Abstracts from XVII Mexican Congress of Hepatology
More infoThis study aimed to estimate risk factors for viral exposure in patients with spontaneous elimination of HCV in the Hepatitis clinic of CMN La Raza.
Materials and MethodsRetrospective, observational, descriptive, cross-sectional and single-center study. Records of patients with antibodies against HCV determined by third-generation ELISA from July 2017 to February 2020 were reviewed; those that did not have sufficient information to carry out the analysis were eliminated, patients with the positive anti-HCV test were selected, confirmatory test with HCV PCR detectable by Abbot's real-time PCR. Risk factors for exposure to HCV and demographic data were collected. The results were analyzed with measures of relative frequencies and obtaining percentages, mean and average.
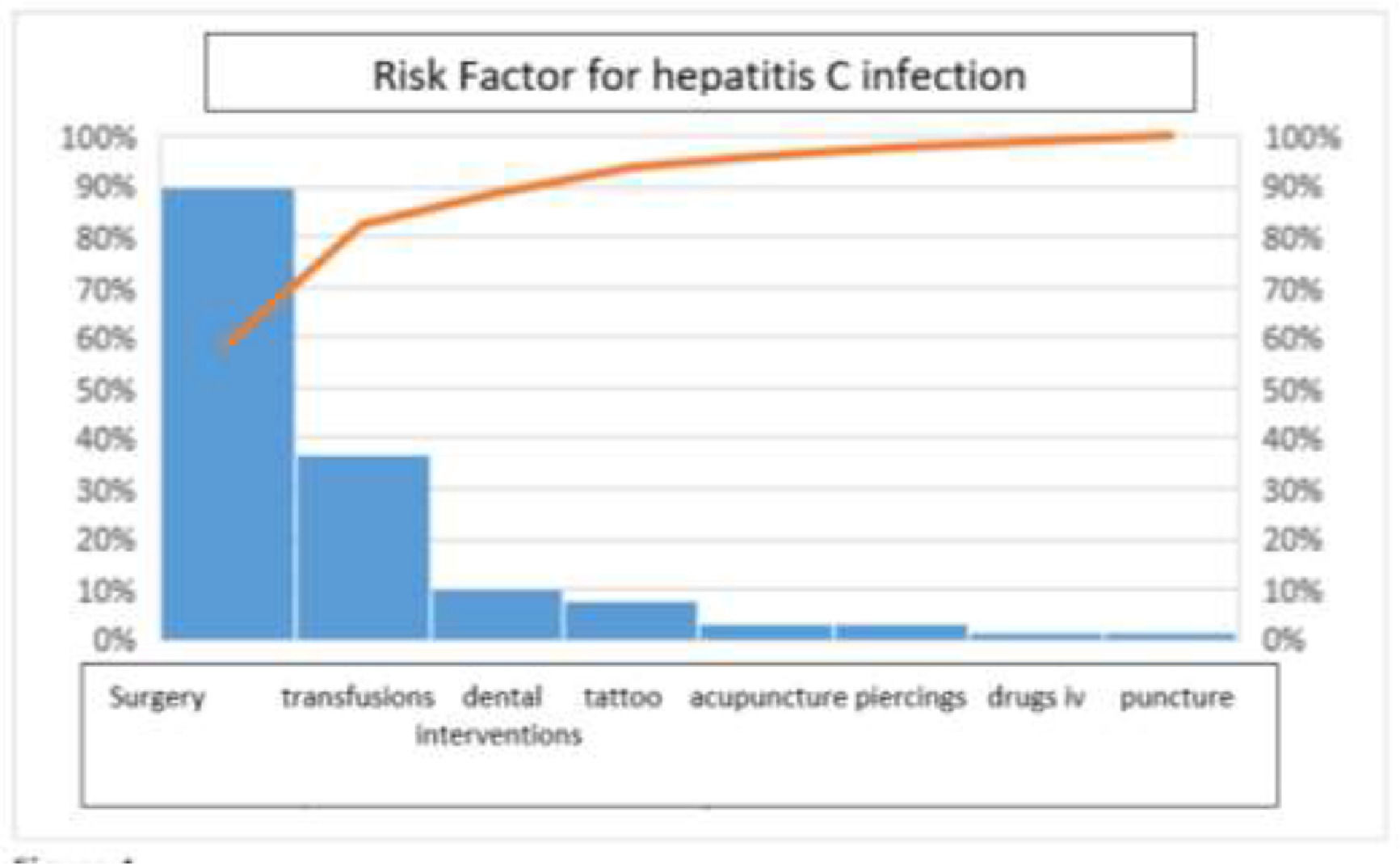
ResultsSixty patients (12.4%) with undetectable anti HCV+/PCR were included; 22 were men (35%) and 40 were women (65%), mean age of 54.4 years. Risk factors for exposure to HCV were: surgery (90%), transfusions (37%), dental interventions (10%). None presented a clinical picture suggestive of viral hepatitis. Associated comorbidities: systemic arterial hypertension (25%), Diabetes mellitus 2 (14%), obesity (8%).
ConclusionsAll the patients studied had risk factors for exposure to HCV, as reported in the literature. A higher frequency of spontaneous elimination of HCV was found in the female gender. All patients with an anti-HCV + test must undergo an HCV RNA test to confirm infection and start antiviral treatment since the spontaneous elimination of HCV is low.
FundingThe resources used in this study were from the hospital without any additional financing
Declaration of interestThe authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.