Emerging arbovirus infections have classic symptoms such as fever, arthralgia, or rash. As some of them have ophthalmic symptoms/signs, the main objective is to evaluate whether these help clarify the clinical diagnosis.
Material and methodsA descriptive and retrospective study was conducted, in which cases of adults who attended an evaluation in 2016. The general and ophthalmic symptoms were analysed on those meeting the definition of dengue, Zika, and chikungunya.
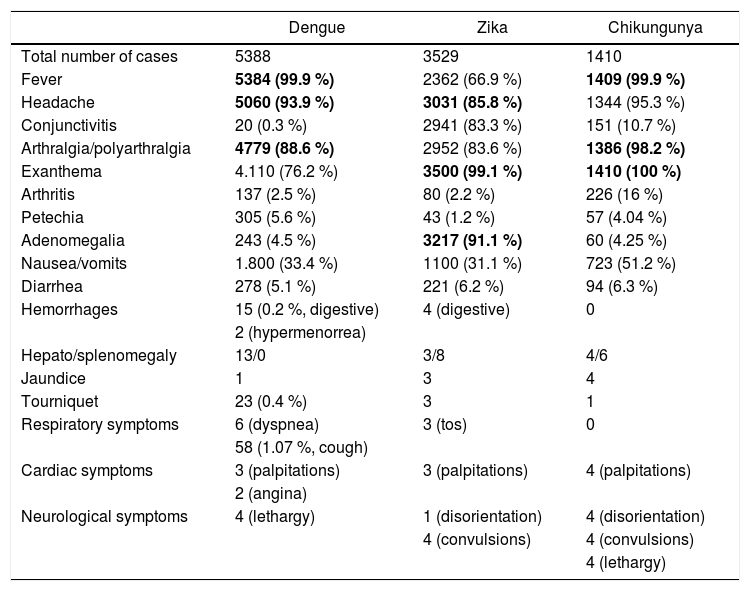
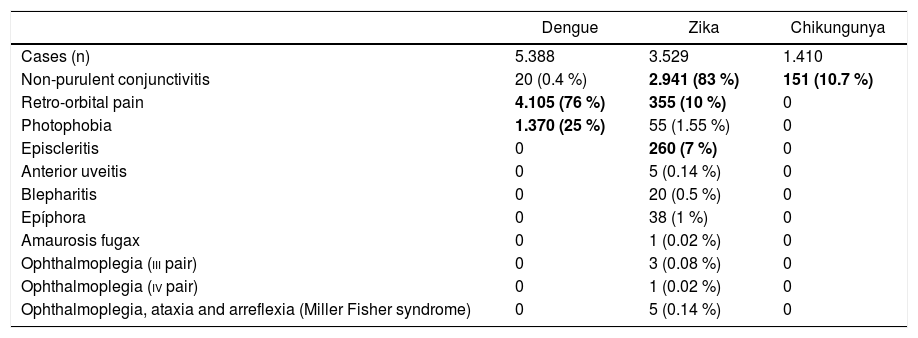
ResultsA total of 10,327 cases of arbovirosis were recorded, of which 5388 (52.2 %) were Dengue, 3529 (34.1 %) Zika, and 1410 (13.6 %) were Chikungunya. The main symptoms and signs of Dengue were: fever, headache/retro-orbital pain, arthralgia, rash, and nausea/vomiting. For Zika cases they were: exanthema, swollen glands, headache, arthralgia, and conjunctivitis, and for Chikungunya cases: rash, fever, arthritis, headache, and nausea/vomiting. The group with the most ophthalmic signs/symptoms was Zika, predominantly non-purulent conjunctivitis and retro-orbital pain, epiphora, episcleritis, anterior uveitis, as well as neurological syndromes such as isolated cranial nerve palsy (III and IV) or Miller Fisher syndrome.
ConclusionsOphthalmic signs/symptoms of Zika infection can help the clinical diagnosis of these arbovirosis.
Las infecciones por arbovirus emergentes tienen síntomas clásicos como fiebre, artralgias o rash, dado que algunas tienen síntomas/signos oftálmicos, el objetivo central es evaluar si estos ayudan a esclarecer el diagnóstico clínico.
Material y métodosEstudio descriptivo y retrospectivo, se analizan los casos de adultos que acudieron a evaluación en 2016, cumpliendo la definición de caso de dengue, zika y chikungunya, se analiza la sintomatología general y la oftálmica.
ResultadosSe registró un total de 10,327 casos de arbovirosis, de las cuales 5388 fueron Dengue (52.2 %), 3529 Zika (34.1 %) y 1410 Chikungunya (13.6 %); los principales síntomas y signos de Dengue fueron: fiebre, cefalea/dolor retroorbitario, artralgias, exantema y náuseas/vómito; para los casos de Zika: exantema, adenomegalias, cefalea, artralgias y conjuntivitis; para los casos de Chikungunya: exantema, fiebre, artritis, cefalea y nauseas/vómito. El grupo con más signos/síntomas oftálmicos es el de Zika, predominando conjuntivitis no purulenta y dolor retroorbitario, epífora, epiescleritis, uveitis anterior, hasta síndromes neurológicos como parálisis aisladas de pares craneales (III y IV) o síndrome de Miller Fisher.
ConclusionesLos signos/síntomas oftálmicos de la infección por zika pueden ayudar al diagnóstico clínico entra estas arbovirosis.