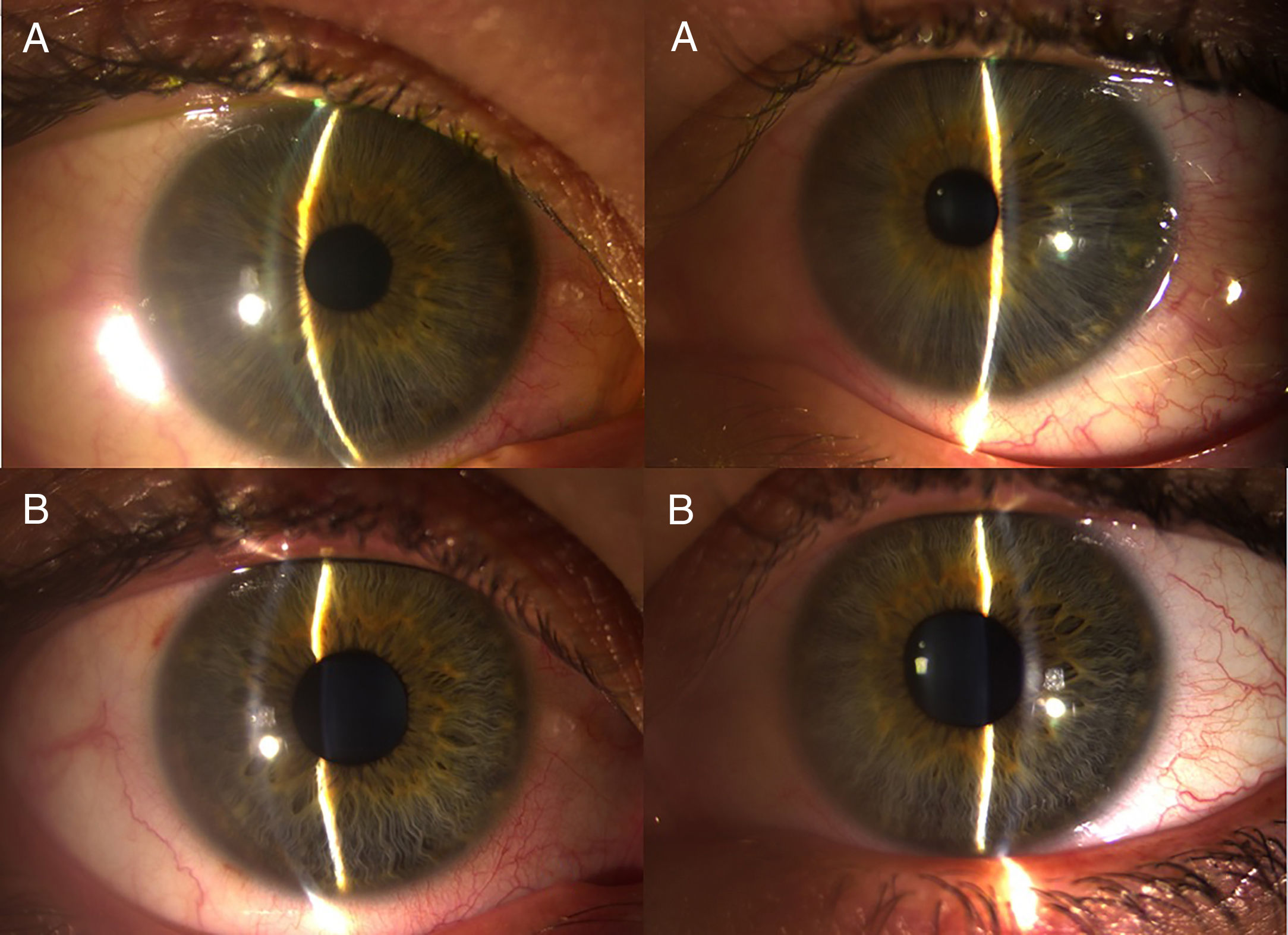
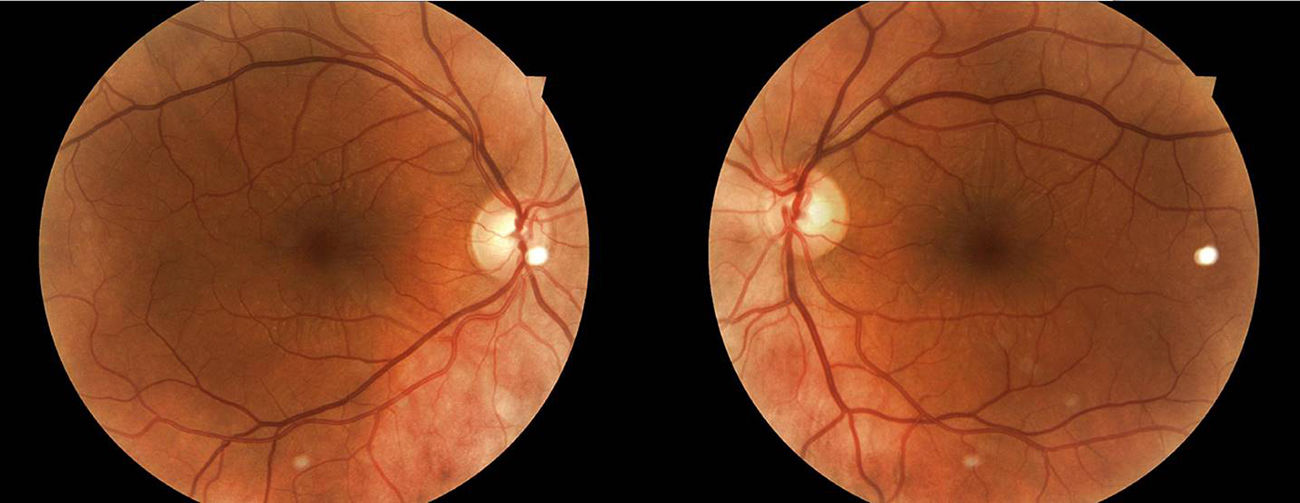
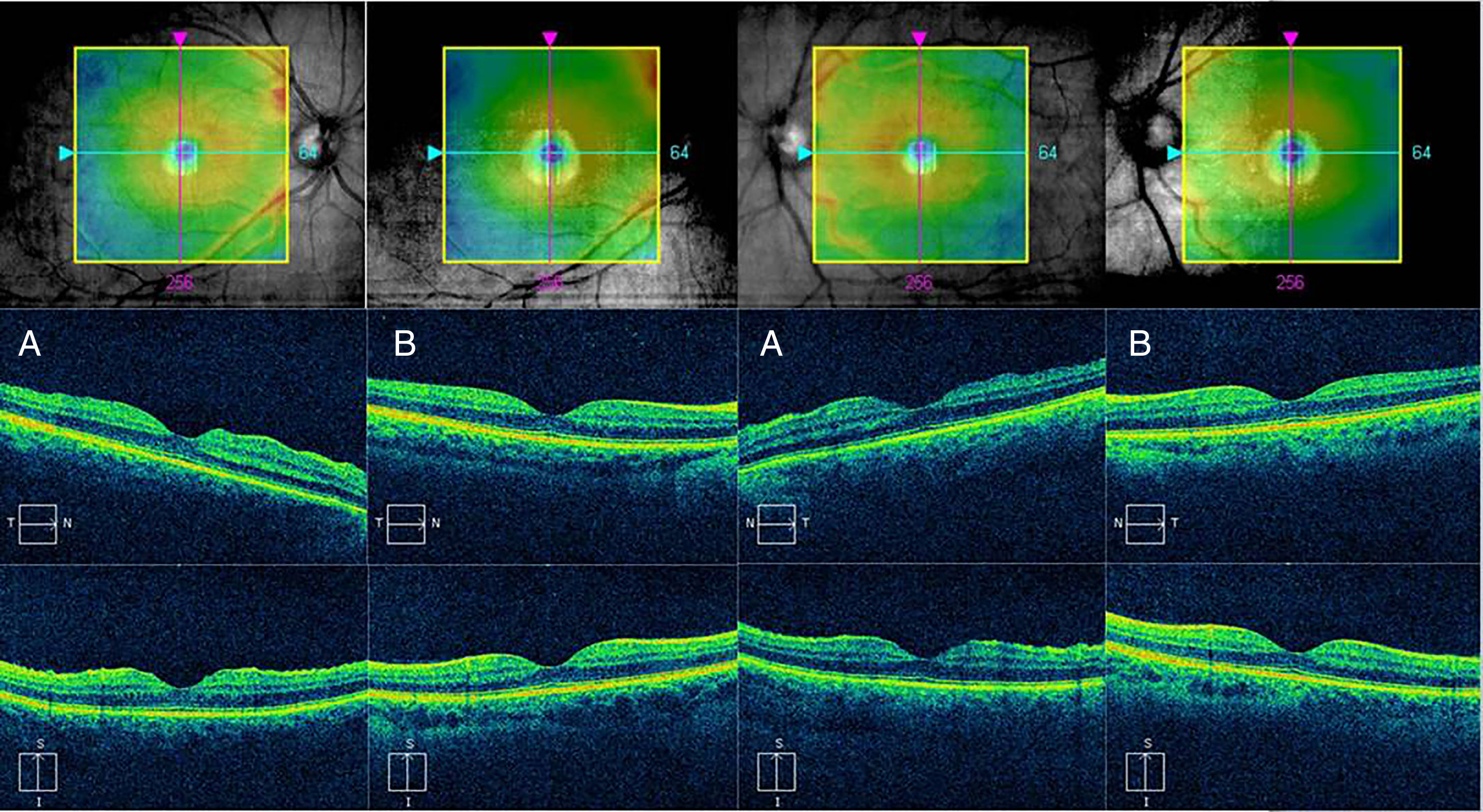
We report the case of a 29-year-old epileptic woman who had been on treatment with topiramate 25mg/day for 9 days. She was referred to the Emergency Department due to reduction in far visual acuity (VA) after increasing the dose to 50mg/day two days before. The ocular examination showed bilateral acute angle closure glaucoma (AACG) and macular striae in both eyes (AO) observed by Retinography and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). The AACG is a well-known side effect of topiramate, but the macular striae rarely accompanies it. Although macular striae have been previously described in other cases, very few document those using retinography and OCT images. Therefore, it is important to differentiate a case of AACG induced by topiramate from a case of primary AACG, since they differ in their clinical presentation, mechanism of action, and treatment. Mismanagement can have potentially serious consequences.
Presentamos el caso clínico de una mujer epiléptica de 29 años en tratamiento con topiramato 25mg/día desde 9 días previos a la presentación del cuadro, que acude a urgencias por disminución de la agudeza visual (AV) tras incrementar la dosis a 50mg/día 2 días antes. En la exploración presenta un glaucoma agudo de ángulo cerrado (GAAC) bilateral y estrías maculares en ambos ojos (AO) objetivadas mediante retinografía y tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT). El GAAC es un efecto secundario conocido y ampliamente descrito del topiramato, sin embargo, las estrías maculares que ocasionalmente acompañan al GAAC, aunque se han descrito anteriormente en otros casos, muy pocos las documentan mediante imágenes de retinografía y OCT. Es importante diferenciar un caso de GAAC inducido por topiramato de un caso de GAAC primario ya que difieren en su presentación clínica, mecanismo de acción y tratamiento. Su manejo inadecuado puede tener consecuencias potencialmente graves.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora