To evaluate the diagnostic ability of the vessel density (VD) of the optic nerve head (ONH) and the macula on optical coherence tomography (OCT) angiography and the retinal nerve layer thickness (RNFL) thickness and the macular ganglion cell complex (GCC) thickness on OCT in patients with pseudoexfoliative glaucoma (PXG).
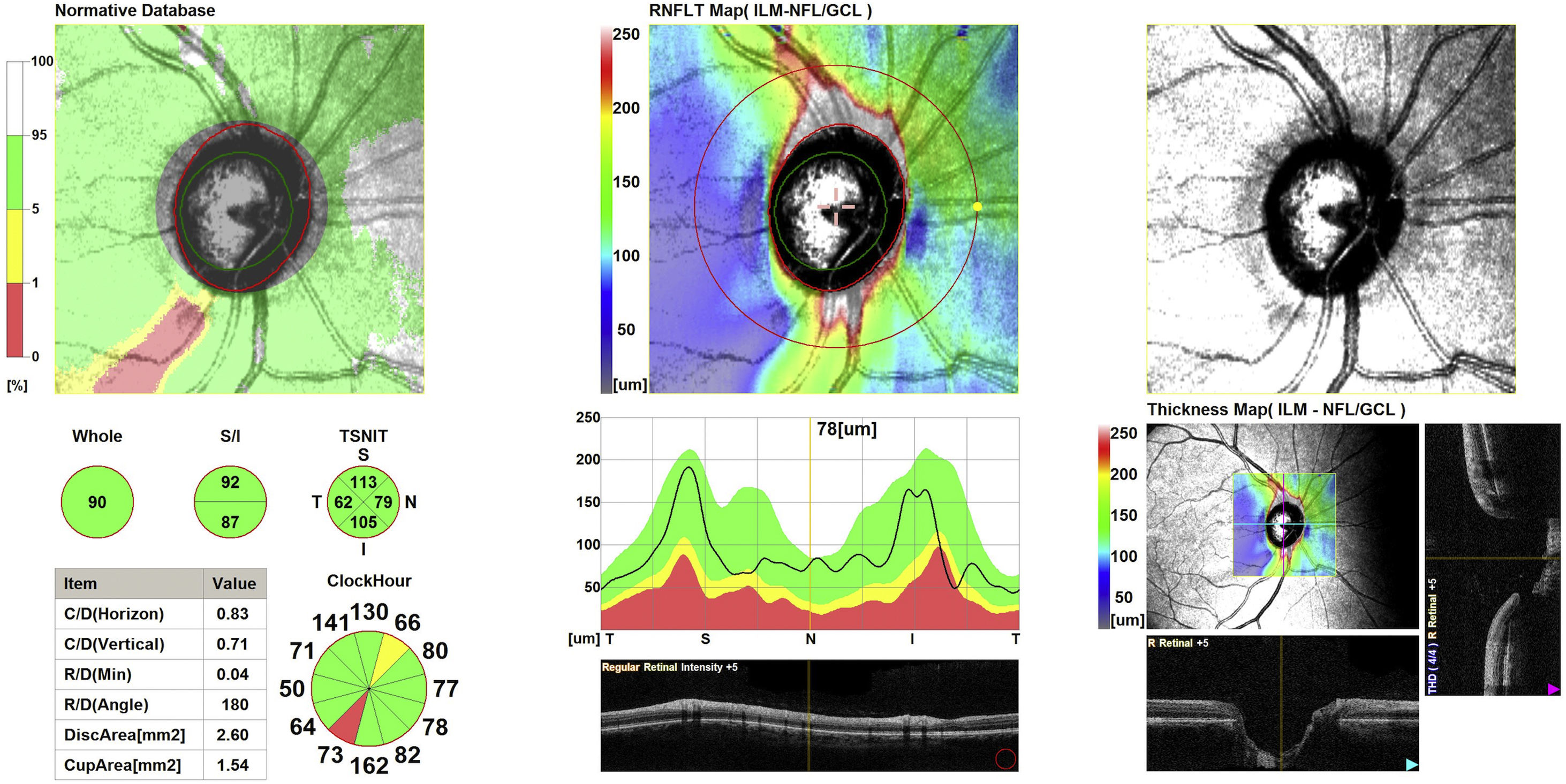
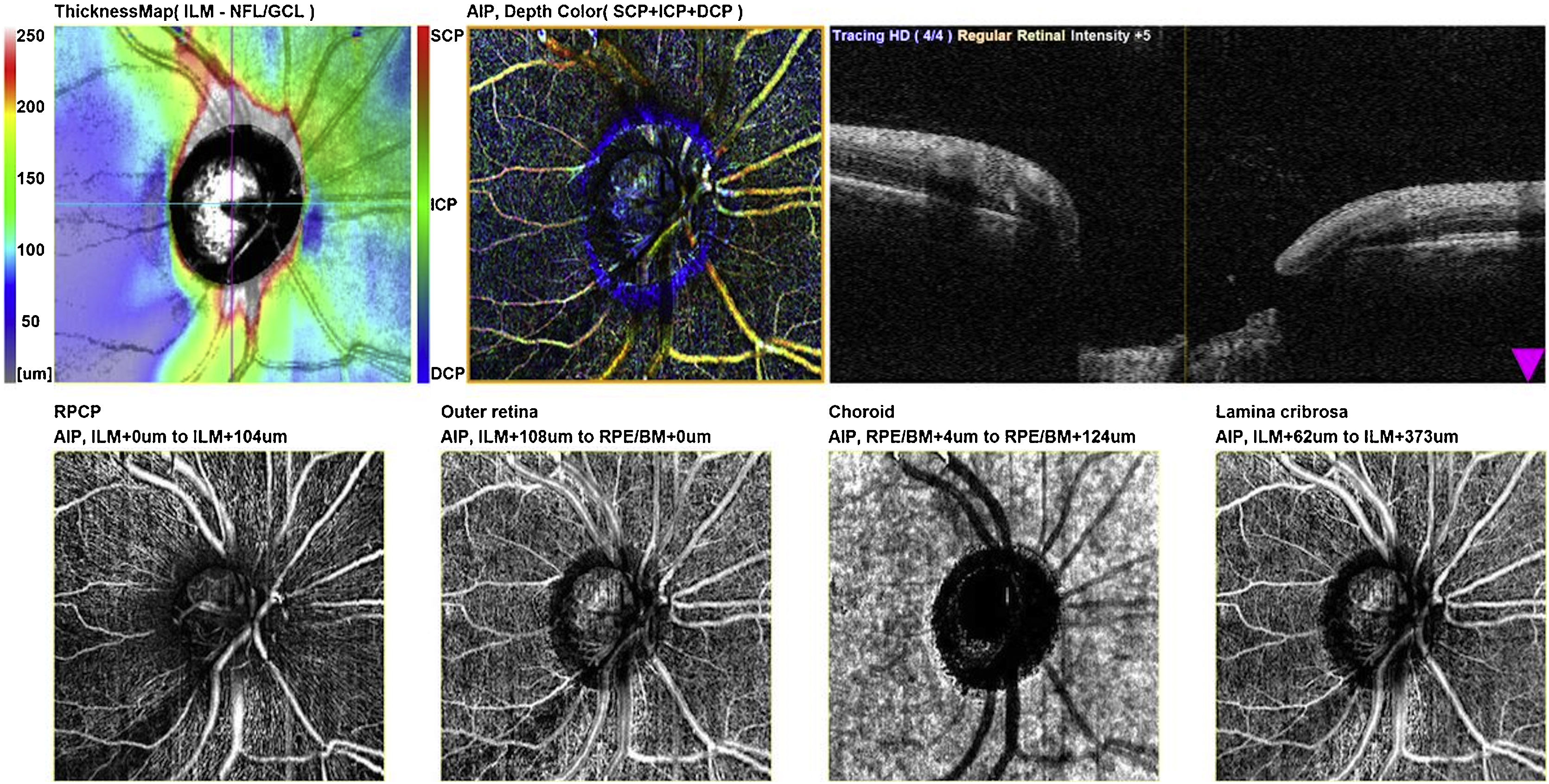
MethodsCross-sectional study including PXG patients and healthy controls. Demographic and clinical data were noted for all participants. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) and OCT angiography (OCTA) images of the ONH and macular area were obtained with the RS-3000 Advance OCT (Nidek Co., Gamagori, Japan). The RNFL and GCC thickness of different sectors was provided by the software. Macular VD of the superficial capillary plexus (SCP) and ONH VD of the radial peripapillary capillary plexus (RPCP) were registered. Groups were compared and area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curves were used to determine the power of discrimination of each parameter.
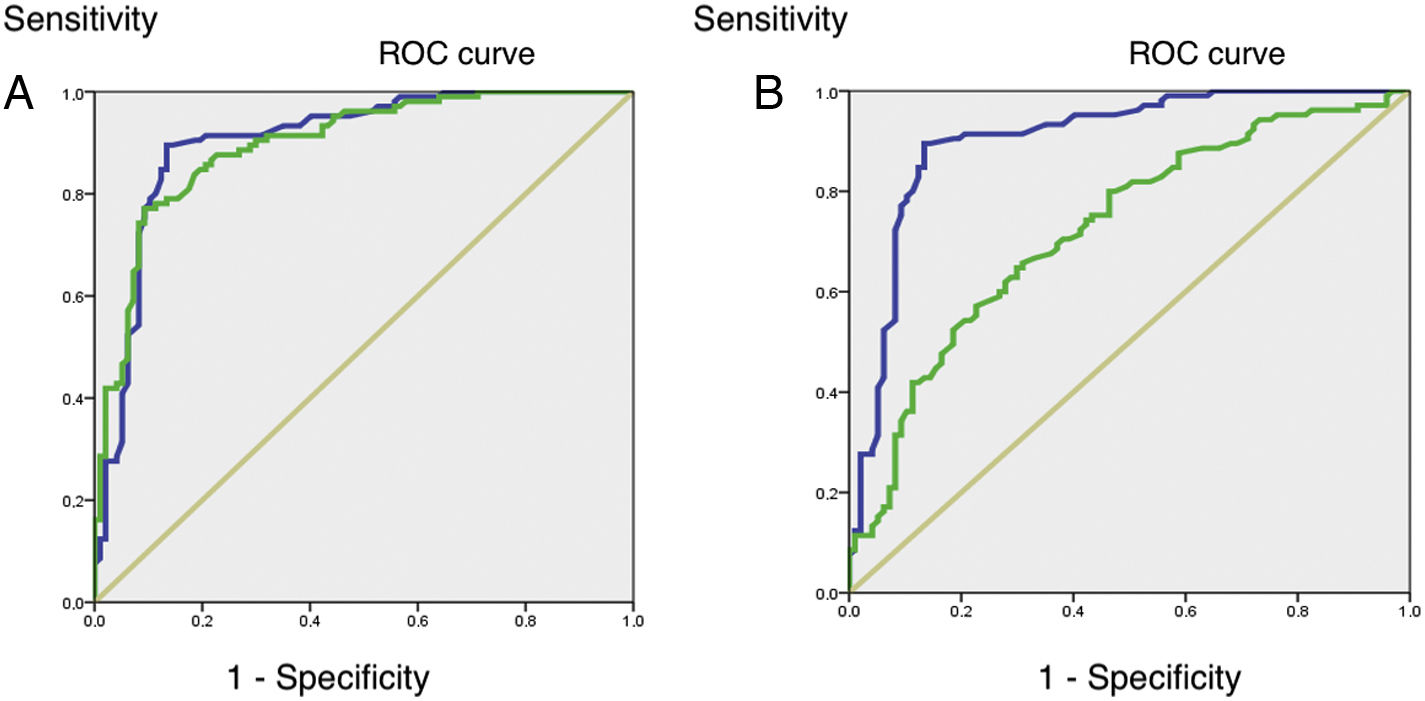
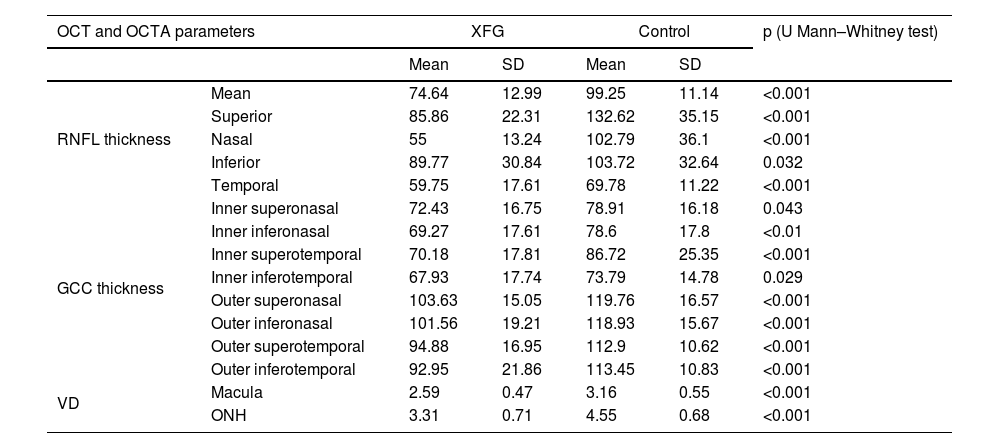
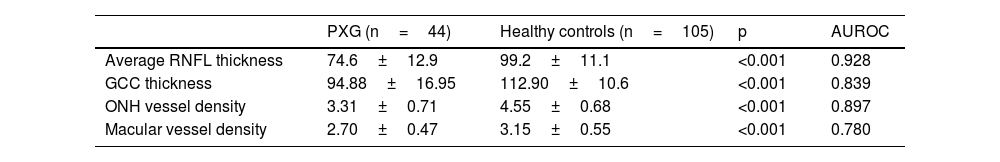
ResultsRNFL and GCC thickness and ONH and macular VD were significantly lower in PXG patients compared with healthy controls (all, p<0.05). The best discrimination parameter was the average RNFL thickness (AUROC: 0.928). ONH VD AUROC was better than that of macular VD (AUROC: 0.897 and 0.780, respectively). ONH VD AUROC was comparable to RNFL thickness (p<0.001).
ConclusionsThe diagnostic ability of ONH vessel density in PXG appears comparable to that of the structural parameters, RNFL and GCC thickness, obtained with OCT, and may be a valuable tool in clinical practice.
Evaluar la capacidad diagnóstica de la densidad de vasos (DV) papilar y macular mediante angiografía por tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCTA) y el grosor de la capa de fibras nerviosas de la retina (CFNR) y complejo de células ganglionares (CCG) maculares mediante tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) en los pacientes con glaucoma seudoexfoliativo (GPX).
MétodosEstudio transversal que incluyó GPX y controles sanos. Se realizó OCT y OCTA de la papila y el área macular con el OCT RS-3000 Advance (Nidek Co., Gamagori, Japón). Se registró la DV macular del plexo capilar superficial (SCP) y la DV papilar del plexo capilar peripapilar radial (RPCP). Se empleó el área bajo la curva característica operativa del receptor (AUROC) para determinar el poder discriminatorio de cada parámetro.
ResultadosEl grosor de la CFNR y del CCG, así como la DV a nivel papilar y macular, fueron significativamente menores en los pacientes con GPX que en los controles sanos (todos, p<0,05). El mejor parámetro discriminante fue el grosor medio de la CFNR (AUROC: 0,928). El AUROC de la DV papilar fue mejor que el de la VD macular (AUROC: 0,897 y 0,780, respectivamente). AUROC de la DV papilar fue comparable a la del grosor de la CFNR (p<0,001).
ConclusionesLa capacidad diagnóstica de la DV papilar en el GPS parece comparable a la de los parámetros estructurales, espesor de la CFNR y CCG, obtenidos mediante OCT, por lo que la OCTA podría ser una herramienta valiosa en el GPX.