To assess if there are any differences in macular and papillary thickness using optical coherence tomography (OCT) in patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) compared with a control group, including if there are differences between ADHD patients with and without treatment.
MethodsProspective observational study including 92 eyes of 46 patients divided into 2 groups: 46 eyes of 23 patients with ADHD, and a control group of 46 eyes of 23 healthy patients. The group of patients with ADHD was subdivided into those on treatment with methylphenidate (n=28) and those not on treatment (n=18). The macular thickness, the ganglion cell complex (GCC), and the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) at the papillary level were measured in 12 sectors.
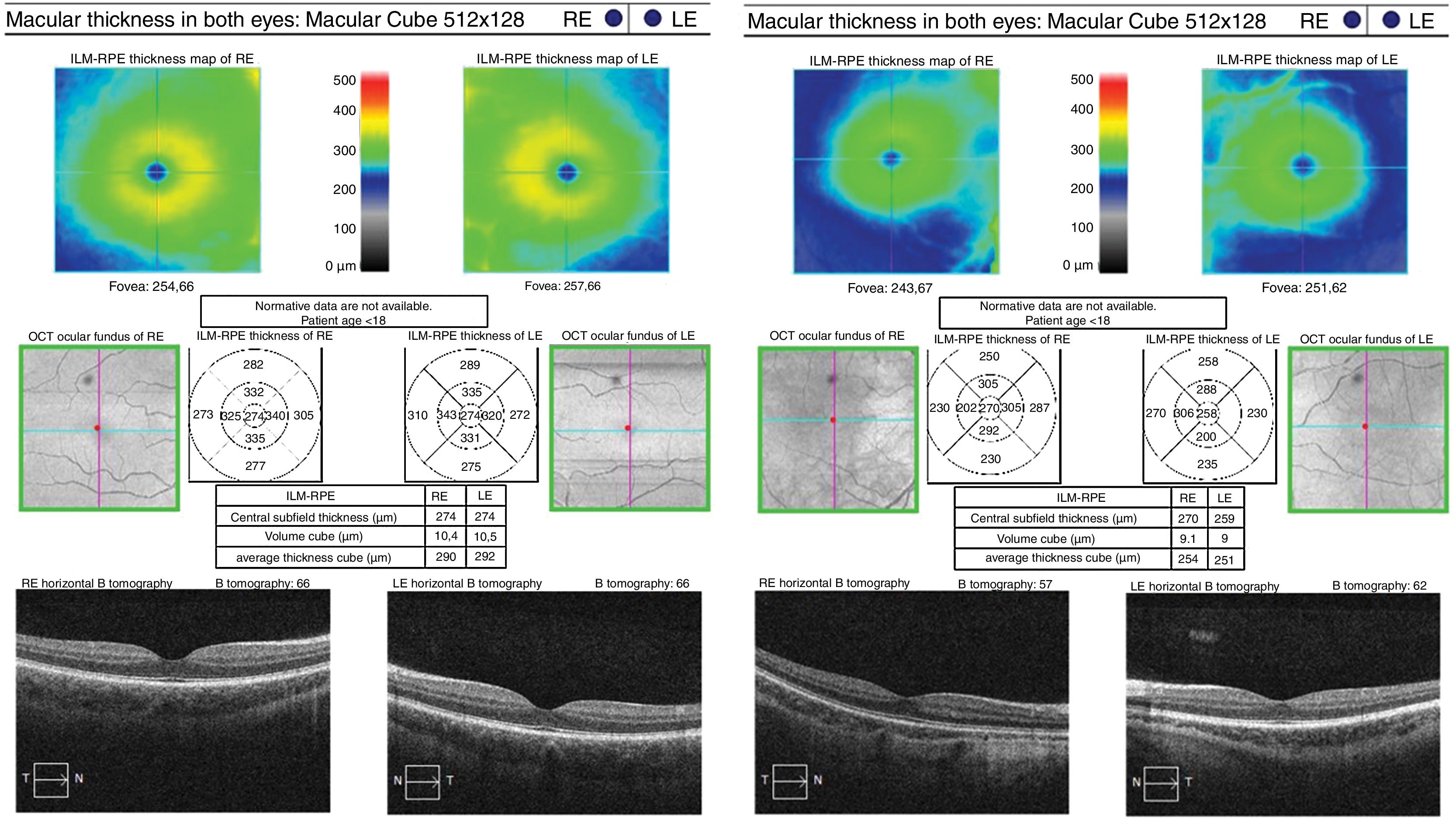
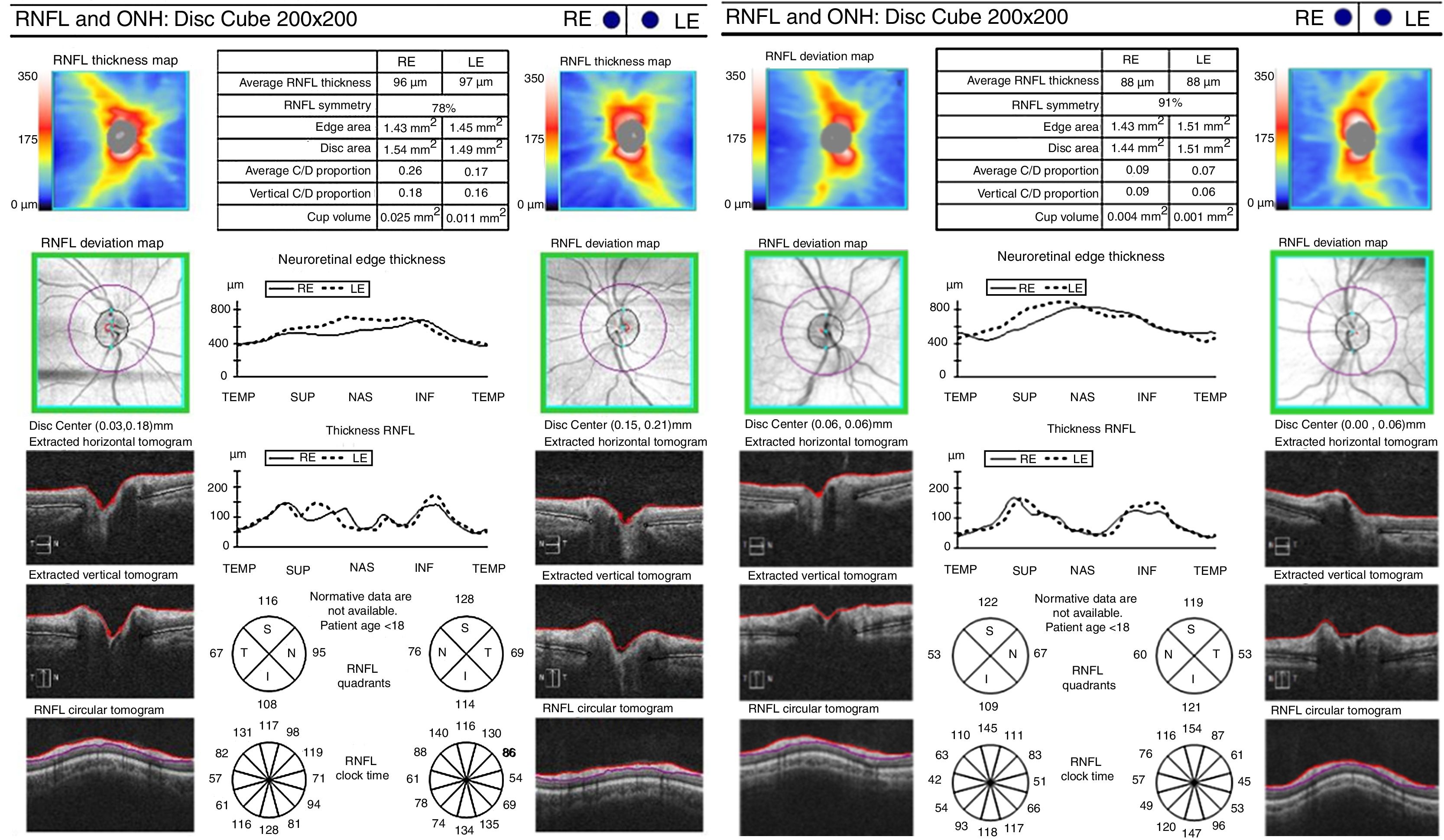
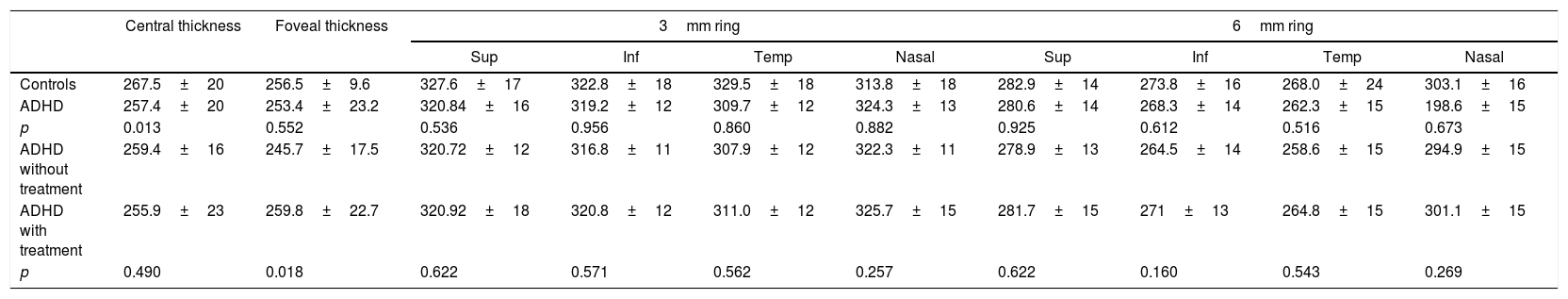
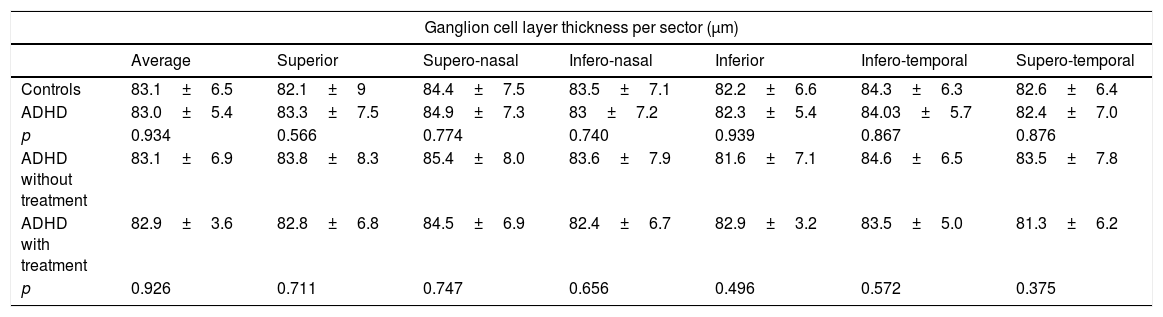
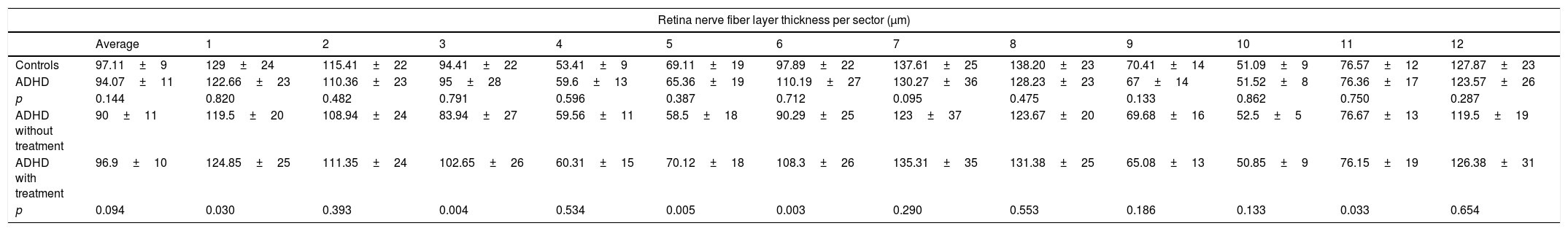
ResultsA lower central macular thickness was observed in the ADHD patients than in the controls (257.4±20μm versus 267.5±20μm, p=0.013), with no differences observed in the GCC (p=0.566), or in the RNFL (p=0.095). There were no differences in the patients with ADHD with and without treatment, as regards macular thickness and the GCC (p=0.160 and p=0.375 respectively), but a lower foveal thickness (p=0.018) and RNFL in 5/12 sectors at the papillary level (p=0.033) were observed in those without treatment.
ConclusionsA lower macular thickness was observed in patients with ADHD than in controls. In addition, patients with ADHD without treatment had a lower thickness of the fovea and RNFL than those patients on treatment.
Determinar si existen diferencias en el grosor macular y papilar mediante tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT) en pacientes con trastorno por déficit de atención e hiperactividad (TDAH) comparando con un grupo control, evaluando además si existen diferencias entre pacientes con TDAH con y sin tratamiento.
MétodosEstudio transversal en el que se incluyó a 92 ojos de 46 pacientes, divididos en 2 grupos: 46 ojos de 23 pacientes con TDAH y un grupo control de 46 ojos de 23 sujetos. El grupo de pacientes con TDAH se subdividió en aquellos con tratamiento con metilfenidato o derivados (n=28) y aquellos sin tratamiento (n=18). Se midió el grosor macular, el complejo de células ganglionares (CCG) y la capa de fibras nerviosas de la retina (CFNR) a nivel papilar en 12 sectores.
ResultadosSe observó un menor grosor macular central en los TDAH que en controles (257,4±20μm vs. 267,5±20μm; p=0,013), no observándose diferencias en el CCG (p ≥ 0,566), ni en la CFNR (p ≥ 0,095). En los pacientes con TDAH con y sin tratamiento no se observaron diferencias en el grosor macular ni en el CCG (p ≥ 0,160 y 0,375, respectivamente), pero se objetivó un menor grosor foveal (p=0,018) y de la CFNR en 5/12 sectores a nivel papilar (p ≤ 0,033) en aquellos sin tratamiento.
ConclusionesSe observó un menor grosor macular en los pacientes con TDAH que en controles. Además, los pacientes con TDAH sin tratamiento presentaron un menor grosor foveal y de la CFNR que aquellos pacientes en tratamiento.