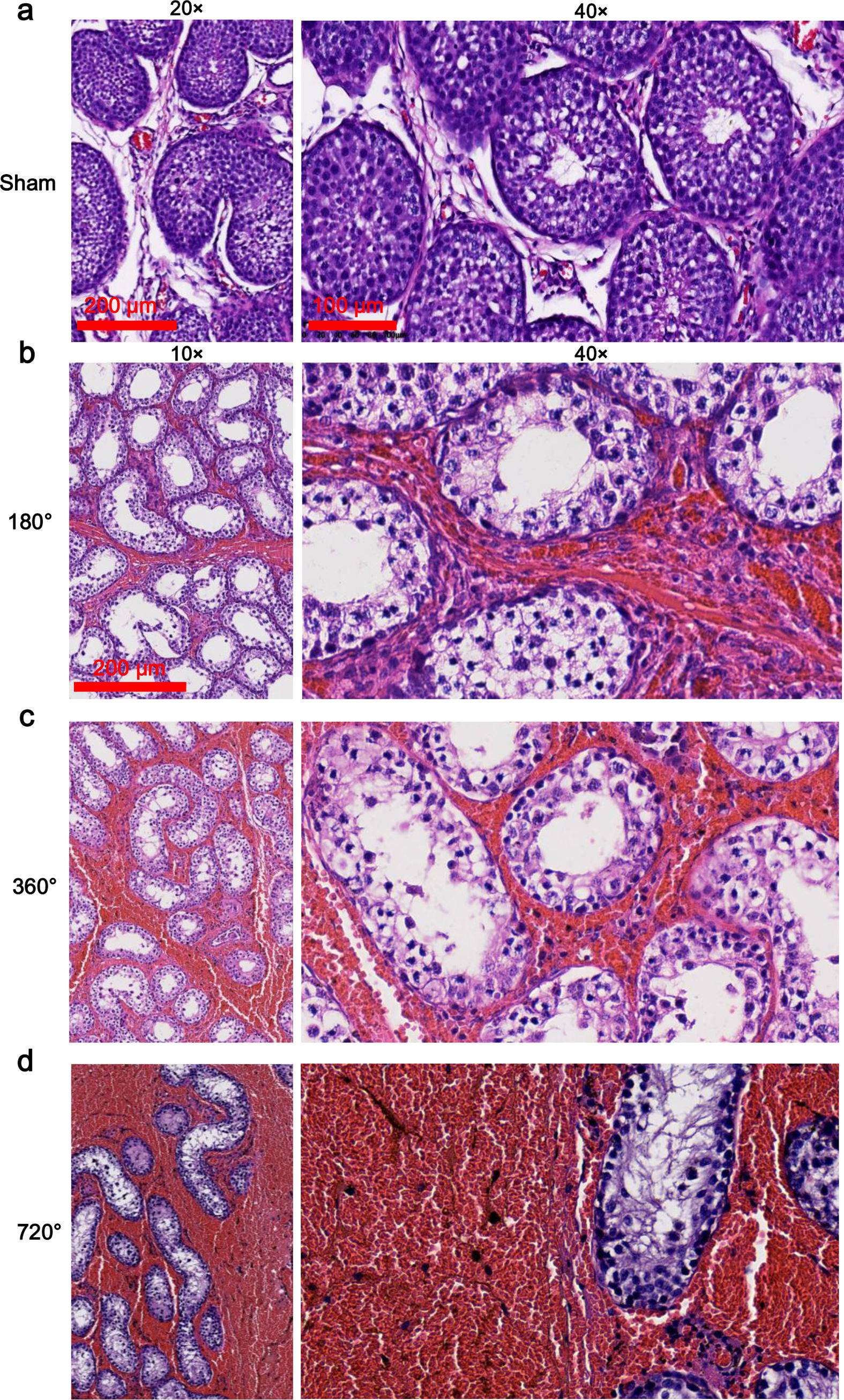
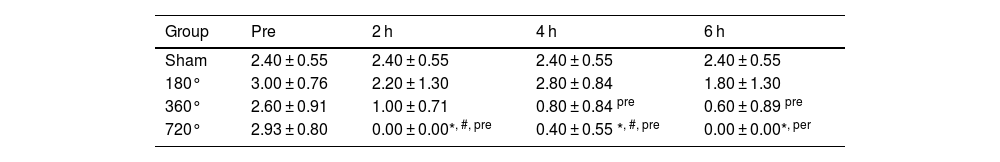
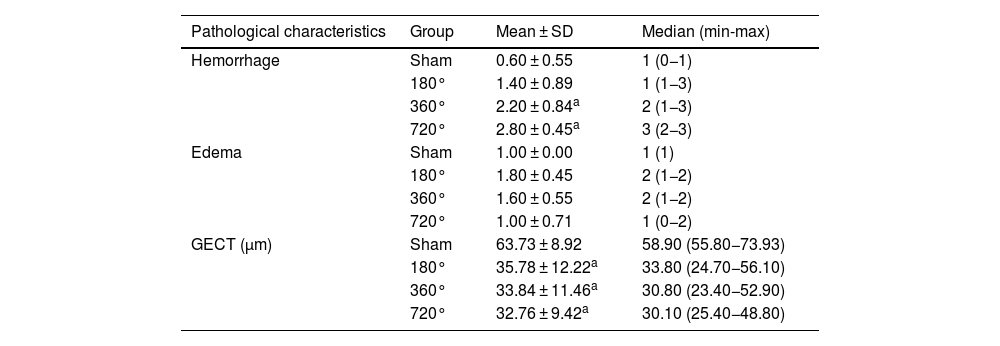
ResultsCDFI signals were gradually decreased as the degree of testicular torsion increased, and scores of CDFI in the 360 ° and 720 ° groups were significantly decreased at postoperative six hours compared to pre-surgery. Compared to the sham, the testicle in the 180 ° group exhibited slight congestion, whereas the testicles in the 360 ° and 720 ° groups were dark red in color and had severe congestion and unrecognizable vessels. Hematoxylin and Eosin staining showed mild spermatogenic cell reduction and testicular interstitial hemorrhage in the 180 ° group. In the 360 ° and 720 ° groups, disordered seminiferous tubules, shed spermatogenic cells in tubules, inflammatory cell infiltration, and severe hemorrhage were found. In comparison with the sham, interstitial hemorrhage scores in the 360 ° and 720 ° groups were significantly higher, and scores of germinal epithelial cell thickness in the three testicular torsion groups were significantly decreased.
ConclusionsCollectively, we successfully constructed a testicular torsion model with different degrees in rabbits.
La gravedad del daño testicular provocado por la torsión del cordón espermático depende del grado de la torsión, lo que a su vez determina las opciones de tratamiento y los resultados. Por este motivo consideramos necesario elaborar un modelo con diferentes grados de torsión testicular para mejorar el diagnóstico clínico.
Materiales y métodosLos conejos se asignaron de forma aleatoria a cuatro grupos con diferentes grados de torsión del cordón espermático: 0 °, 180 °, 360 ° y 720 °. Se evaluó el flujo sanguíneo de los testículos mediante imágenes de flujo eco Doppler color (CDFI). Los testículos torsionados se extrajeron quirúrgicamente a las seis horas de realizar la torsión y se analizaron sus características morfológicas mediante tinción con hematoxilina-eosina.
ResultadosLas señales de CDFI disminuyeron gradualmente a medida que el grado de torsión aumentaba, y las puntuaciones de CDFI en los grupos de 360 ° y 720 ° fueron significativamente más bajas a la sexta hora de evolución de la torsión, en comparación con los valores preoperatorios. Frente al grupo de intervención quirúrgica simulada, los testículos con torsión de 180 ° presentaban una ligera congestión, mientras que los testículos de los grupos con torsiones de 360 ° y 720 ° presentaban un color rojo oscuro, congestión severa y vasos indistinguibles. La tinción con hematoxilina-eosina mostró una leve reducción de las células espermatogénicas y hemorragia intersticial testicular en el grupo de 180 °. En los grupos con torsiones de 360 ° y 720 ° se observaron túbulos seminíferos desordenados, descamación de células espermatogénicas en los túbulos, infiltración de células inflamatorias y hemorragia severa. Frente al grupo de intervención simulada, los grupos con torsiones de 360 ° y 720 ° presentaron puntuaciones de hemorragia intersticial significativamente más elevadas, y las puntuaciones del grosor de las células del epitelio germinal de los tres grupos de torsión testicular disminuyeron significativamente.
ConclusiónConsideramos que hemos elaborado un modelo exitoso para evaluar los efectos de los diferentes grados de torsión testicular en conejos.