Shiitake fungi (Lentinus edodes) from China, is the second most commonly produced edible mushroom in the world. Its consumption is spreading in the Eastern world and therefore adverse effects are being reported regarding production and intake. The most frequent reaction related to Shiitake is an itching toxicoderma similar to eczema that appears in scratching areas related to raw or lightly cooked Shiitake intake. In some patients, skin prick and/or patch tests were positive for Shiitake, however, not in every cases, and controls also showed similar results. Thus this dermatitis seems to be a toxic, non-allergic disease.1,2 Clinical manifestation related to hypersensitivity to Shiitake has been reported related mainly as an occupational disease. Thus, allergic contact dermatitis,3 contact urticaria,4 asthma, rhinitis and conjunctivitis,5 and many cases of hypersensitivity pneumonitis (mushroom workers’ lung)6,7 have been reported in workers involved with Shiitake cultivation and marketing. However, to our knowledge, no food allergy to Shiitake with gastrointestinal symptoms has been reported. Thus, we describe a case of an atopic patient with allergy to Shiitake mushroom showing oesophageal symptoms.
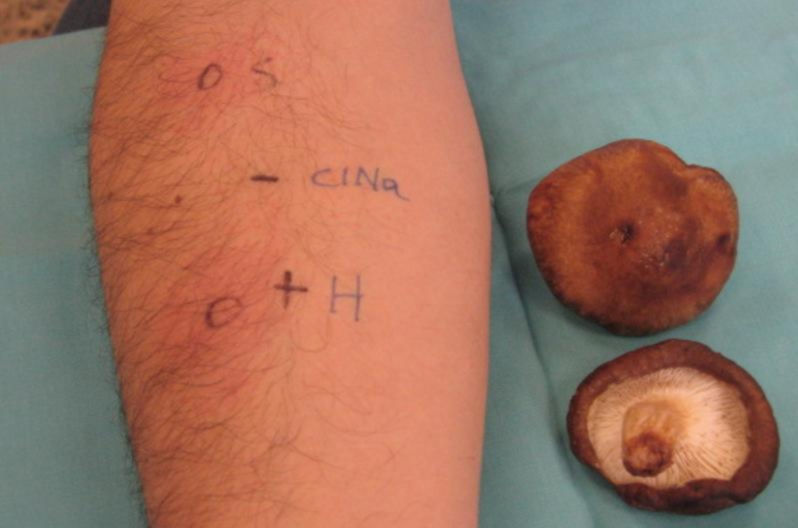
We report a case of a 37-year old man with a studied history of seasonal rhinoconjuntivitis due to grass pollen for 20 years who started referring oesophagic autolimited stop after eating the fungi Shiitake. He also referred choking of some minutes of duration followed by a discomfort at that level which lasted for 1–2h without needing any emergent attention for food impact. Consumption of other mushrooms was well tolerated. Allergological in vivo study was performed by skin prick test to standard aeroallergens including moulds. Skin test was negative except for grass pollen, as was known, and for Plantago lanceolata pollen, a new sensitisation detected. Prick-to-prick test was performed using fresh Shiitake as well as other edible fresh mushrooms that the patient usually ate (Lactorius deliciosus, Lepista personata, Tuber nigrum, Pleurotus ostreatus, Cantharellus tubaeformis, Agrocybe aegerita, Agaricus campestris, Trichocoma Potatorum, Pleurotus eryngii, Hydnum Repandum). Skin test was positive for Shiitake mushroom (7×4mm) (Fig. 1) and negative for the other fungi. Prick-to-prick was negative for Shiitake in seven controls. A Shiitake home-made extract was prepared in PBS (30%). Basophile activation test (BAT) and histamine release test (HRT) were performed using Shiitake extract at different concentrations (4.9mg/ml, 0.49mg/ml, 0.049mg/ml and 0.0049mg/ml). Both BAT and HRT for Shiitake were positive for the four concentrations tested (Table 1). BAT and HRT were negative to Shiitake in two controls. An endoscopy study was performed showing contractions on the medium and distal third of oesophagus like a bamboo joint and the histological study showed up to nine eosinophils in the oesophageal mucosa.
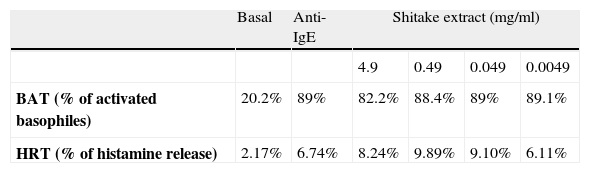
| Basal | Anti-IgE | Shitake extract (mg/ml) | ||||
| 4.9 | 0.49 | 0.049 | 0.0049 | |||
| BAT (% of activated basophiles) | 20.2% | 89% | 82.2% | 88.4% | 89% | 89.1% |
| HRT (% of histamine release) | 2.17% | 6.74% | 8.24% | 9.89% | 9.10% | 6.11% |
BAT (%): Results of percentage of basophiles activated incubated with buffer (basal), Anti-IgE, and four different concentrations of Shiitake extract.
HRT (%): Results of percentage of histamine release test with buffer (basal), Anti-IgE, and four different concentrations of Shiitake extract.
Although clinical symptoms and macroscopic images from the endoscopic study suggested an eosinophilic oesophagitis, the number of eosinophils was not diagnostic. However, some authors suggest that a number of 7–20 eosinophils in oesophagic mucosa could be a probable eosinophilic oesophagitis.8 The fact that the Shiitake is not a frequent food and that the patient refused to eat it due to the symptoms could be responsible for the microscopic findings. Moreover, as there is not a commercial extract available for this mushroom, prick-to-prick has to be done and a home-made extract has been obtained from Shiitake showing specific positive results in in vitro tests supporting the in vivo test findings.
We describe a case of food allergy manifested as oesophageal symptoms due to Shiitake mushroom. Moreover, in vitro tests such as BAT and HRT using home-made extract is a useful technique to diagnose food allergy.