Abstracts of the 2024 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoNo
Introduction and ObjectivesRecent studies have indicated that certain polymorphisms may be associated with the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
To construct a predictive fibrosis score and evaluate the association of the risk genetic polymorphisms rs738409 PNPLA3, rs58542926 TM6SF2, rs641738 MBOAT7, rs1260326 and rs780094 GCKR, rs72613567 HSD17B13 and rs2642438 MARC1 in MASLD.
Patients / Materials and MethodsThis cross-sectional and retrospective study analyzed 212 biopsy-proven MASLD patient samples from the Hospital das Clínicas, Faculty of Medicine, University of São Paulo. Samples were divided into two groups: Group 1: absent and mild fibrosis (F0-1, n=113) and Group 2: significant and advanced fibrosis (F2-4, n=99). Demographic, laboratory, and histological data were compared, along with their association and frequency with the polymorphisms. Genotyping was performed by real-time PCR allele discrimination, and statistical analysis was conducted using Jasp® and Jamovi® software. The significance level adopted was 5%.
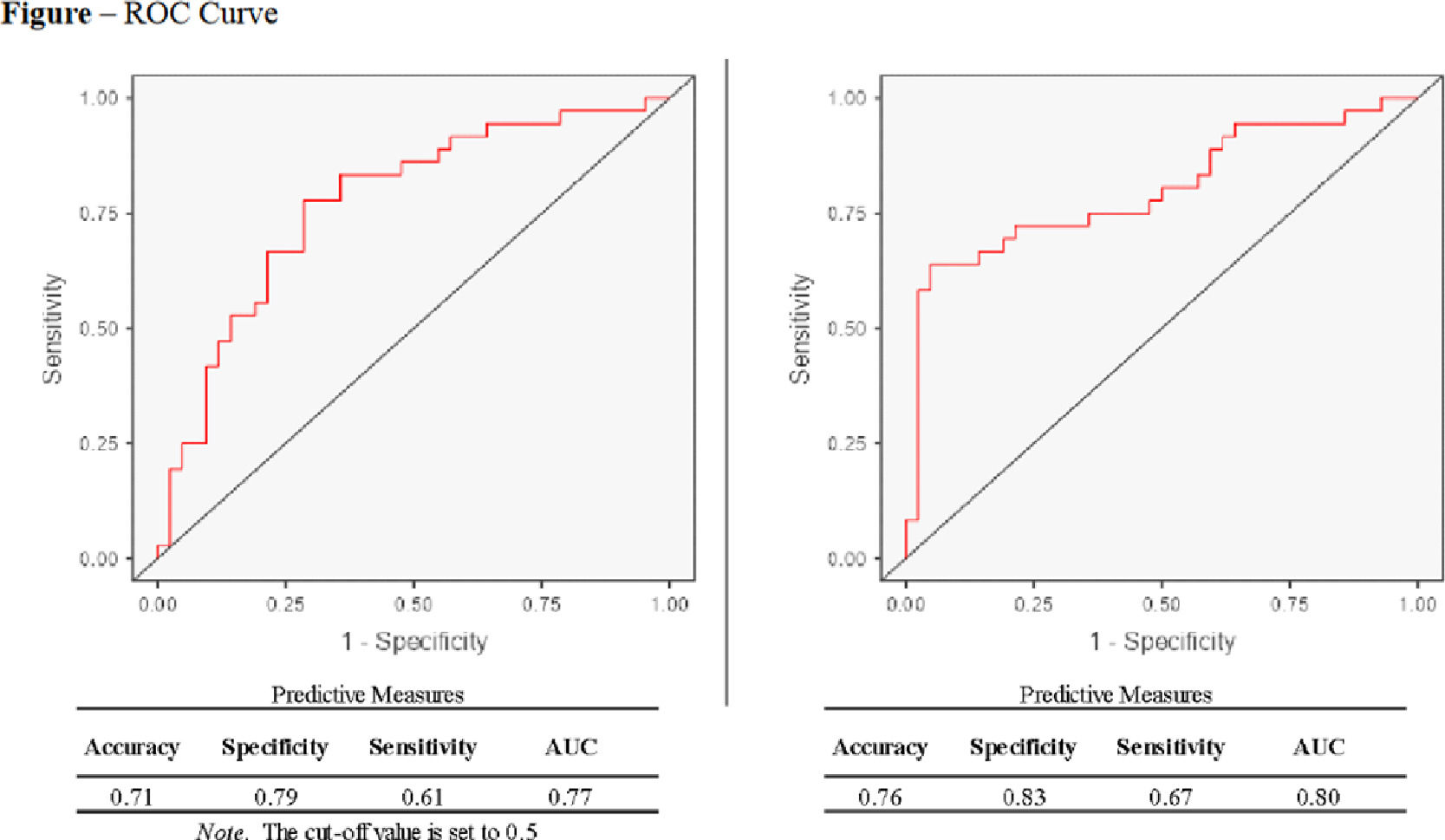
Results and DiscussionMost patients were female (146; 68.9%) with an average age of 56 years and were obese (BMI of 30.7). Group 1 had a higher frequency of dyslipidemia and NAS score 0-4 (71%), higher total cholesterol levels, and lower levels of AST, ALT, GGT, and alpha-fetoprotein compared to Group 2 (p < 0.05). The regression model (ROC Curve) used the TT genotype of the MBOAT7 gene associated with age, ALT, AST, GGT, TG, HDL, LDL, and total cholesterol to predict fibrosis (AUC: 0.77; Sen: 0.61; Spe: 0.79; Acc: 0.71; R²: 0.14) (Fig. 1A). Another model with AFP (n = 76) showed (AUC: 0.80; Sen: 0.67; Spe: 0.83; Acc: 0.76; R²: 0.24) (Fig. 1B). The polymorphisms of the PNPLA3, TM6SF2, GCKR, HSD17B13, and MARC1 genes did not demonstrate risk or protection in this cohort.
ConclusionsThis study underscores the rs641738 MBOAT7 polymorphism as a potential predictor of fibrosis in MASLD, highlighting its value in clinical assessment and management.