Abstracts from XVII Mexican Congress of Hepatology
More infoMinimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE) is an important cause of morbi-mortality in patients with cirrhosis; its timely identification has an impact on prognosis; the Stroop Test is a diagnostic tool that can be useful and practical in these patients. Validating this test and calculating the cut-off point for the diagnosis of MHE in our population is important. This study aimed to validate the Stroop Test application and estimate the cut-off point for the diagnosis of MHE in our population.
Materials and MethodsObservational, cross-sectional and prolective study to validate and calculate the cut-off point of the Stroop Test; patients with cirrhosis with and without manifest hepatic encephalopathy will be included, who will undergo the Stroop Test, psychometric score of hepatic encephalopathy (PHES) and the critical flicker frequency test (CFF): ROC curves will be calculated to measure sensitivity, specificity and its cut-off point, healthy subjects will also be included for comparison. The trial was approved by the research ethics committee, and informed consent was obtained.
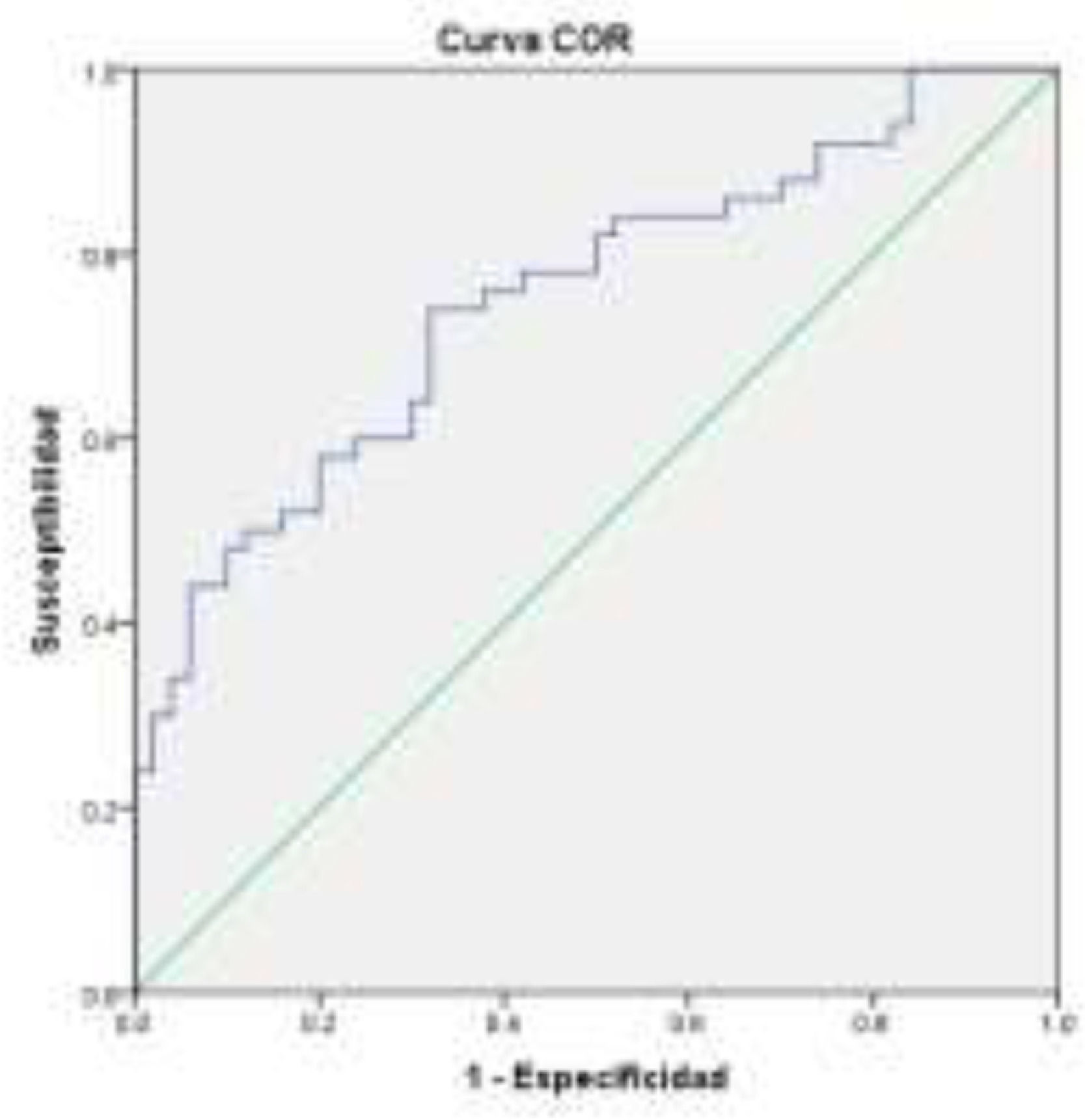
ResultsOne hundred subjects participated: 50 controls, 33 females (66%) age =43.2±12.1 years; and 50 patients with hepatic cirrhosis: 27 females (54%) age 53.2±8.2 years, of which 54%, 42% and 2% were in Child-Pugh A, B and C, respectively. AUROC was calculated for patients with cirrhosis with and without MHE, AUROC= 0.751 (CI=0.656-.846); cut-off point=183.5 sensitivity (SE)=60% specificity (SP)=74% (Figure 1).
ConclusionsFor our study sample, we found that the Stroop Test is a good diagnostic tool, taking into account a cut-off point of 183.5 sec. as opposed to 274.9 sec. that the apple application gives us, which is validated in a different population (grade and quality of education).
FundingDonation by the volunteer ladies of the Hospital General de México “Dr. Eduardo Liceaga.”
Declaration of interestThe authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.