To analyze the disease burden in patients with diabetic macular oedema (DMO) or with retinal vein occlusion macular oedema (RVOMO) from a societal perspective.
MethodsObservational, cross-sectional, multicentre study conducted on patients >18 years old diagnosed with uni- or bilateral DMO or unilateral RVOMO. Data on the use of health resources from diagnosis was collected, and the impact of disease on work life was assessed. Costs were annualized (euros, January 2014). Differences were contrasted using Chi-squared test (or Fisher Exact test), Mann Whitney-U test or Kruskal–Wallis test (Dunn contrast).
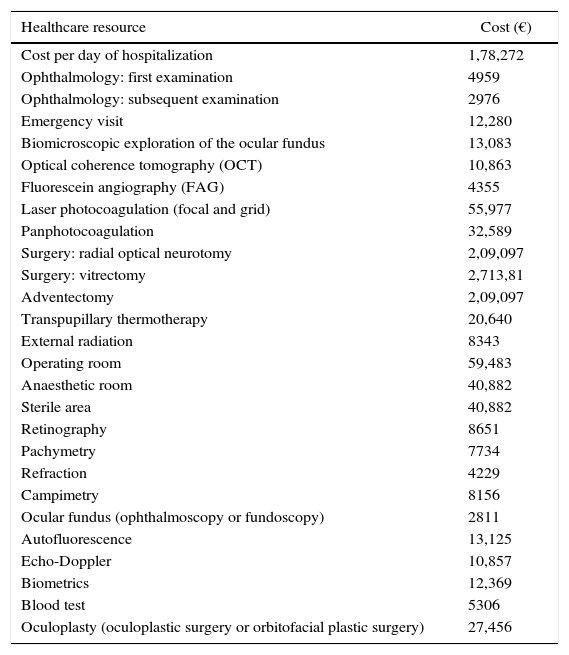
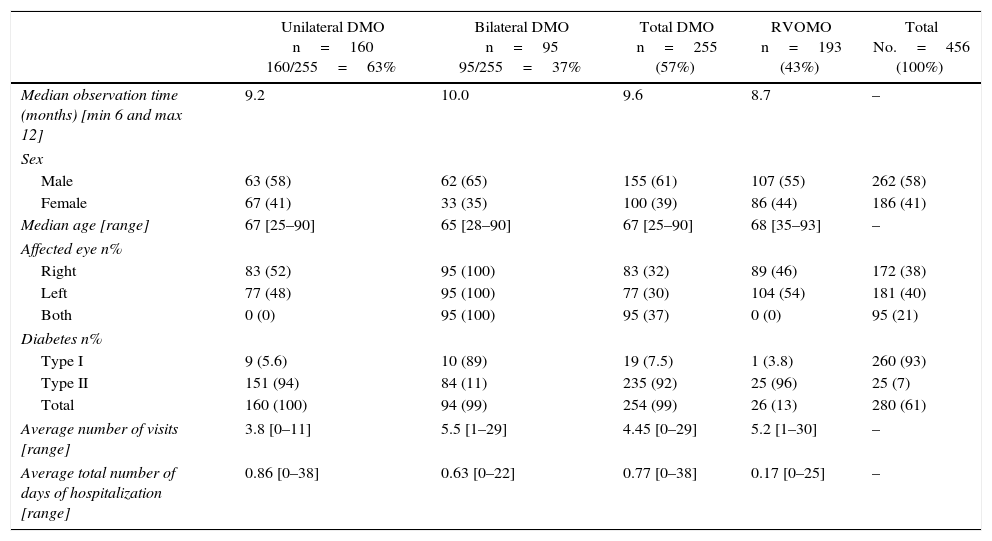
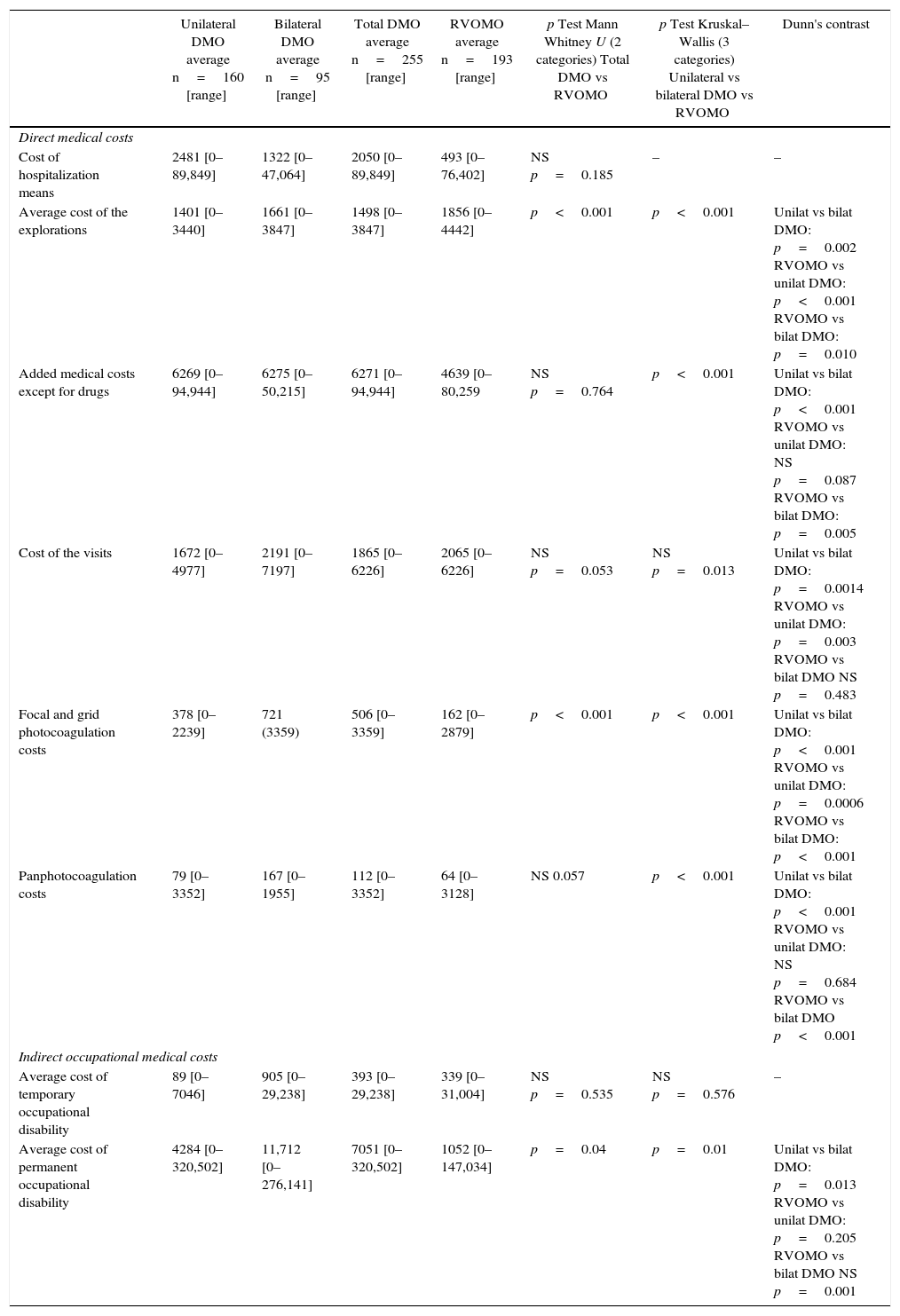
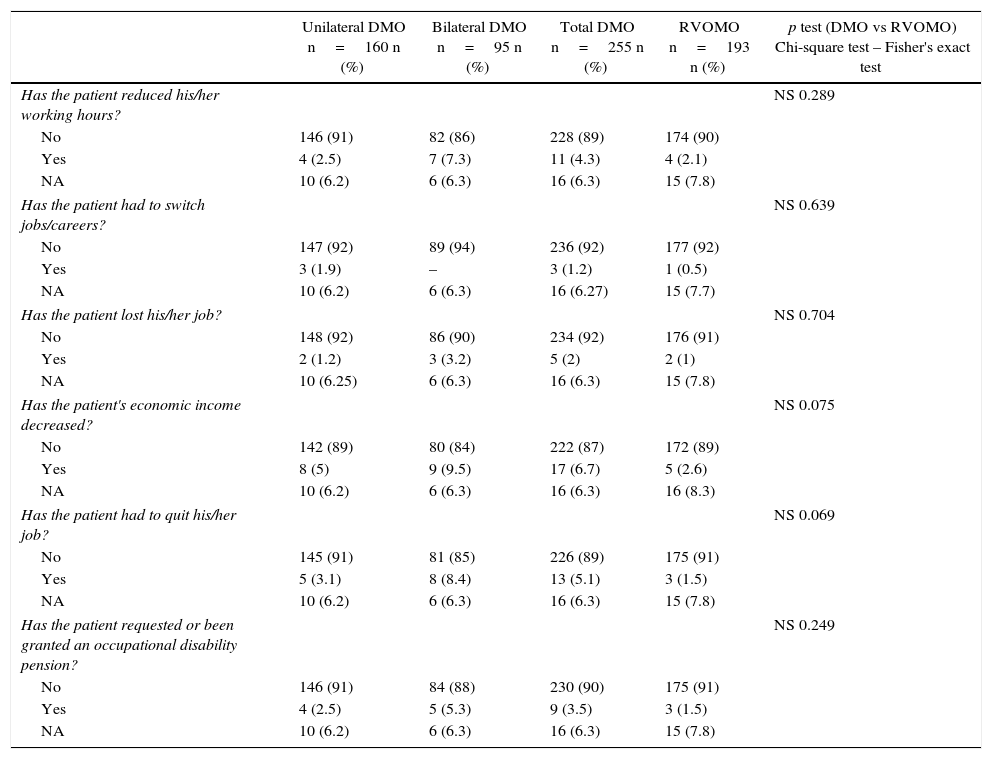
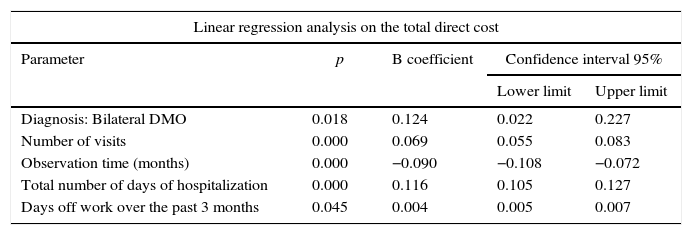
ResultsA total of 448 patients were included (DMO 255; RVOMO 193). There were significant differences in costs of diagnosis: RVOMO €1856, bilateral DMO €1661, and unilateral DMO €1401 (p<0.001) and the aggregate medical costs: RVOMO €4639, bilateral DMO 6275€ and unilateral DMO 6269€ (p<0.001). Cost by permanent time off work was higher in bilateral DMO €11712, than in unilateral DMO €4284€, and than in RVOMO €1052 (p<0.05). Linear regression analysis showed that variables associated with direct health costs were: Diagnosis (bilateral DMO was associated with higher cost), as well as number of days in hospital, number of visits, time of observation, and number of days of time off work.
ConclusionsPatients with bilateral DMO are associated with a higher direct health cost, as well as a higher indirect cost by impact of the disease on work life.
Analizar el coste de la enfermedad en pacientes con edema macular diabético (EMD) o edema macular secundario a oclusión venosa de la retina (EMOVR), desde la perspectiva de la sociedad.
MétodosEstudio observacional, transversal, multicéntrico. Se incluyó a adultos (>18 años) con EMD uni- o bilateral o EMOVR unilateral. Se recogió el consumo de recursos sanitarios desde el diagnóstico y se evaluó el impacto de la enfermedad en la vida laboral. Los costes fueron anualizados (euros, en enero de 2014). Se adoptó la perspectiva de la sociedad. Las diferencias se contrastaron mediante los estadísticos Chi cuadrado (o test de Fisher), U de Mann Whitney o Kruskal–Wallis (contraste de Dunn).
ResultadosSe incluyó a 448 pacientes (EMD 255; EMOVR 193). Se encontraron diferencias significativas en costes de diagnóstico: EMOVR 1.856€, EMD bilateral 1.661€ y EMD unilateral 1.401€ (p<0,001) y en los costes médicos agregados: EMOVR 4.639€, EMD bilateral 6.275€ y EMD unilateral 6.269€ (p<0,001). El coste por incapacidad laboral permanente fue mayor en EMD bilateral (11.712€) que en EMD unilateral (4.284€) y en EMOVR (1.052€; p<0,05). En el análisis de regresión lineal, las variables asociadas con los costes sanitarios directos fueron: diagnóstico (EMD bilateral estaba asociado a un mayor coste) así como número de días de hospitalización, número de visitas, tiempo de observación y número de días de baja laboral.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con EMD bilateral suponen un mayor impacto en el coste directo sanitario así como un mayor coste indirecto por afectación en la vida laboral.