The corneal biomechanical properties in naïve, untreated glaucoma and ocular hypertension (OHT) eyes is interesting, because it may be a source of error in intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements by Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT) and Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA)
The main objective of this study was to evaluate the IOP values obtained using GAT and the ORA, in primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) and in OHT untreated eyes.
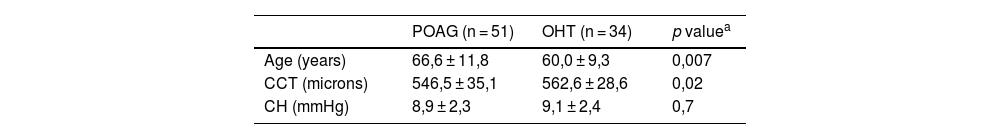
Material and MethodsObservational, masked, cross sectional observational study. Newly diagnosed, untreated POAG and OHT eyes were included.
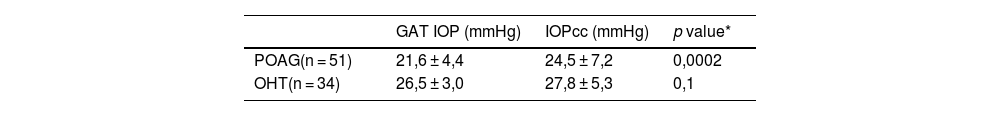
Results51 POAG and 34 OHT eyes were analyzed. We found that IOPcc (IOP corneal-compensated) was significantly higher than GAT IOP in POAG (p = 0.0002) while we did not find any significant difference between both tonometers in OHT (p = 0.1).
ConclusionsGAT seems to underestimate the real IOP in untreated POAG eyes and it seems to be quite accurate in OHT eyes.
Las propiedades biomecánicas corneales en ojos de pacientes recién diagnosticados de glaucoma e hipertensión oculares (HTO) y que no han recibido tratamiento previo son de gran interés, porque pueden suponer una fuente de error en la medida de la presión intraocular (PIO) medida mediante tonometría de aplanación Goldmann (TAG) y Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA).
El principal objetivo de este estudio es evaluar los valores de PIO obtenidos con el TAG y ORA, en pacientes con glaucoma primario de ángulo abierto (GPAA) e HTO que no han recibido tratamiento antiglaucomatoso previo.
Materiales y métodosEstudio transversal, observacional con observador enmascarado. Se incluyeron pacientes recién diagnosticados de GPAA e HTO, que no habían recibido tratamiento tópico hipotensor previo.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 51 pacientes con GPAA y 34 pacientes con HTO. Se encontró un valor de PIOcc (PIO corneo compensada) significativamente mayor que el de la PIO TAG en el grupo de GPAA (p = 0.0002), mientras que no se encontraron diferencias significativas entre ambos tonómetros en el grupo de HTO (p = 0.1).
ConclusionesLa TAG parece infraestimar la PIO “real” en pacientes con GPAA sin tratamiento hipotensor previo, mientras que parece ser más exacta en pacientes con HTO.