Abstracts of the 2023 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoIntroduction: Patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) with advanced fibrosis (F3/4) still presented a significant risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). There are models for HCC risk prediction, such as the HCC risk score developed by Iannou et al 2018. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence and risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma development in previously treated chronic HCV patients in an outpatient hepatology clinic at Hospital das Clinicas of University of São Paulo School of Medicine, Brazil.
Materials and MethodsThis is a retrospective, observational and descriptive study in a series of 267 HCV patients. Review of patients’ medical records, applying HCC risk score immediately before and 6 months after SVR, excluding cases with insufficient data and HCC before treatment of HCV. Data collection is still in progress and final results will be available at presentation.
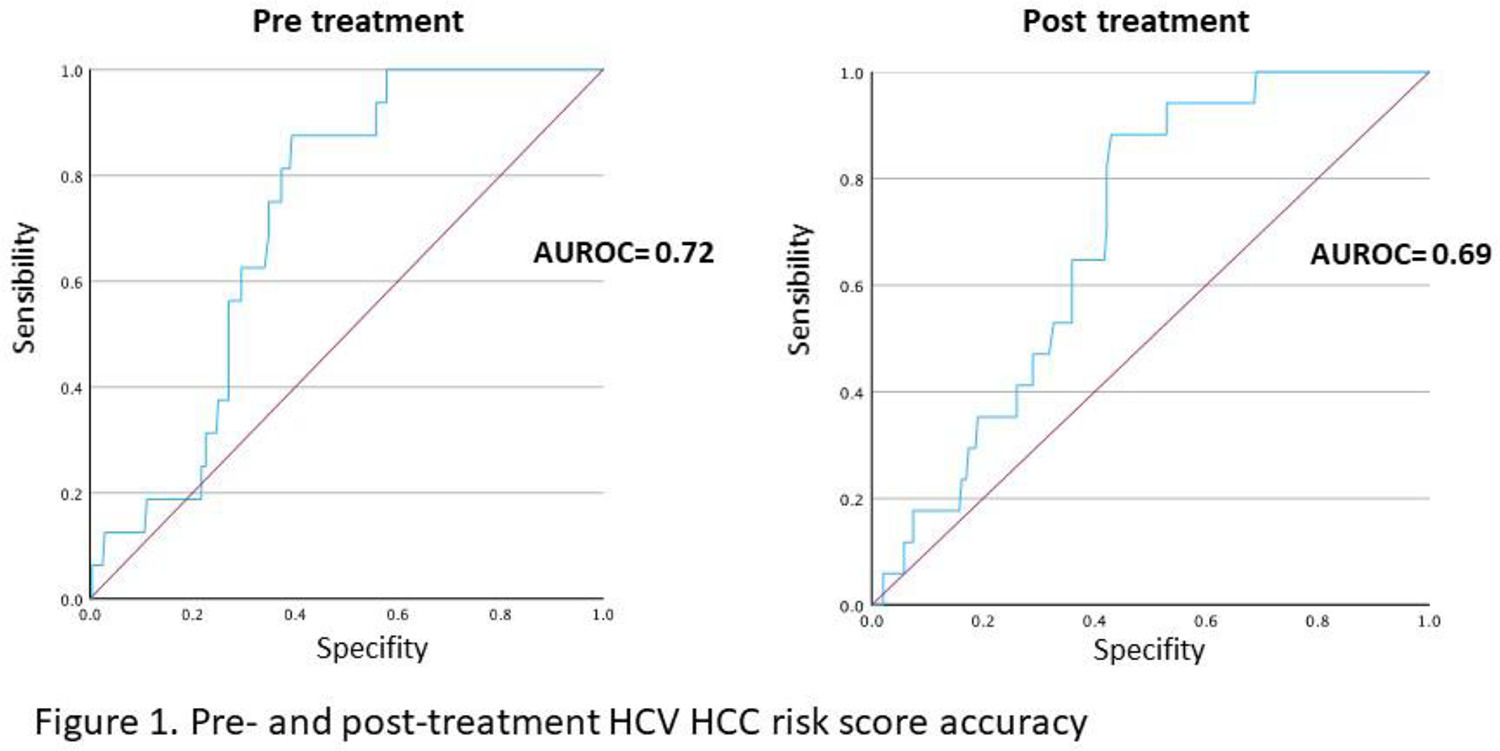
ResultsThe total sample of this study consists of 267 patients, of whom, 127 (47.6%) had F4 degree fibrosis. Overall, 17 patients developed HCC after a median follow up period of 3 years (6.4%). The mean of HCC risk score at 3 years calculated in pre treatment was 9.64% and post treatment was 4.32% (p=0.002). An accuracy of this score was slightly better in the pre treatment (AUROC=0.72) versus post treatment (AUROC=0.69) (Figure 1).
ConclusionsHCC risk score post treatment declines more than 50% compared to pre treatment of HCV, as expected in in patients with HCV cure.