To report a case of spontaneous-onset unilateral scleritis and keratitis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus who partially responded to antibiotic therapy and achieved complete resolution after IV immunotherapy. A 30-year-old woman with a past medical history of hypothyroidism and systemic lupus erythematosus and on irregular therapy presented with a long-history of thinning of the sclera and cornea refractory to antibiotic therapy despite a positive culture for P. aeruginosa, which eventually resolved with the implementation of immunotherapy. Infectious scleritis is an uncommon and diagnostically challenging scleral inflammation. However; we must rule it out in patients with autoimmune diseases due to the inherent risk of these patients as their immune system has been impaired.
Comunicar un caso de escleritis y queratitis unilateral de aparición espontánea debidas a Pseudomonas aeruginosa en una paciente con lupus eritematoso sistémico que respondió parcialmente al tratamiento antibiótico y alcanzó la resolución completa tras inmunoterapia intravenosa. Una paciente de 30 años de edad con antecedentes médicos de hipotiroidismo y lupus eritematoso sistémico que ha estado recibiendo una terapia irregular, presentó adelgazamiento de la esclerótica y la córnea. La afección tuvo una progresión prolongada, refractaria al tratamiento antibiótico a pesar de un cultivo positivo para P. aeruginosa, pero finalmente se resolvió con la aplicación de inmunoterapia. La escleritis infecciosa es una inflamación escleral infrecuente y difícil de diagnosticar. Sin embargo; debemos descartarla en pacientes con enfermedades autoinmunes debido al riesgo inherente de estos pacientes al tener alterado su sistema inmune.
Inflammatory disorders involving the ocular surface may show in diverse ways, ranging from subtle subclinical changes to rapidly progressing and deleterious processes. Conversely, infectious scleritis is a rare yet significant source of scleral inflammation,1 with Pseudomonas aeruginosa being the most prevalent microorganism associated with it.1–3
Infectious scleritis has diverse etiologies, which can be categorized as either exogenous or endogenous. The former typically arises from post-traumatic and postoperative infections, as well as from the extension of contiguous infections such as keratitis. The latter is less common and can mimic non-infectious diffuse, nodular, or necrotizing scleritis. This type includes scleritis associated with systemic diseases such as syphilis and tuberculosis.4 Predisposing factors for primary infections include systemic infections, the use of systemic or topical steroids, and a previous diagnosis of autoimmune scleritis. Surgery on the eye, such as surgery to remove a pterygium, scleral buckle, or cataracts, or surgery for strabismus, glaucoma, suture removal, or vitreoretinal interventions, has been associated with the development of infectious scleritis. Secondary infectious scleritis specifically refers to the extension of primary corneal infection, known as corneoscleritis.1 The disease has a grim prognosis, and most cases require surgery and aggressive optimal medical therapy. Recurrences may be noted on rare occasions after cessation of the treatment and thereby require prolonged close observation despite clinical resolution.
Infectious scleritis typically correlates with an underlying ocular risk factor, such as previous ocular surgery or trauma, or systemic factors like diabetes and liver disease.5 We report a case of spontaneous-onset unilateral scleritis and keratitis due to Pseudomonas in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who partially responded to antibiotic therapy with complete resolution after IV pulses of cyclophosphamide.
Case presentationA 30-year-old woman with a past medical history of hypothyroidism and SLE on irregular treatment presented, for the first time, to our service with blurred vision, pain, and a 5-day history of redness in her right eye, with no previous record of any injury or use of contact lenses. Upon questioning, she complained of repeated episodes of episcleritis.
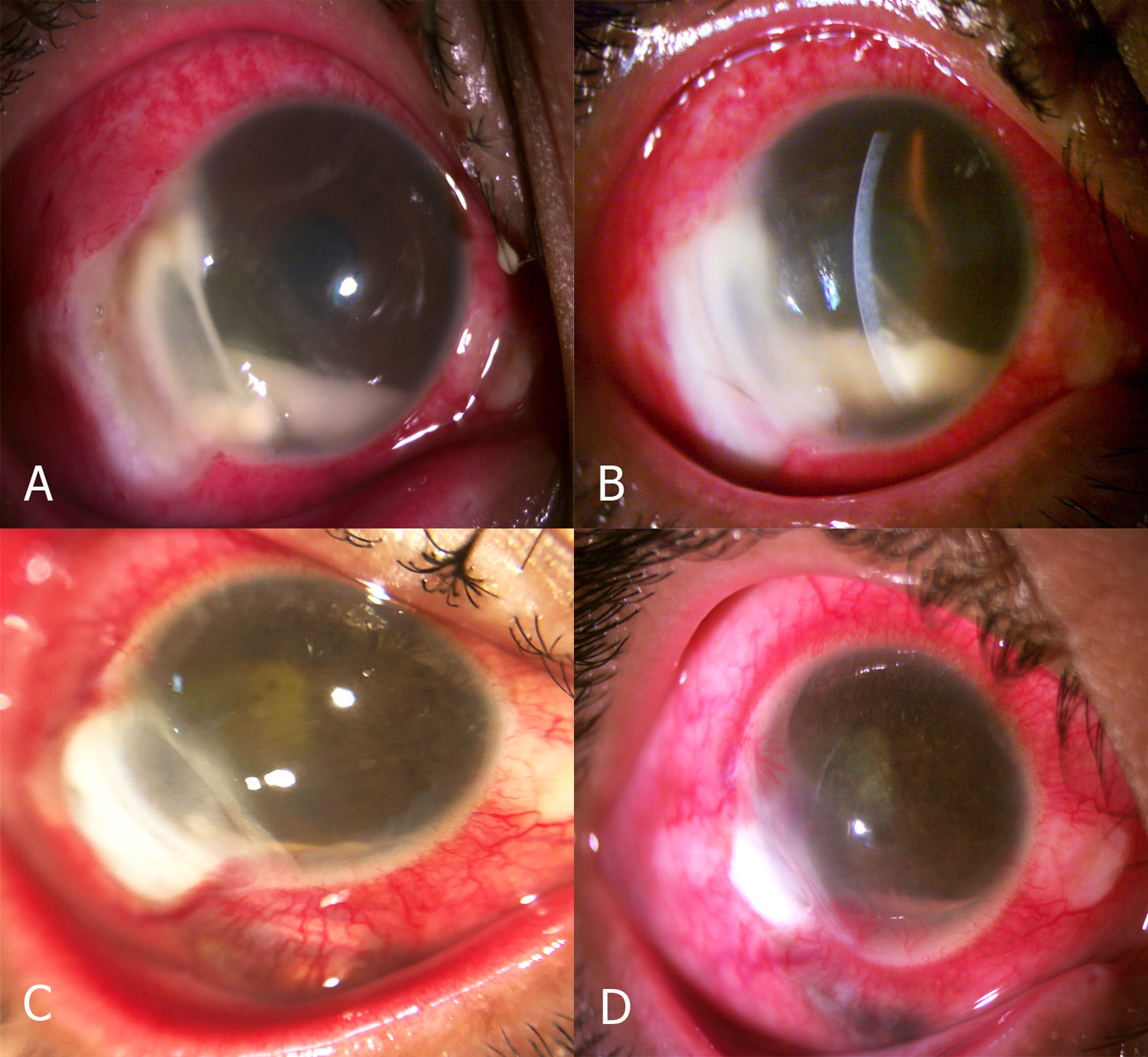
At the time of presentation, she was on methotrexate at a dosage of 7.5 mg/week. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 20/300 in her right eye (RE) and 20/20 in the her eye (LE). Slit-lamp of the RE revealed localized inferotemporal corneal edema 2+ (extending diagonally from the 6 o’clock to 9 o’clock positions), with dense suppurative stromal inflammation, corneal thinning with a 6 mm x 8 mm-diameter corneal epithelial defect adjacent to the limbus, and 7 mm x 7 mm scleral thinning located in the same sector with dilation of deep scleral vessels. In addition, the anterior chamber exhibited anterior uveitis with 4+ inflammatory cells and a 2.2 mm hypopyon level. A normal intraocular pressure (IOP) and the fundus are not assessable on the RE (Fig. 1). The LE fell within normal ranges.
A. Slit-lamp photograph of the RE of the patient at initial presentation showing a corneal epithelial defect, stromal infiltration, melting, scleral thinning, and hypopyon. B. Photograph of the RE 2 days after the administration of IV antibiotic treatment (ciprofloxacin and vancomycin). C. Photographs on 14 days after completing IV antibiotic treatment showing the resolution of uveitis. D. Photograph 40 days after immunosuppression treatment with cyclophosphamide.
A B-scan ultrasonography of the posterior segment of the eye revealed the presence diffuse punctate vitreous opacities of 2 to 3+, serous superior choroidal detachment, and retinochoroidal thickness of 1.62 mm in the macula (increased). An emergency referral to an experienced rheumatologist was immediately sought, and a systemic evaluation was performed to assess SLE activity, finding a Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) score of 6 (moderate activity), which suggested that the ocular inflammatory condition could also be associated with active systemic disease. The patient underwent a microbiological culture (MC) and was immediately put on broad-spectrum topical antibiotics for presumed microbial keratitis. However, progression was quickly unfavorable. Due to the lack of a confirmed pathogen and the suspicion of an autoimmune inflammatory process as the cause, on admission day 2, high-dose IV steroids (methylprednisolone 1 g QD for 3 days) were started, with a stable progression under control.
Surprisingly, in day 3, MC results revealed Pseudomona aeruginosa sensitivity to ciprofloxacin and vancomycin. Subsequently, IV treatment was prescribed for 14 days, involving a dosage of 400 mg BID for ciprofloxacin and 1 g BID for vancomycin. The epithelial defect was partially closed, the scleral thinning was stabilized, and the hypopyon was almost completely reduced. Due to the lack of control over the systemic disease, IV boluses of cyclophosphamide (1 g per month for 2 months) were prescribed. This intervention led to the complete resolution of the issues affecting the cornea and sclera, albeit with the persistence of previously incurred consequences. No recurrence was noted following the conclusive treatment; however, due to the profound inflammation and severity of the condition, the ultimate BCVA value for the LE was limited to light perception.
DiscussionScleritis is an inflammatory disease of the deeper scleral tissues, associated with ocular pain and tissue destruction.4,6,7 An underlying systemic disease is diagnosed in about one-half of the patients with scleritis, being the rate of prevalence in SLE, 2.4%.8 Infectious causes are less common and the most related agent is Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Necrotizing scleritis is the most serious form of presentation, and may, sometimes, contribute to the development of uveitis, which seriously compromises vision. Therefore, the cause must be promptly investigated to establish timely treatment. The initial presentation of infectious scleritis is often similar to autoimmune scleritis and differentiation is challenging.
Our patient with SLE presented with necrotizing scleritis that led to adjacent peripheral ulcerative keratitis and uveitis with hypopyon. The presence of systemic disease activity (according to SLEDAI), the increased retinochoroidal thickness and the absence of typical signs of typical infectious keratitis suggested a possible underlying serious ocular immunological disorder. Additionally, there was a favorable initial response to immunotherapy. However, surprisingly, on day 3, preliminary culture tests results confirmed the presence of P. aeruginosa bacterial infection, which made us change our therapeutic behavior immediately.
Of note, this positive culture test results raised questions about whether it represented a superinfection or whether Pseudomonas actually started the initial symptoms.
It is crucial to recognize that changes to the immune system’s regulatory mechanisms of SLE renders individuals to become susceptible to infections. Consequently, it is imperative to exclude infectious disease as potential causes of inflammatory conditions in the anterior segment of SLE patients before attributing the inflammation to the disease, especially in cases where ocular signs are atypical or rare.
An accurate diagnostic approach is of paramount importance to preventing complications significantly affecting visual health. On the other hand, physicians must know which are the ocular signs associated with autoimmune diseases, since the eye could be the first or even the only organ affected and can alert us on the systemic activity of the disease.9,10 Our case underscores the intricacies involved in the diagnosis and management of infectious keratitis-related corneoscleritis in a patient with uncontrolled autoimmune disease, highlighting the need for timely interventions.
FundingThere is no source of funding.
Informed consentWritten informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of details of her case report and accompanying images.