To describe the clinical features at presentation, delivered treatment and follow-up of a case series of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) associated intermediate uveitis.
Patients and methodsRetrospective, descriptive and longitudinal study of patients with HTLV-1 associated intermediate uveitis treated at a reference ophthalmology facility in Lima, Peru, during the years 2012 to 2018.
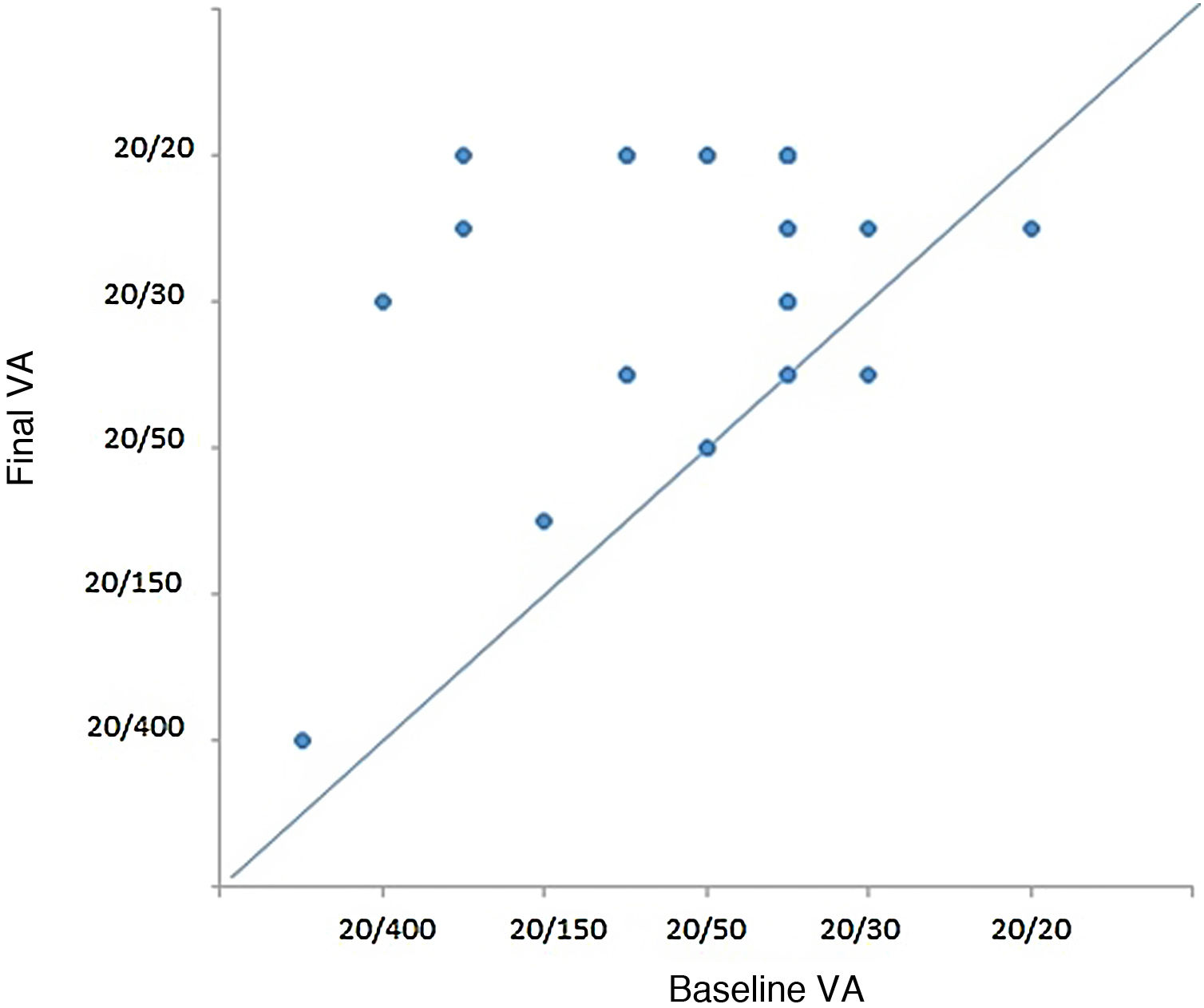
ResultsA total of 18 patients (28 eyes) were included, the average age at presentation was 57.3 years, 66.6% were women, and the average follow-up time was 1,280 days. The most frequent symptoms were blurred or diminished vision (78.6%) and floaters (57.1%). Best corrected visual acuity was 20/40 or better in 53.6%. The mean initial intraocular pressure was 14.95 mmHg. Keratic precipitates were observed in 50% of eyes, 17.9% were of the stellate type. The most frequent treatment was periocular corticosteroid injections (53.6%). Complications such as epimacular membrane (50%), cataract (21.4%) and glaucoma (7.1%) occurred. At the end of follow-up, only 2 eyes lost one line of vision; the final best corrected visual acuity was 20/40 or better in 85.7%, and 20/70 or better in 96.4%. Patients with both eyes affected increased from 33% at presentation to 55.5%. The course of the disease was chronic in 60.7%.
ConclusionHTLV-1 associated intermediate uveitis mainly occurred in patients in the second half of life, developing a chronic course and with good visual prognosis.
Describir las características asociadas a la presentación, tratamiento y seguimiento de una serie de casos de uveítis intermedia asociada al virus linfotrópico de células T humano de tipo 1 (HTLV-1).
Pacientes y métodosEstudio retrospectivo, descriptivo y longitudinal. Se incluyó a pacientes con uveítis intermedia asociada a infección por HTLV-1 atendidos en una clínica oftalmológica de referencia de Lima (Perú), durante 2012-2018.
ResultadosSe incluyó a 18 pacientes (28 ojos). La edad promedio a la presentación fue de 57,3 años; el 66,6% fueron mujeres. El tiempo de seguimiento promedio fue de 1.280 días. Los síntomas más frecuentes fueron visión borrosa o disminuida (78,6%) y visión de cuerpos flotantes (57,1%). La agudeza visual mejor corregida fue de 20/40 o mejor en el 53,6%. La presión intraocular inicial promedio fue de 14,95 mmHg. Se observaron precipitados retroqueráticos en el 50% de ojos, siendo el tipo más frecuente el espiculado (17,9% de los ojos). El tratamiento más frecuente fue la inyección periocular de corticoides (en el 53,6% de los ojos). Se presentaron complicaciones como membrana epimacular (50%), catarata (21,4%) y glaucoma (7,1%). Al final del seguimiento, solo 2 ojos perdieron una línea de visión; la agudeza visual mejor corregida final fue de 20/40 o mejor en el 85,7%, y de 20/70 o mejor en el 96,4%. Los pacientes afectados en ambos ojos aumentaron de 33% a la presentación a 55,5%. El curso de la enfermedad fue crónico en el 60,7%.
ConclusiónLa uveítis intermedia asociada a infección por HTLV-1 se presentó principalmente en la segunda mitad de la vida, con curso crónico y buen pronóstico visual.