Abstracts of the 2024 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoNo
Introduction and ObjectivesLiver fibrosis is an important prognostic factor in alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis liver disease (MASLD). New drugs in steatotic liver disease (SLD), such as Resmetirom, are indicated in individuals with at least significant fibrosis. Cytokeratin-18 is a hepatocyte cytoskeleton protein that is released during apoptosis in its cleaved form by caspases (M30) and can be used as a non-invasive test (NIT) to stratify liver fibrosis. However, data on its performance is scarce in the Hispanic population. We aim to evaluate the diagnostic performance and additive value of M30 to identify significant fibrosis in a cohort of patients with ALD and MASLD.
Patients / Materials and MethodsWe conducted a cross-sectional cohort study of patients with ALD and MASLD who underwent liver biopsy or transient elastography between 2014–2023. The cutoff points for significant fibrosis (F2) and cirrhosis by transient elastography were ≥7.8 and ≥12.5 kPa, respectively. A receiver operator characteristic (ROC) was used to assess the performance of M30 and FIB-4.
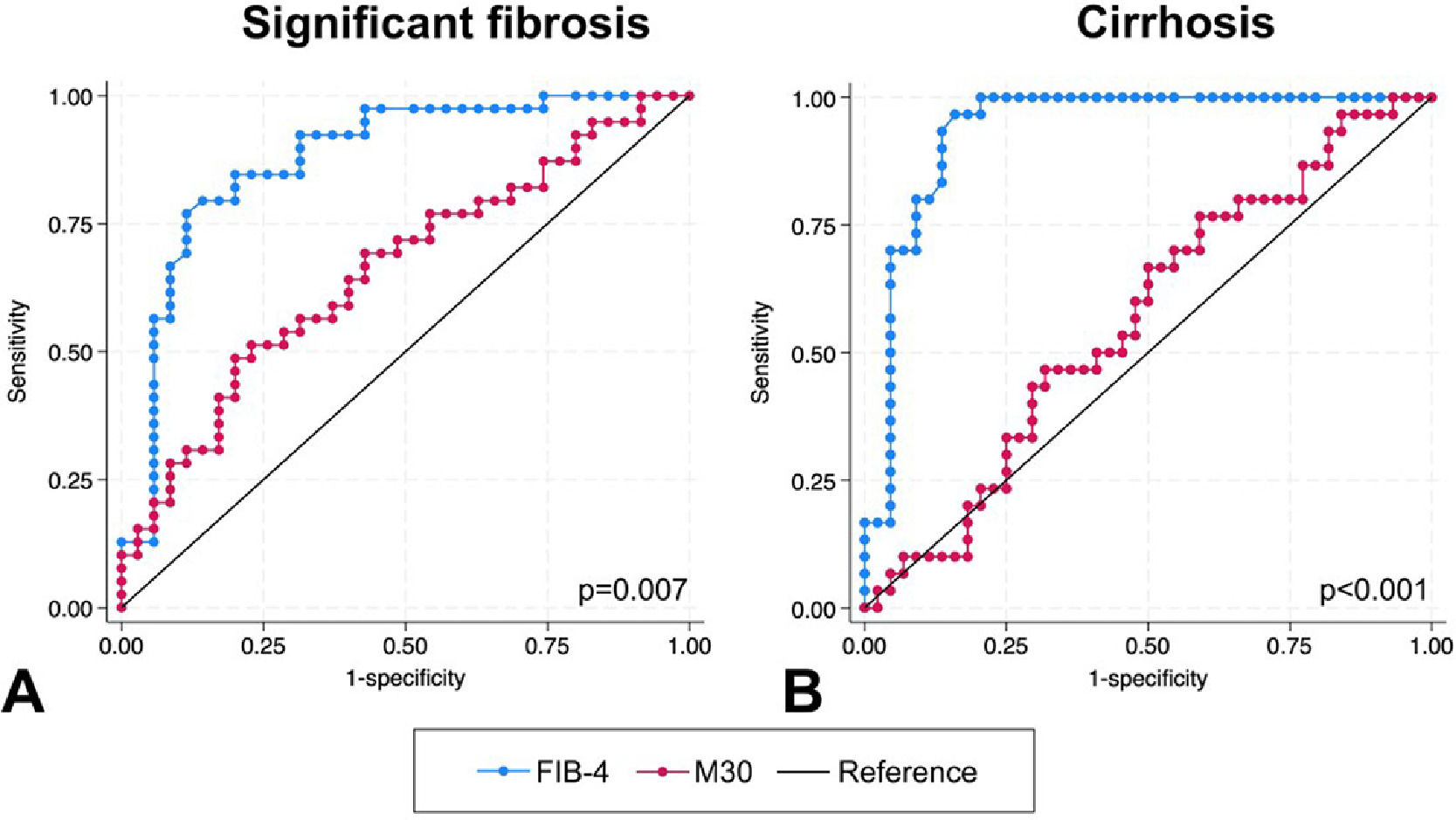
Results and DiscussionWe included 55 ALD and 43 MASLD patients. The median age was 51 [42–60] years and 70.4% were male. Median liver stiffness was 6.8 [4.6–27.9] kPa and median M30 190.4 [146-274.8] U/l. Around 41.8% had F2 and 33.6% had cirrhosis. FIB-4 outperformed M30 in predicting significant fibrosis (AUROC 0.88 vs. 0.66, p-value=0.007) and cirrhosis (AUROC 0.93 vs. 0.56, p-value<0.001) (Figure 1). Five out of 29 (17.2%) patients had a low FIB-4 (<1.3) but significant fibrosis; in this scenario, M30 correctly identified F2 in 4 (80%) of them. Thus, the misclassification of significant fibrosis was reduced from 5.1% to 1.0% using a stepwise assessment with FIB-4 and then M30.
ConclusionsM30 had limited diagnostic value in detecting liver fibrosis in the Hispanic population, but its use in combination with FIB-4 can identify more patients with significant fibrosis than FIB-4 alone.