To analyze the functional recovery using a pro re nata (PRN) dosing strategy with intravitreal injections of ranibizumab for patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
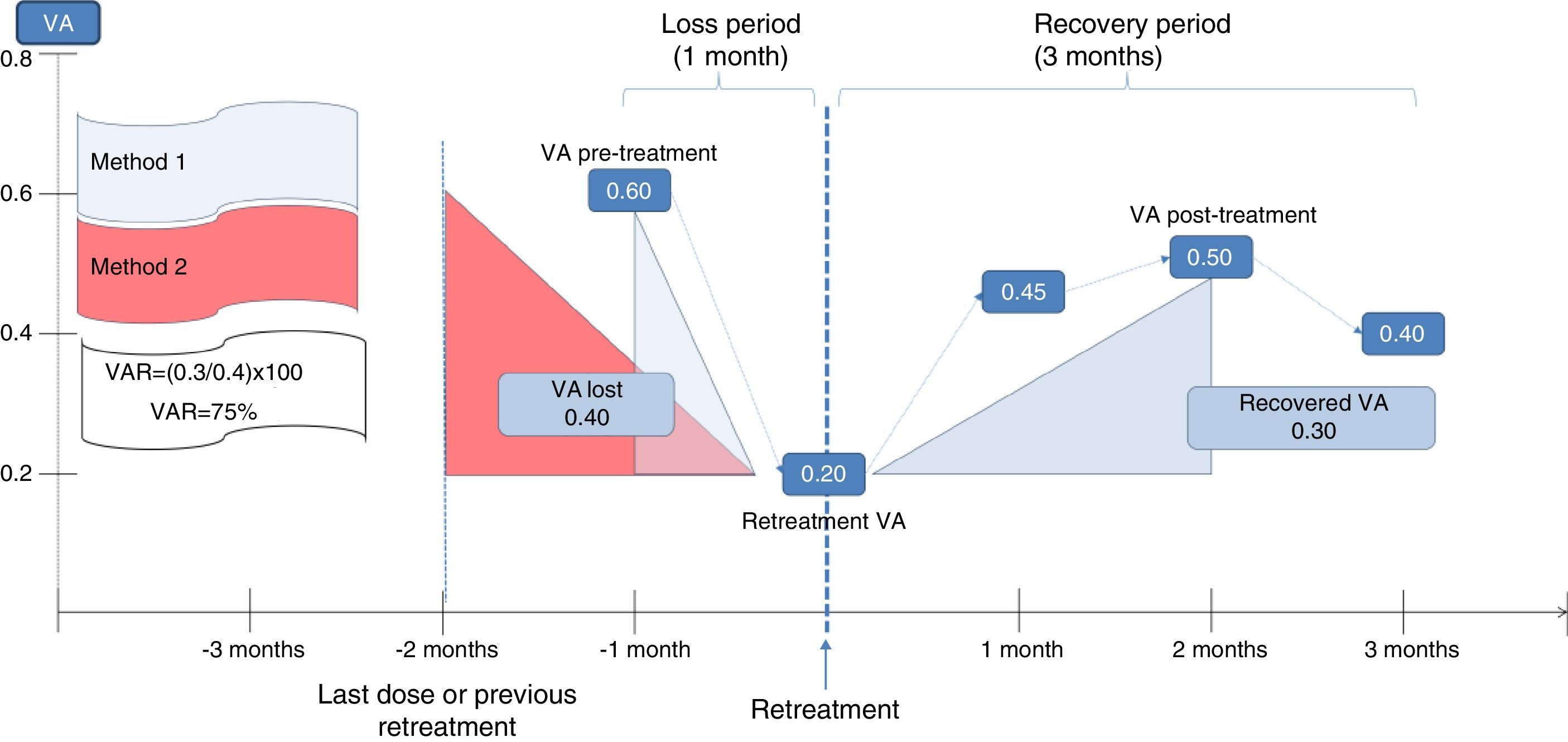
Material and methodsAn observational, retrospective, single-center study, was conducted on patients with neovascular AMD managed with a PRN strategy with ranibizumab, and were followed-up for a minimum of 18 months. Sociodemographic and clinical data were collected from medical records. The percentage of visual acuity (VA) recovered after losing 5 or more letters was calculated taking into account the previous visit, as well as considering the best VA recorded prior to the retreament.
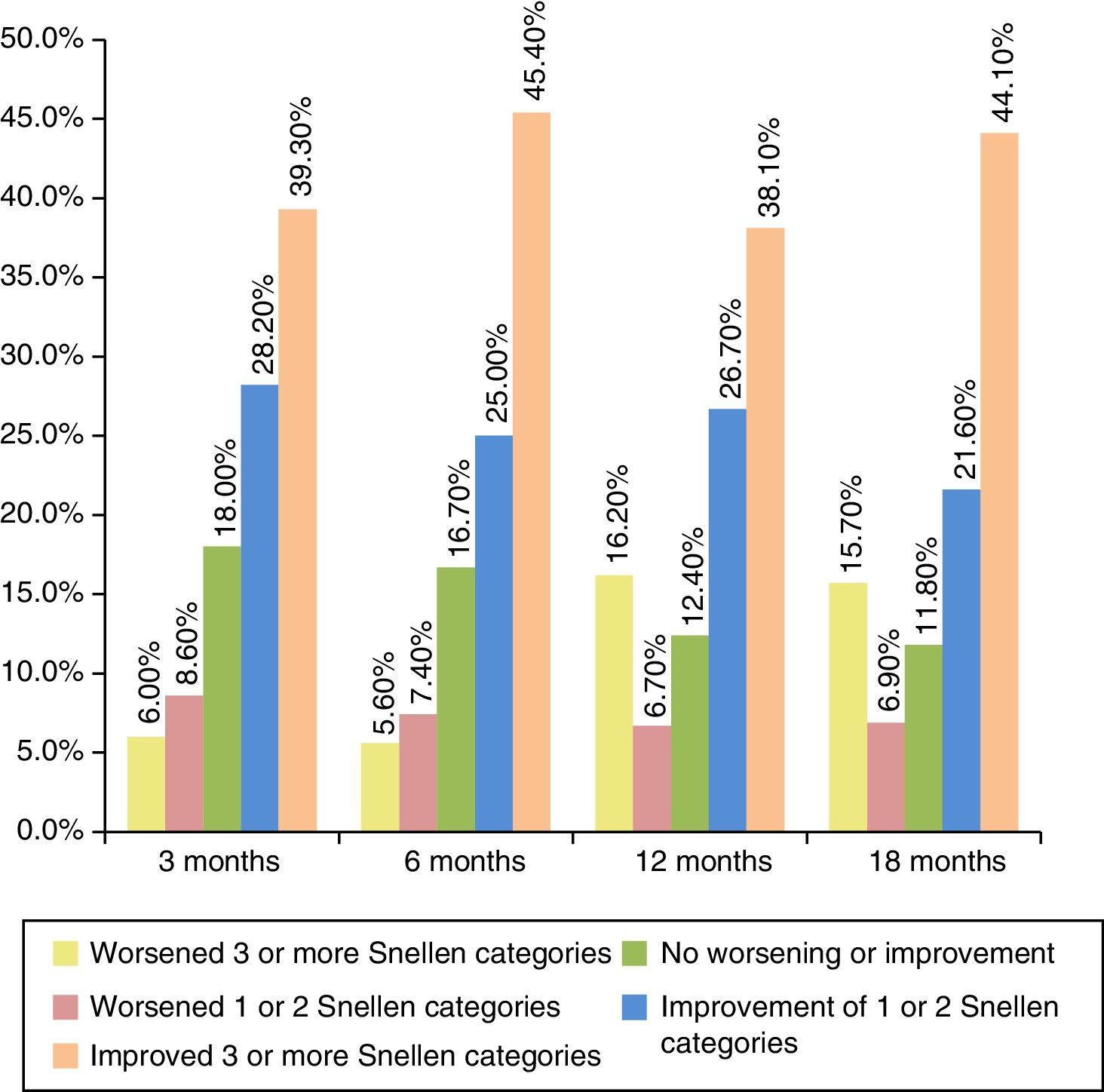
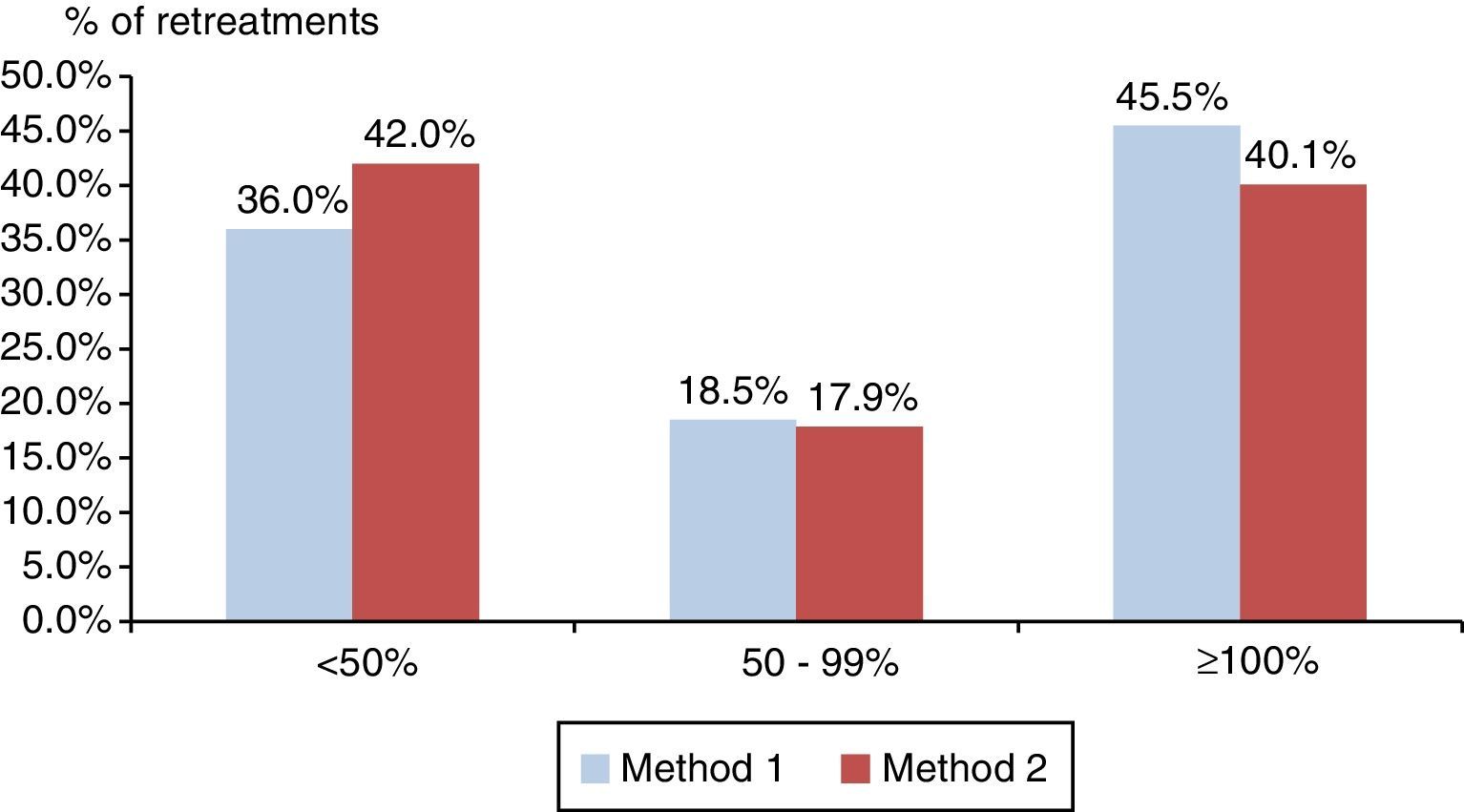
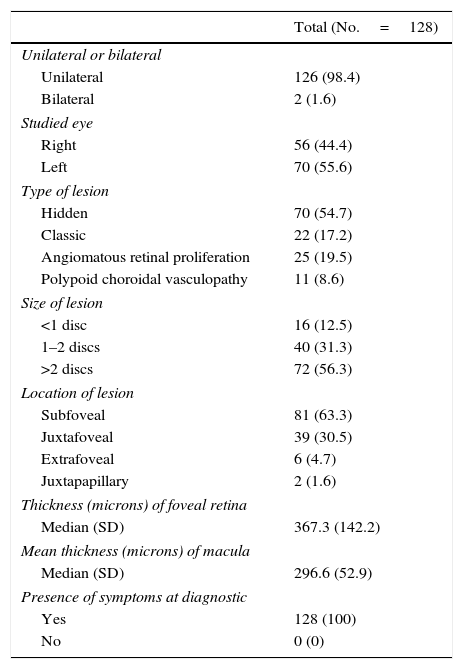
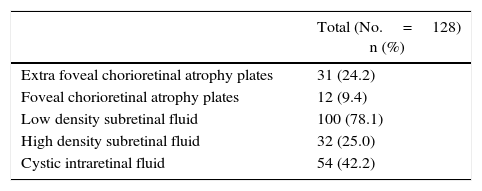
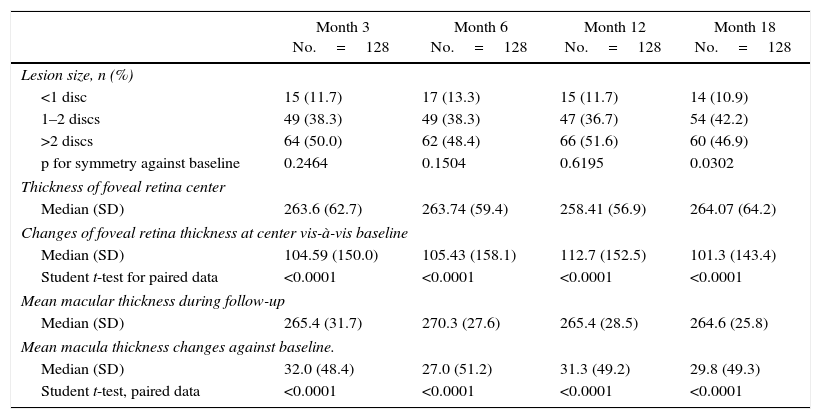
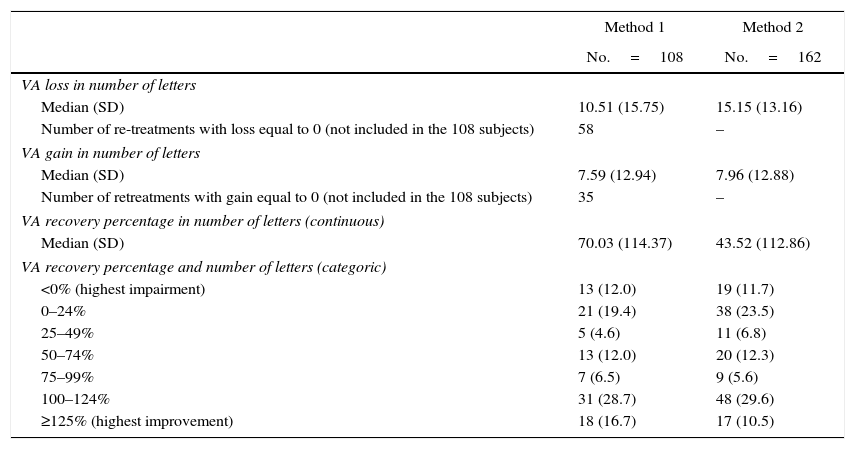
ResultsThe analysis included 128 patients. The mean (SD) follow-up period was 18.9 (2.3) months. The mean (SD) elapsed days between onset of symptoms and diagnosis, and between prescription and administration of treatment was 50.2 (57.4) and 10.9 (16.0), respectively. Only 108 patients were prescribed ranibizumab after losing 5 or more letters of VA. The mean (SD) VA recovery compared to the previous VA was 70.3% (114.4). On the other hand, the mean (SD) VA recovery when considering the best VA registered before the retreatment was 43.5% (112.9), with 59.4% of re-treatments having a VA recovery below 75%, and with 11.7% not presenting any VA recovery.
ConclusionsA PRN dosing strategy with intravitreal ranibizumab for neovascular AMD may not be efficient in preserving and/or recovering VA in the long-term, due to a cumulative irreversible VA loss.
Conocer el porcentaje de recuperación funcional, según estrategia pro re nata (PRN) con inyecciones intravítreas con ranibizumab en pacientes con degeneración macular asociada a la edad (DMAE).
Material y métodosEstudio observacional, retrospectivo, unicéntrico. Se incluyó a pacientes con DMAE tratados con ranibizumab según estrategia PRN y seguimiento mínimo de 18 meses. Se recogieron variables sociodemográficas y clínicas de la historia clínica. El porcentaje de recuperación de agudeza visual (AV) después de perder 5 o más letras fue calculado considerando la AV del mes anterior, así como la mejor AV previa al retratamiento.
ResultadosSe analizó a 128 pacientes. La media (DE) de seguimiento fue de 18,9 (2,3) meses; la media (DE) entre los primeros síntomas y el diagnóstico y entre la prescripción e inicio de tratamiento fue de 50,2 (57,4) y 10,9 (16,0) días, respectivamente.
Ranibizumab solo fue prescrito en 108 pacientes tras una pérdida de 5 o más letras de AV.
La media (DE) de recuperación de AV al considerar la AV de la última visita fue 70,3% (114,4). La media (DE) de recuperación de AV considerando la mejor AV antes del retratamiento fue de 43,5 (112,9), con un 59,4% de retratamientos que presentaron una recuperación de AV inferior al 75%, mientras que el 11,7% no presentaron recuperación de la AV.
ConclusionesUna estrategia PRN con inyecciones intravítreas de ranibizumab podría no ser lo suficientemente efectiva en términos de mantenimiento o recuperación de AV en los casos de DMAE a largo plazo, debido a la pérdida irreversible de AV.