Background and aim: Ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury is the leading cause of early graft dysfunction. Many mechanisms are involved in IR injury; activation of apoptosis is one of the most important. The blockade of the Ca2+ channels inhibits apoptosis and has a potential protector effect against IR injury. Calcium channel blockers, like nifedipine, have potential therapeutic activity against this process in organs such as brain, testicle and intestine. In this project, we aimed to assess the hepatoprotective effect of nifedipine in our IR model.
Material and methods: A total of 18 female Wistar rats were divided into three groups: Sham (SH), IR, and nifedipine+IR (NIR, 10mg/kg, p.o., twice a day for three days). A midline laparotomy was performed, exposing the liver hilum and inducing IR injury to the IR and NIR groups, by using an atraumatic vascular clamp (ischemia: 20min; reperfusion: 1 hour). Serum activities of ALT, AST, LDH, and ALP, and serum concentrations of total bilirubin and glucose were measured. Proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) were determined, and oxidative stress biomarkers (superoxide dismutase, malondialdehyde, and glutathione peroxidase) were assessed. Histological parameters, such as congestion, vacuolization, and necrosis, were evaluated in tissue samples stained with hematoxylin and eosin. All rats were handled according to the Official Mexican Norm NOM-062-ZOO-1999. This project was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of our Institution with registry: HI19-00003.
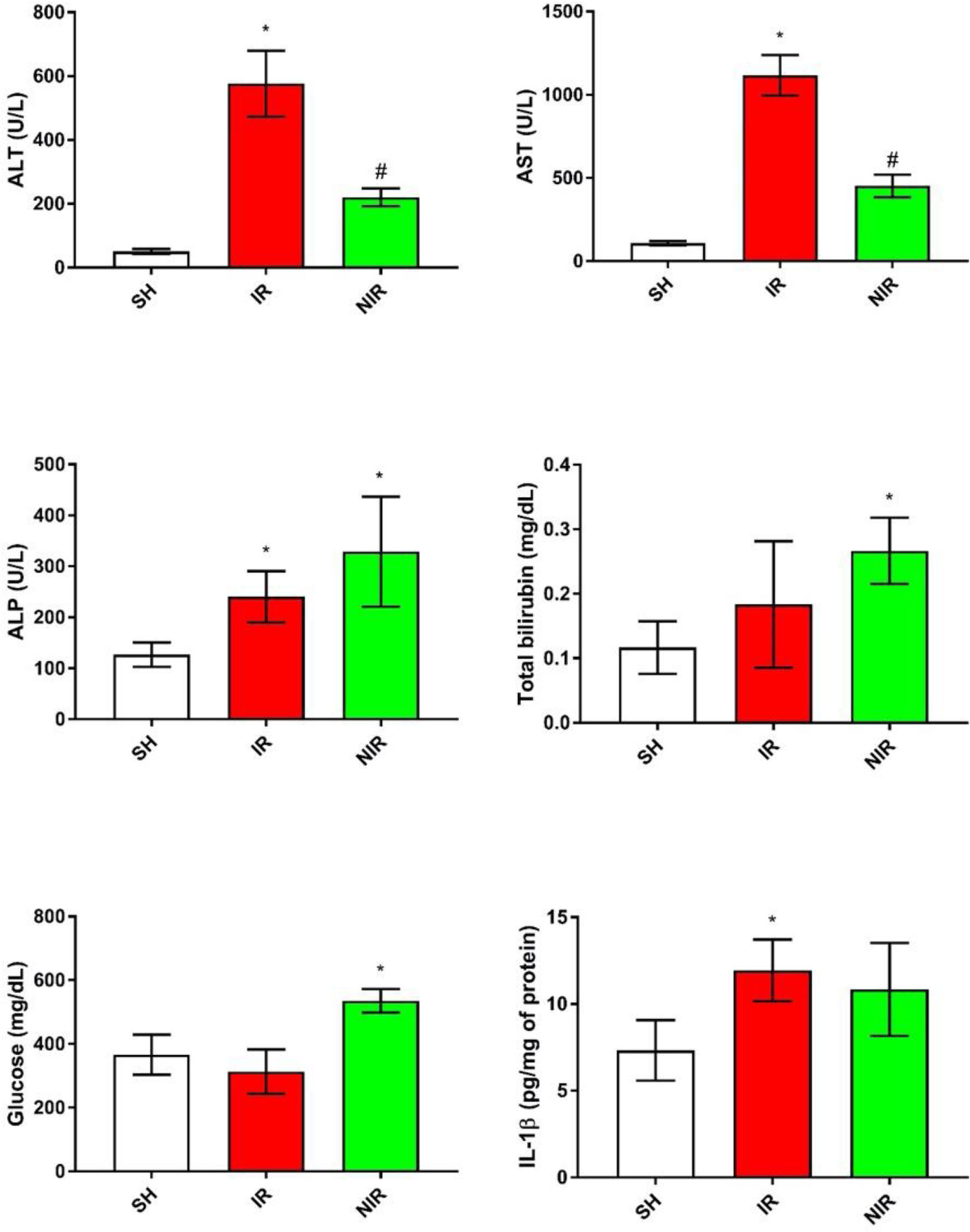
Results: The administration of nifedipine caused a decrease in the serum activities of ALT and AST compared against the IR group. Also, it caused an increase in the activity of ALP probably caused by osteoclastic induction due to nifedipine. The concentration of glucose and total bilirubin compared with the SH group showed an elevation (Figure). There were no significant differences in the other parameters analyzed.
Conclusions: Nifedipine presents a hepatoprotective effect against IR injury, evidenced by the decrease of liver enzymes. This compound does not show an immunomodulator or antioxidant effect.
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.