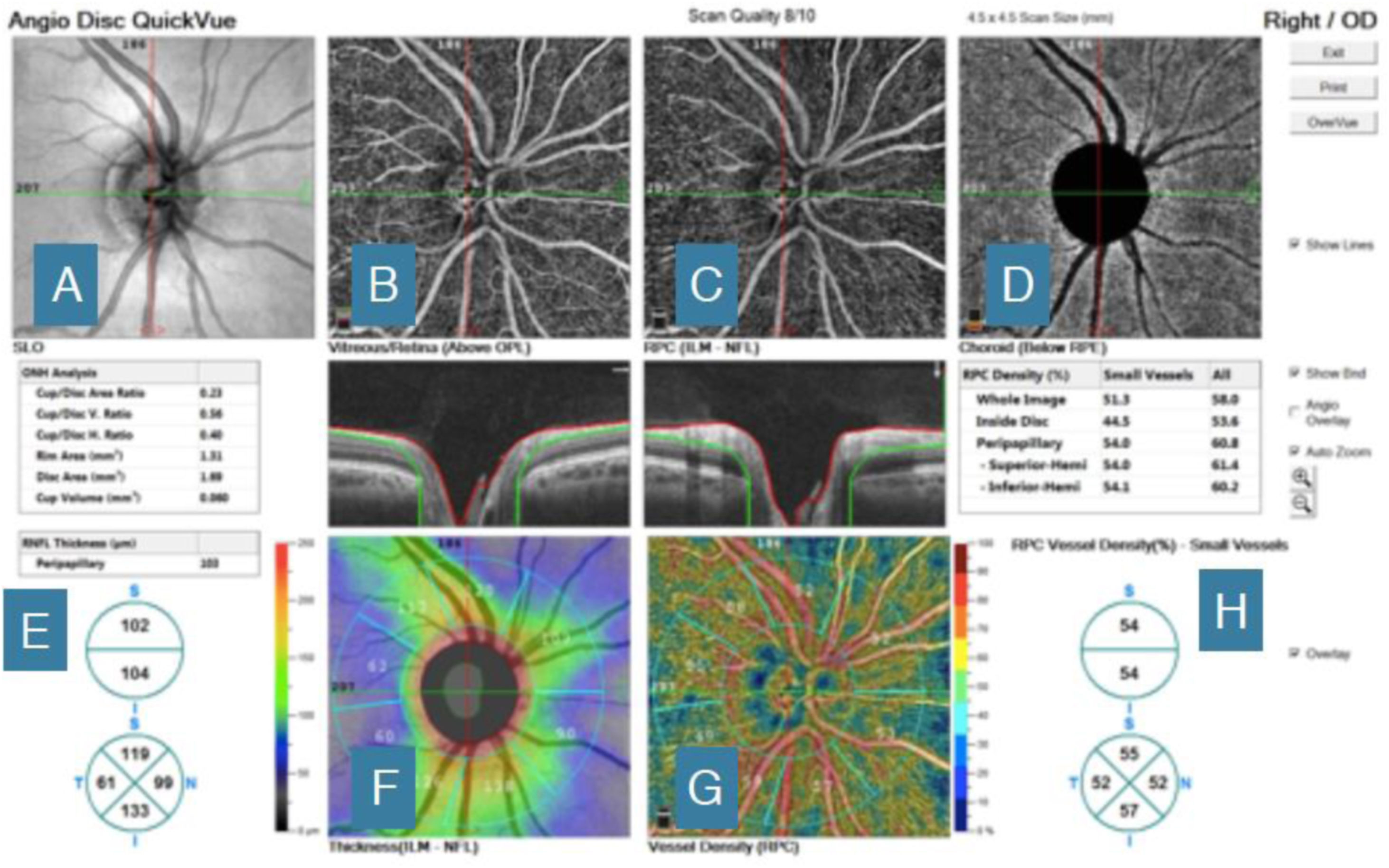
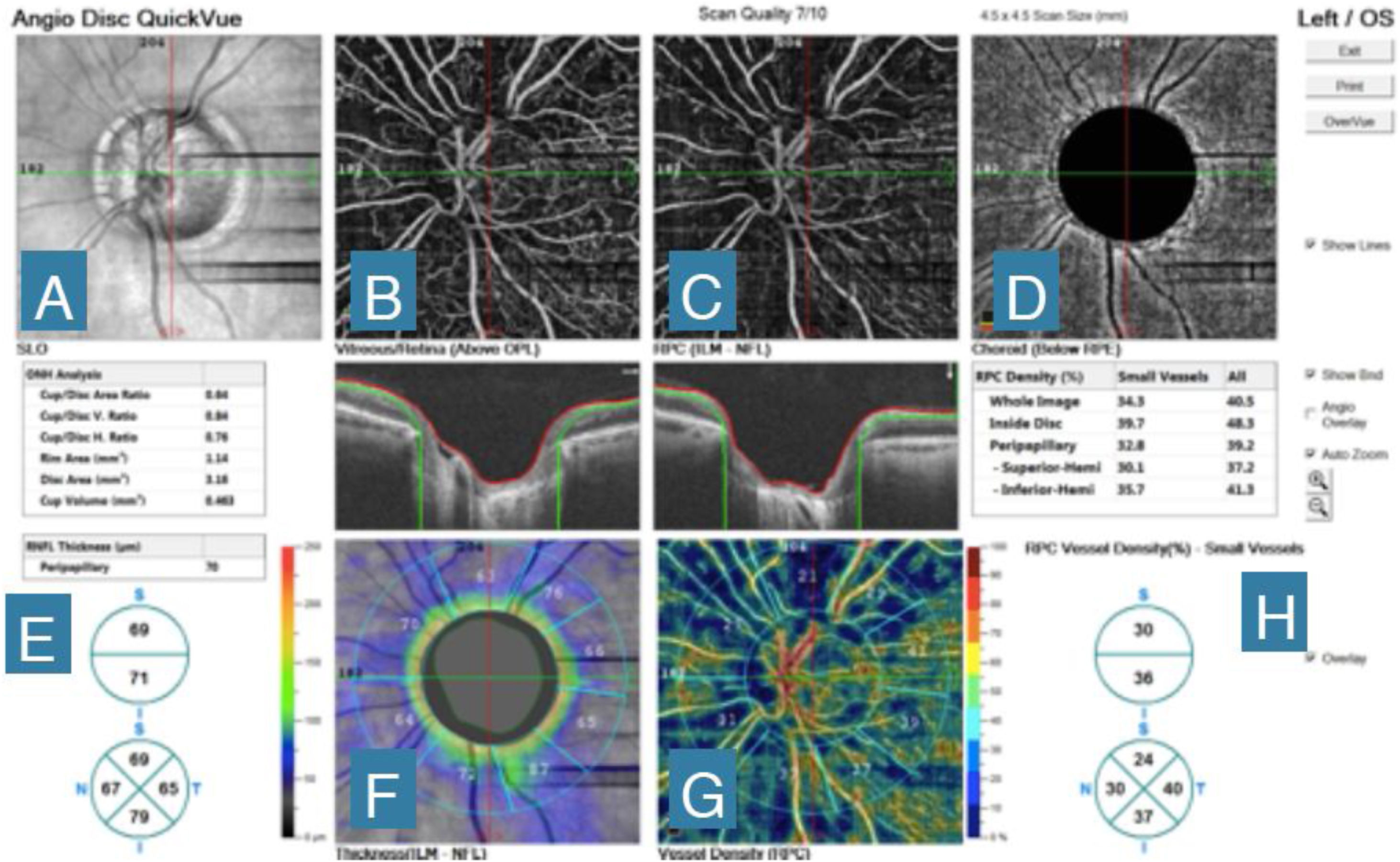
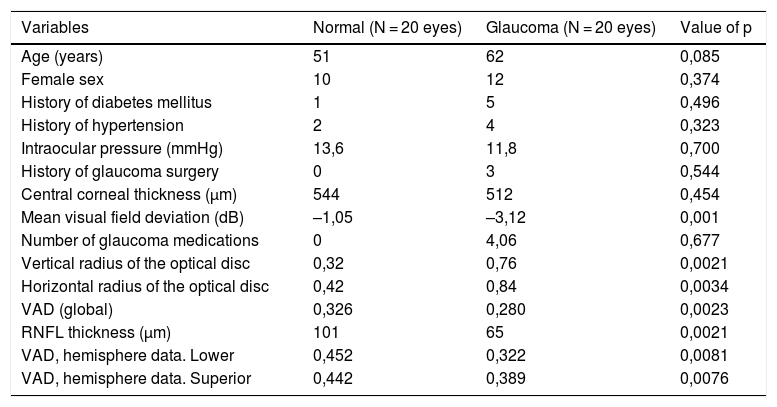
The introduction of optical coherence tomography angiography (OCT-A) has generated interest in evaluating vascular dysfunctions in the optic nerve head for the diagnosis and monitoring of glaucoma. The purpose of this study is to compare perfusion of the optic disc between normal subjects and subjects with glaucoma using OCT-A in order to detect changes in perfusion of the optic disc. Using the OCT-A AngioVue® system, an examination was performed on 40 eyes of 40 patients (20 with glaucoma and 20 healthy controls). Total radial peripapillary flow density (4.5 x 4.5 mm) was measured at different levels of segmentation. The study demonstrated that the peripapillary vascular flow of OCT-A and exploration of the optic nerve head (ONH) was better in the normal eyes compared to glaucoma patients. This review provides a comprehensive summary of the most important current and potential applications of OCT-A in glaucoma.
La introducción de la angiografía por tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT-A) ha generado interés en evaluar las alteraciones vasculares en la cabeza del nervio óptico para el diagnóstico y monitorización del glaucoma. El propósito de este estudio es comparar la perfusión del disco óptico entre sujetos normales y sujetos con glaucoma usando OCT-A para detectar cambios en la perfusión del disco óptico. El sistema OCTA AngioVue examinó 40 ojos de 40 pacientes (20 con glaucoma y 20 controles sanos). La densidad de flujo peripapilar radial total (4.5 x 4.5 mm) se midió en diferentes niveles de segmentación.El estudio demostró que el flujo vascular peripapilar de la OCT-A y la exploración de la cabeza del nervio óptico (ONH) fue mejor en los ojos normales en comparación con los pacientes con glaucoma. Esta revisión proporciona un resumen exhaustivo de las aplicaciones actuales y potenciales más importantes de OCTA en el glaucoma.