To study the differences between solar retinopathy (SR) and the maculopathy produced by laser pointer (LPM) using multimodal imaging.
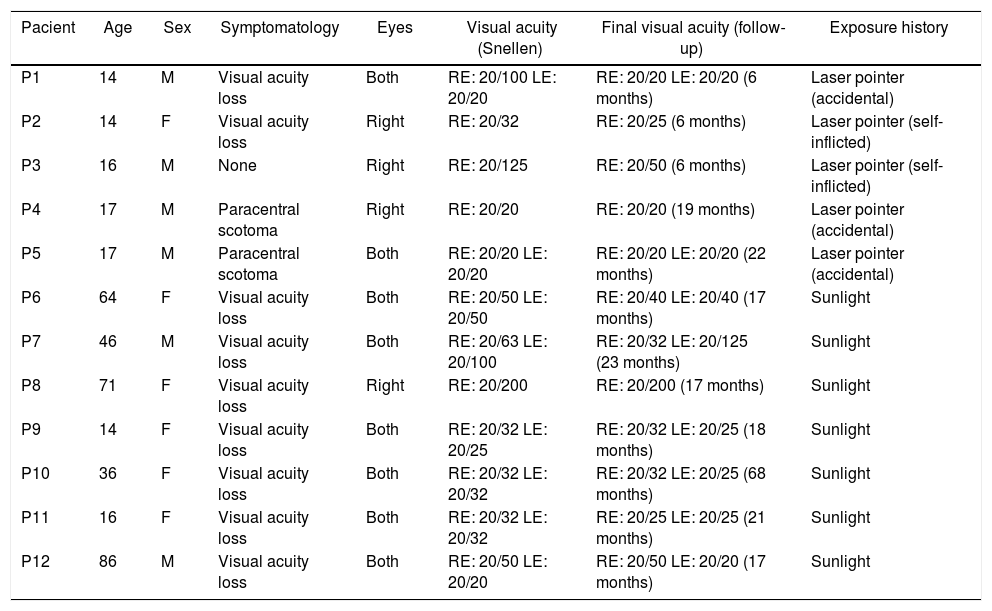
MethodA retrospective series is presented of 20 eyes of 12 patients with injuries associated with light, 7 with SR-compatible injuries, and 5 with LPM. At diagnosis, a complete opht-halmological examination was performed, including visual acuity (VA), retinography, andspectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT). The patients were followed-up for a mean period of 20 months.
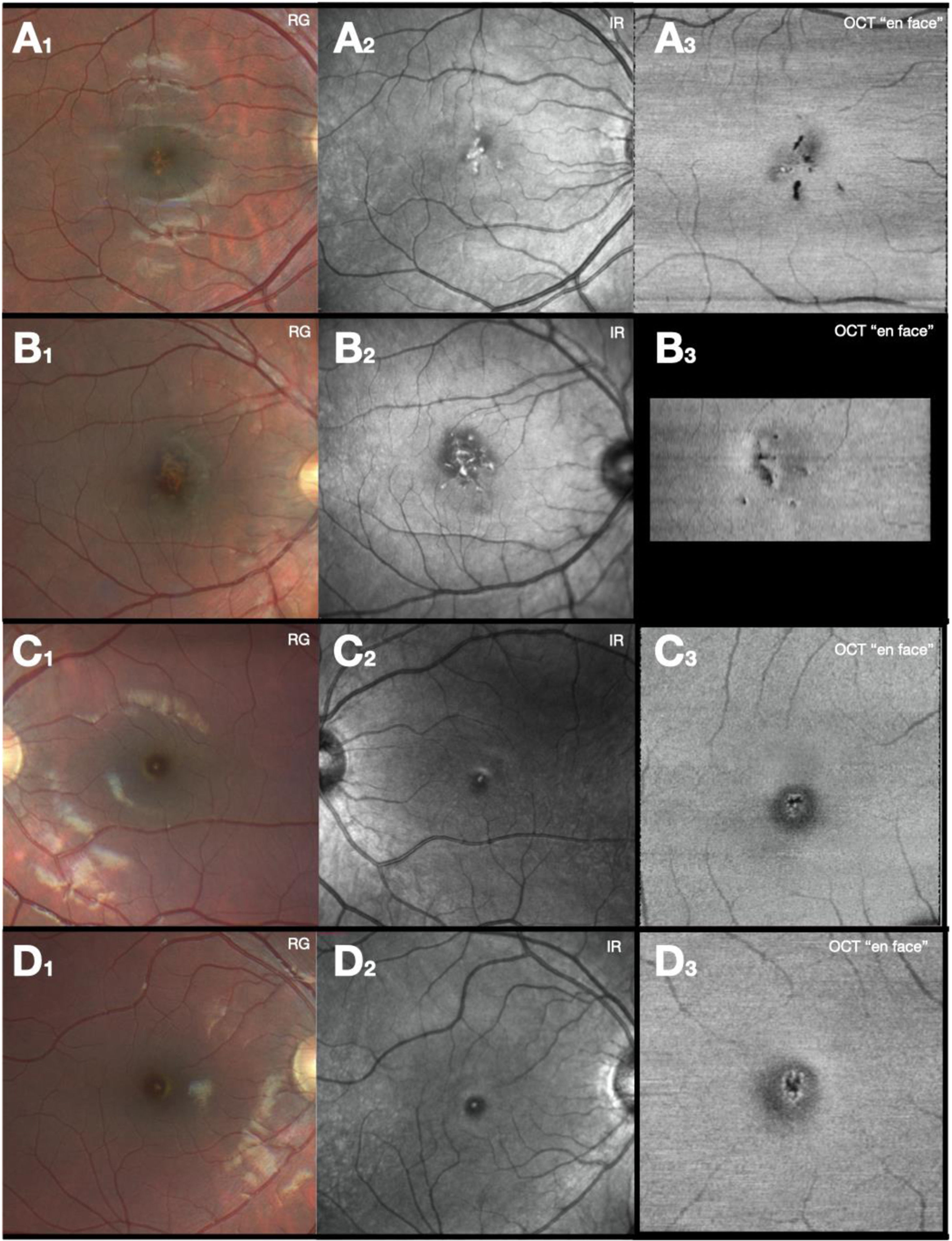
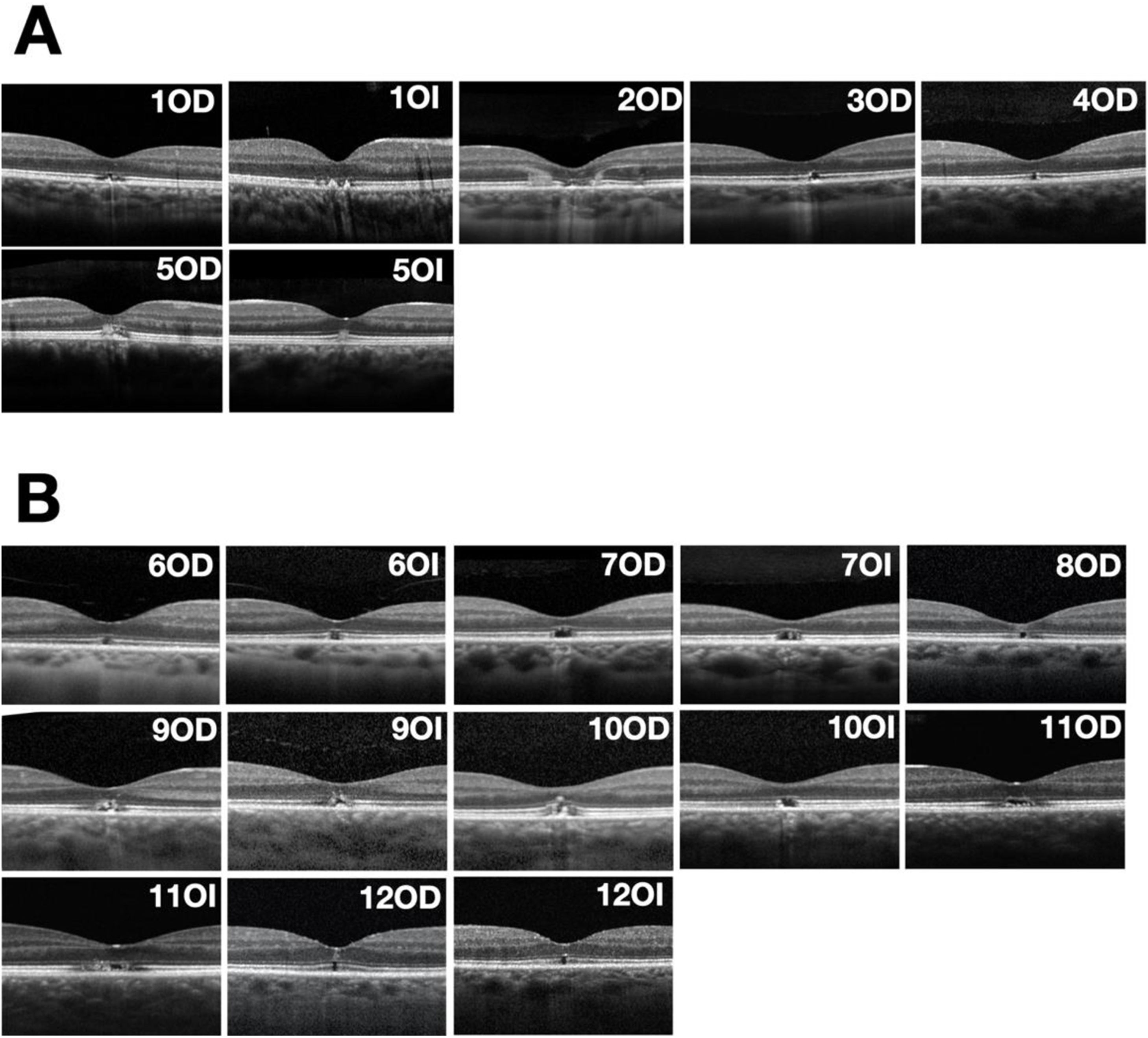
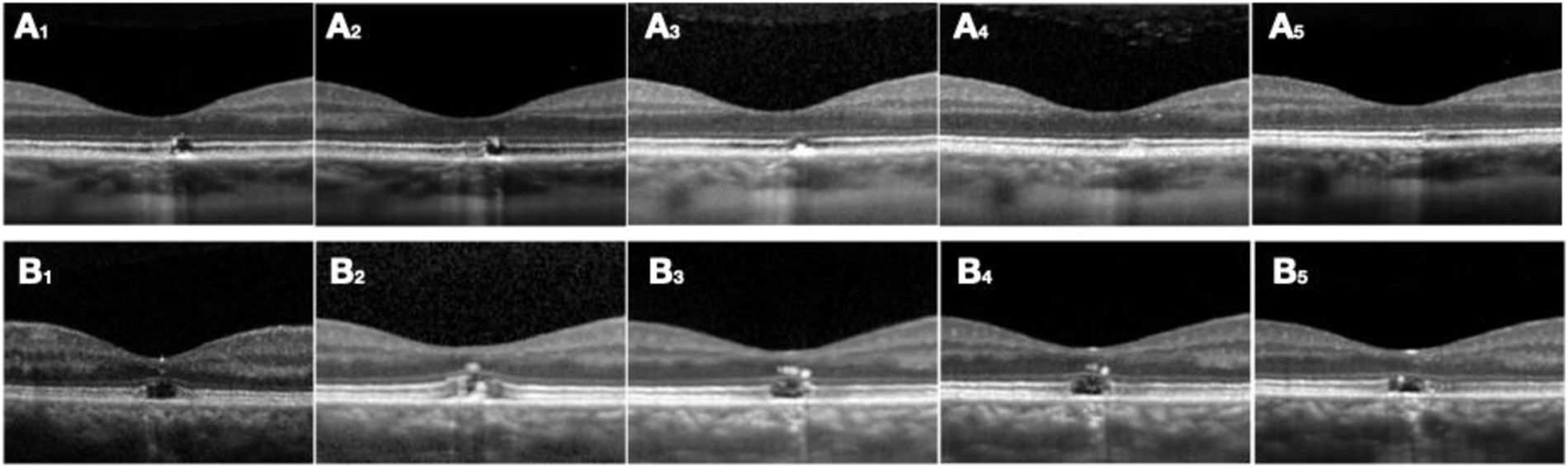
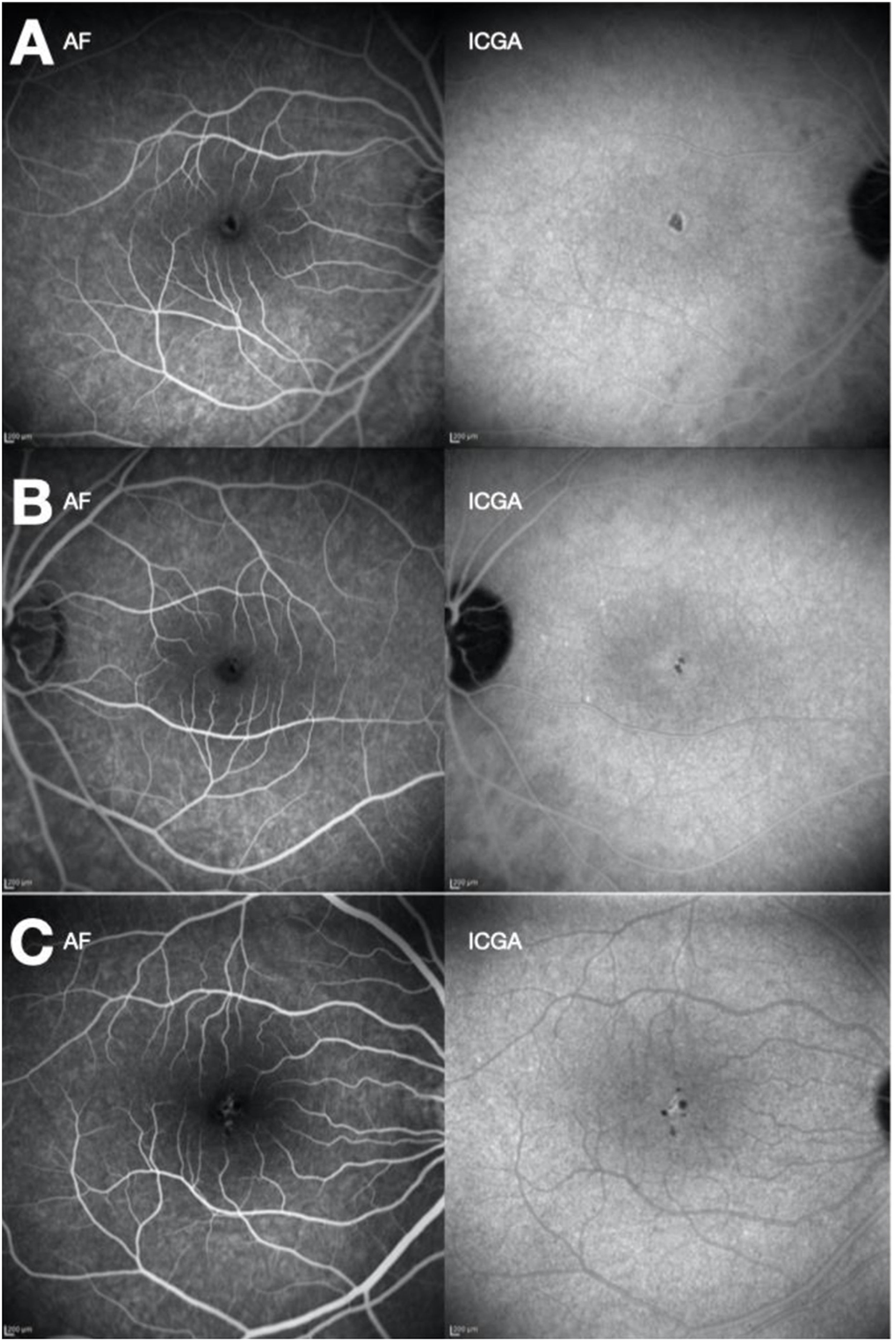
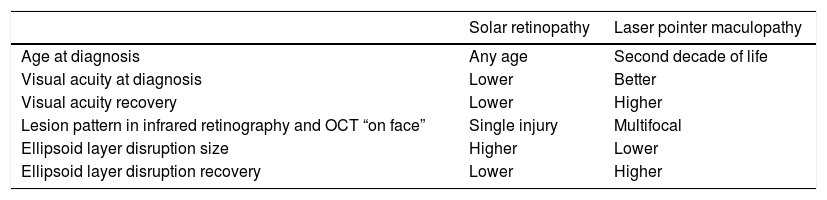
ResultsLPM is common in paediatrics (mean age 15.60 ± 1.5 years), and SR affects patients of all ages (mean age 47.56 ± 1.51 years). VA at diagnosis in LPM is greater, and recovery is more complete than in solar retinopathy. In conventional retinography, SR is shown as a single lesion in the macular area (100% of cases), while LPM usually presents as multifocallesions (86% of cases). Infrared reflectance makes this difference clearer. The main sign in OCT is the disruption of the ellipsoid layer and interdigitation zone. This sign is maintained over time, and its size is greater in the SR than in the LPM. Hyper-reflective columns and hyper-reflective reaction of the retinal pigment epithelium are associated with the acutephase.
ConclusionsLPM and SR show significant differences in the type of patient affected, as well as in the signs in multimodal imaging, as well as in functional impairment and their evolution.
Estudiar mediante imagen multimodal las diferencias entre la retinopatía solar (RS)y la maculopatía producida por puntero láser (MPL).
MétodoPresentamos una serie retrospectiva de casos de 20 ojos de 12 pacientes con lesionesasociadas a fuentes de luz; 7 con lesiones compatibles con RS y 5 con MPL. Al diagnóstico, se realiza exploración oftalmológica completa incluyendo agudeza visual (AV), retinografíay tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) de dominio espectral. Se realiza un seguimiento delas lesiones durante un periodo medio de 20 meses.
ResultadosLa MPL es propia de la edad pediátrica (edad media 15,60 ± 1,51 aňos), mientrasque la RS afecta a pacientes de todas las edades (edad media 47,56 ± 27,55 aňos). La AV aldiagnóstico en la MPL es mayor y la recuperación más completa que en la RS. En retinografíaconvencional, la RS se muestra como una única lesión en el área macular (100% de los casos), mientras que las MPL se suelen presentar como lesiones multifocales (86% de los casos). Lareflectancia infrarroja evidencia de manera más clara esta diferencia. El principal signo enOCT es la disrupción de la capa elipsoides y zona de interdigitación. Este signo se mantieneen el tiempo y su tamaňo es mayor en la RS que en la MPL. Las columnas hiperreflectivas yla reacción hiperreflectiva del epitelio pigmentario de la retina se asocian a la fase aguda.
ConclusionesLa MPL y la RS presentan diferencias significativas tanto en el tipo de pacienteafectado como en los signos en imagen multimodal, así como en la afectación funcional ysu evolución.