To investigate the reproducibility of the water drinking test in determining intraocular pressure peaks and fluctuation.
It has been suggested that there is limited agreement between the water drinking test and diurnal tension curve. This may be because it has only been compared with a 10-h modified diurnal tension curve, missing 70% of IOP peaks that occurred during night.
MethodsThis was a prospective, analytical and comparative study that assesses the correlation, agreement, sensitivity and specificity of the water drinking test.
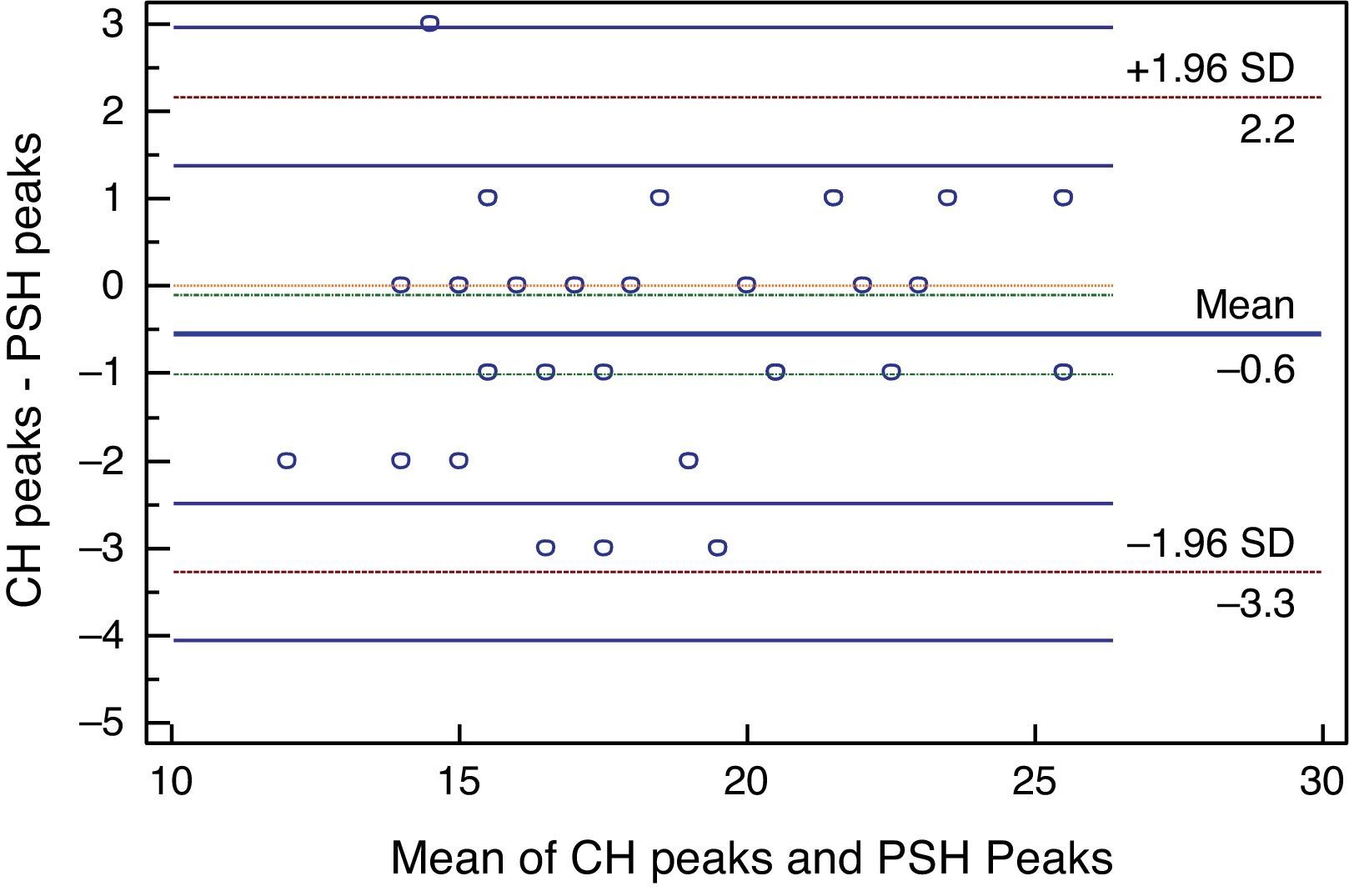
ResultsThe correlation between the water drinking test and diurnal tension curve was significant and strong (r=0.93, confidence interval 95% between 0.79 and 0.96, p<01). A moderate agreement was observed between these measurements (pc=0.93, confidence interval 95% between 0.87 and 0.95, p<.01). The agreement was within ±2mm Hg in 89% of the tests.
DiscussionOur study found a moderate agreement between the water drinking test and diurnal tension curve, in contrast with the poor agreement found in other studies, possibly due to the absence of nocturnal IOP peaks.
ConclusionsThese findings suggest that the water drinking test could be used to determine IOP peaks, as well as for determining baseline IOP.
Investigar la reproducibilidad de la prueba de sobrecarga hídrica para determinar picos y fluctuación de presión intraocular.
Se ha sugerido que la concordancia de la prueba de sobrecarga hídrica con la curva horaria es baja, sin embargo, solo se ha comparado con la curva horaria modificada de 10 horas, prescindiendo del 70% de los picos de presión ocular al no obtener las tomas nocturnas de presión intraocular.
MétodosEstudio prospectivo, analítico y comparativo, en el que se determinó estadísticamente la correlación, la concordancia, así como la sensibilidad y la especificidad de la prueba de sobrecarga hídrica comparándola con la curva horaria diurna.
ResultadosLa correlación de la prueba de sobrecarga hídrica fue alta (r=0,93, IC 95% 0,79-0,96, p<0,01), mientras que la concordancia de la prueba fue moderada (pc=0,93, IC 95% 0,87–0,95, p<0,01). La concordancia de valores entre ±2mm Hg (variabilidad intraobservador) fue del 89,5% IC 95%, 88-99%.
DiscusiónEn nuestro estudio se encontró una concordancia moderada contrastando con la pobre concordancia encontrada en otros estudios entre la prueba de sobrecarga hídrica y la curva horaria, posiblemente generada por la ausencia de tomas nocturnas de presión intraocular.
ConclusiónEstos hallazgos nos sugieren que la sobrecarga hídrica se puede utilizar para determinar picos de presión intraocular en quien se sospecha así como para determinar presión intraocular basal dada la concordancia encontrada en la variabilidad intraobservador.