Non-thrombotic pulmonary embolism is a partial or complete occlusion of the pulmonary vasculature by miscellaneous types of materials that includes neoplasm, infective agents, fat, amniotic fluid, gases and foreign materials. The literature reporting the incidence of coil migration after pelvic embolization and concomitant acute pulmonary embolism is scarce. We report a case of coil migration after pelvic embolization and symptomatic acute pulmonary embolism treated with endovascular extraction and standard anticoagulation.
La embolia pulmonar no trombótica es una oclusión parcial o completa de la vasculatura pulmonar por diversos tipos de materiales que incluyen neoplasias, agentes infecciosos, grasa, líquido amniótico, gases y materiales extraños. La literatura que ha reportado de la incidencia de la migración de coil después de la embolización pélvica con embolia pulmonar aguda concomitante, es escasa. Presentamos un caso de migración de coil tras embolización pélvica y embolia pulmonar aguda sintomática tratada con extracción endovascular y anticoagulación estándar.
Non-thrombotic pulmonary embolism (NTPE) is a partial or complete occlusion of the pulmonary vasculature by miscellaneous types of materials that includes neoplasm, infective agents, fat, amniotic fluid, gases and foreign materials. NTPE can cause local and systemic inflammation causing endothelial and pulmonary parenchymal injury. This entity may present as completely asymptomatic, with nonspecific symptoms or even cause sudden death. The literature reporting the incidence of coil migration after pelvic embolization and concomitant acute pulmonary embolism is scarce. Most cases present as incidental radiological findings in asymptomatic patients.1
We report a case of coil migration after pelvic embolization and symptomatic acute pulmonary embolism treated with endovascular extraction and standard anticoagulation. The patient has agreed to the publication of images and details related to his case.
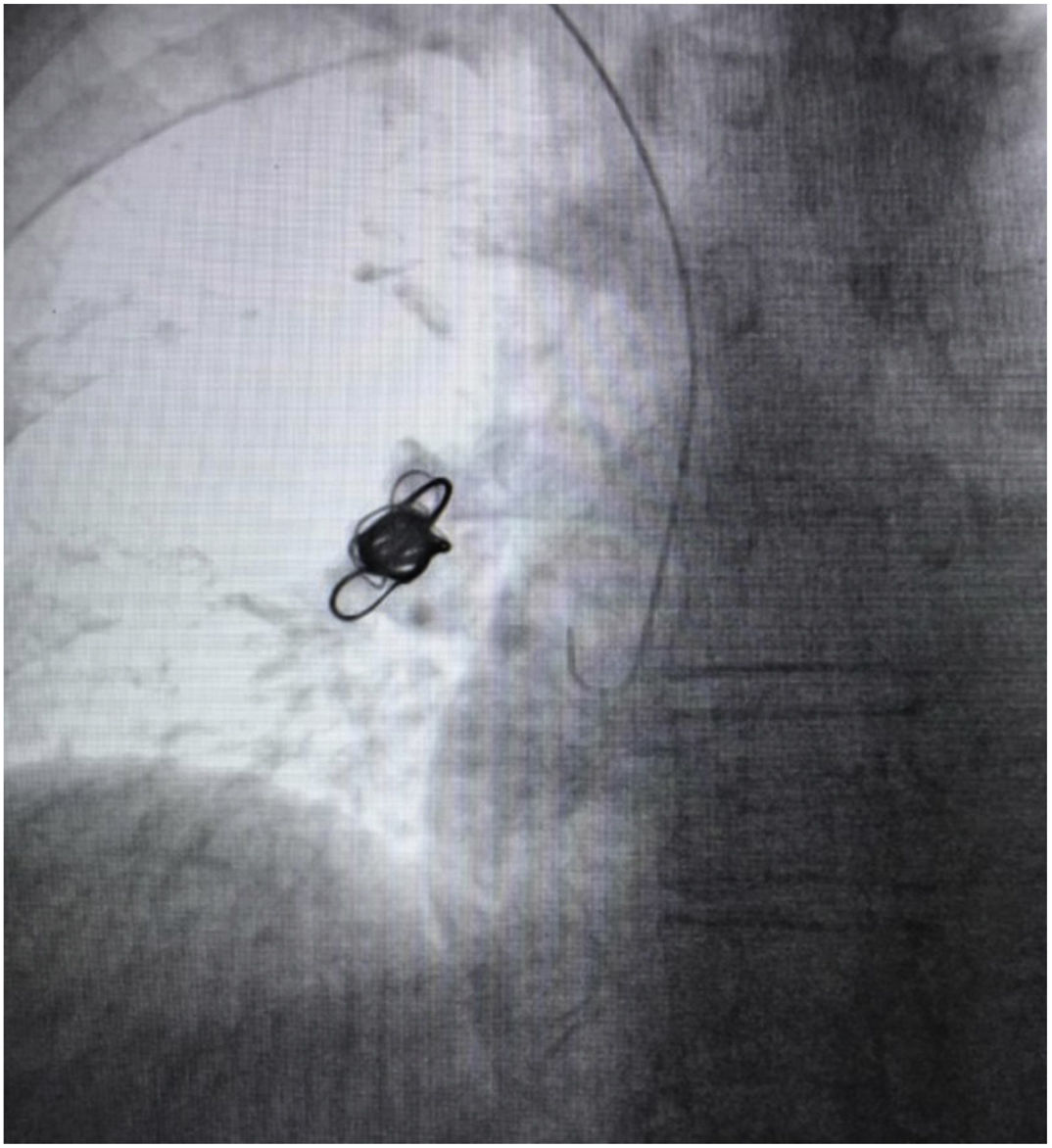
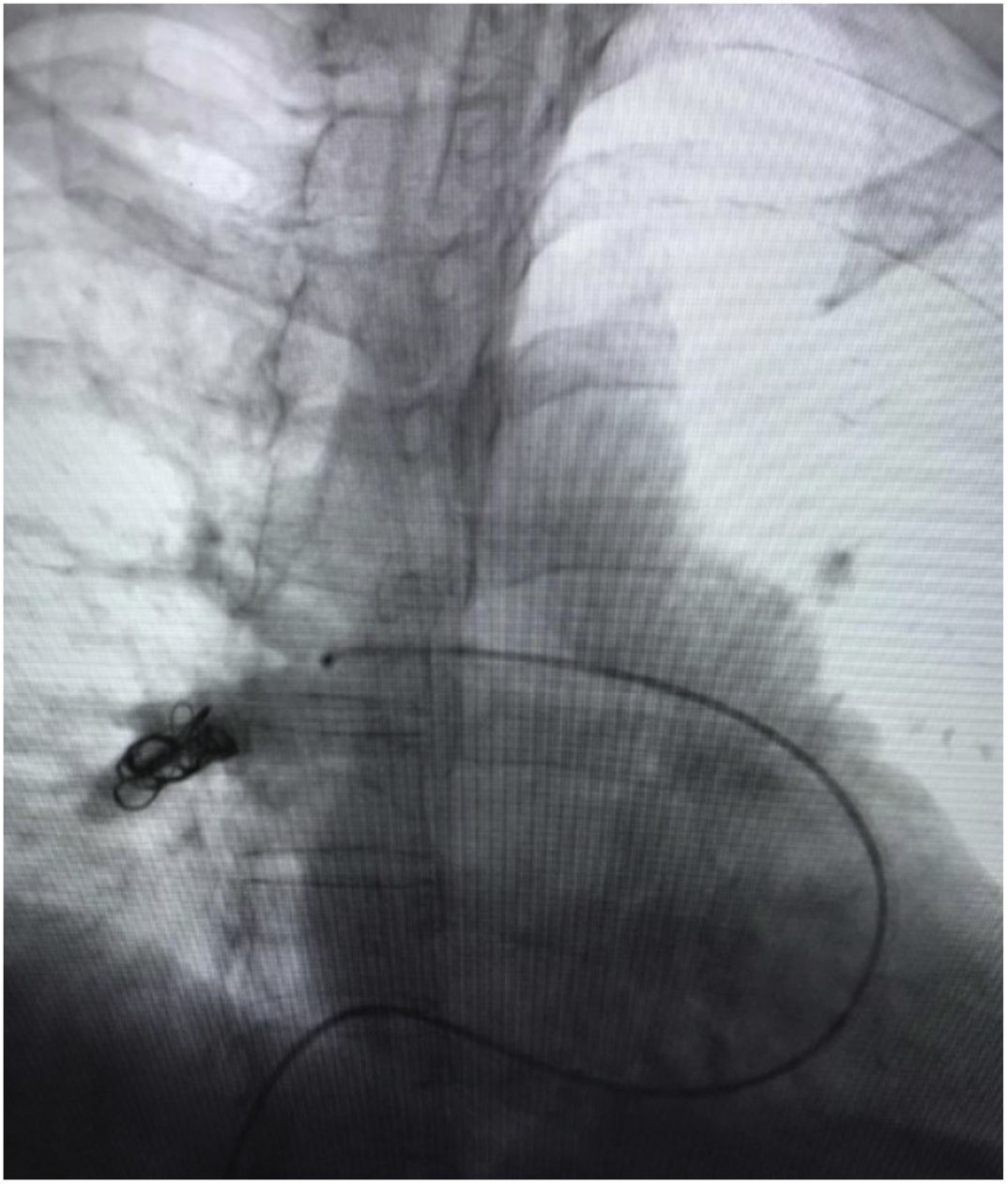
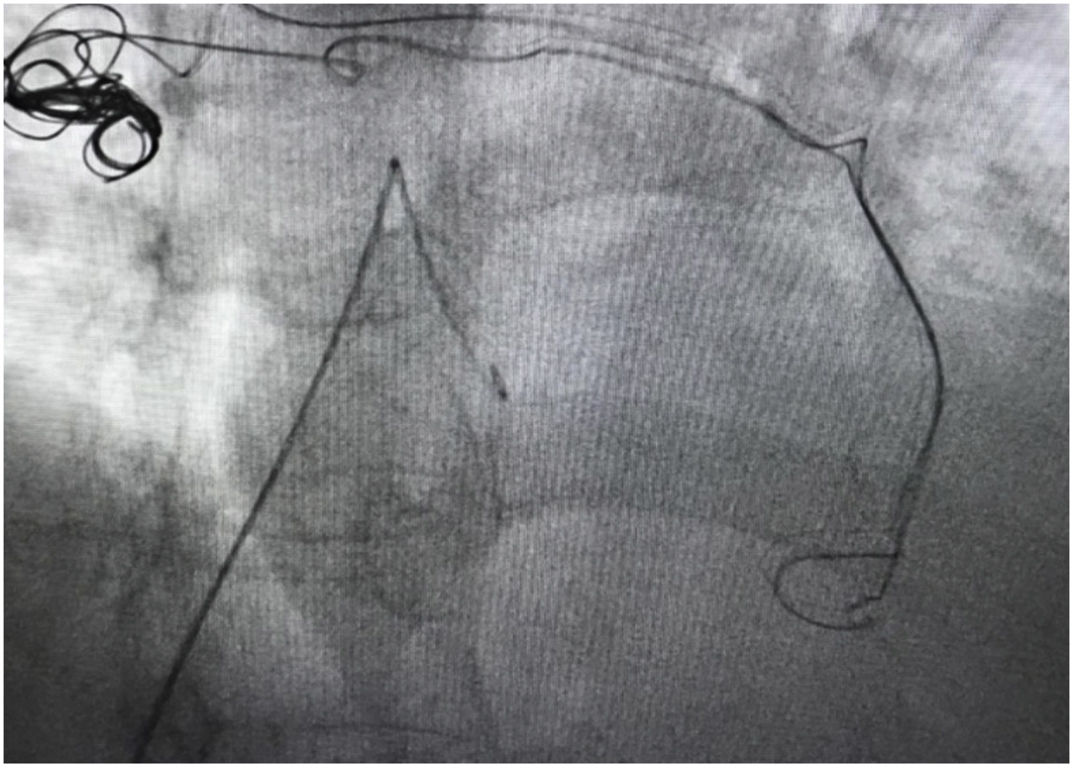
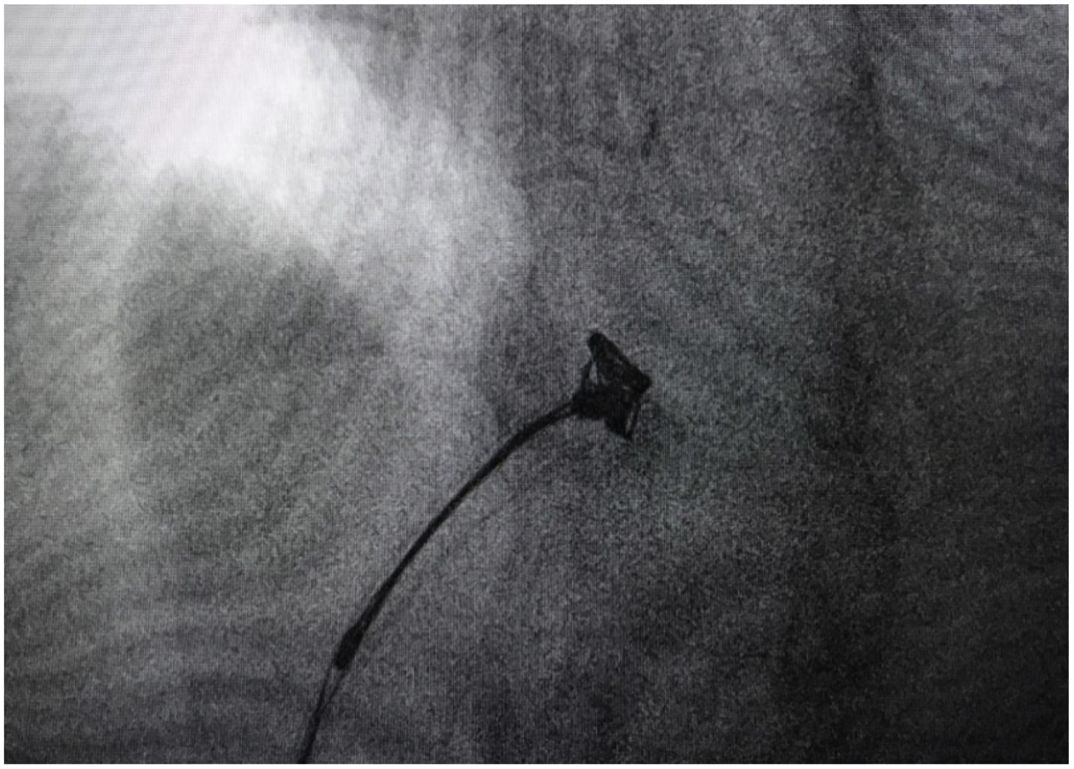
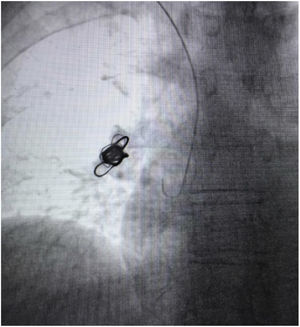
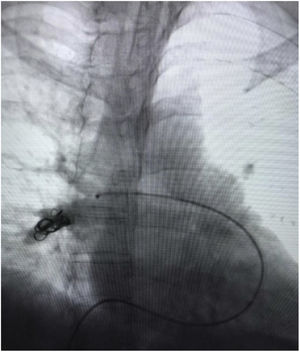
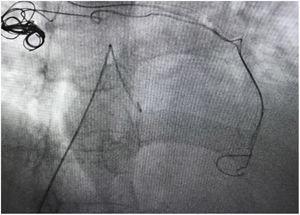
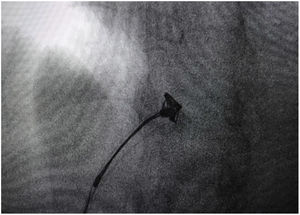
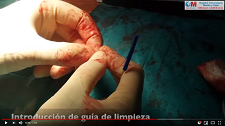
A 53-year-old female with congestive pelvic syndrome due to pelvic varicose vein underwent pelvic veins embolization using 2 coils (20mm×50cm) (Concerto; Medtronic Inc., Minneapolis, USA) for the right gonadal vein. She presented to the emergency department 30 days later with mild chest discomfort. Scout image from computed tomography (CT) pulmonary angiogram showed completely displaced coil nest in the chest. A 12-Fr sheath was placed in the right common femoral vein and pulmonary angiogram was performed, demonstrating occluded right lower lobe segmental arteries (Figs. 1 and 2). A 5-Fr multipurpose catheter supported by a 0.025 guidewire was advanced into the main pulmonary artery. The coil nest was snared with a 25-mm gooseneck snare (Fig. 3) and retracted into the inferior vena cava. The coil nest was then pulled down into the left external iliac vein and removed through the sheath in two extractions procedures repeating the same sequence (Figs. 4 and 5). The patient was discharged home the next day on a therapeutic dose of enoxaparin. She remained asymptomatic at 3-month clinical follow-up visit.
Complications after pelvic embolization are rare.2 Coil migration can occur after pelvic varicose vein embolization and cause a NTPE. The majority of reported cases in the literature are asymptomatic and no need for additional endovascular or open treatment. The chest X-ray may show a linear density at an unusual anatomic location, but CT is the gold standard to confirm the position of the foreign body.1,2 The pattern presented in chest CT will depend on the type of embolization. Disperse radiopaque/metallic small densities, centrilobular ground glass opacities, and micronodules/miliary nodules, as well as fibrotic/consolidative opacities, may indicate NTPE.1 If the patient develops persistent symptoms without improvement after medical treatment with systemic anticoagulation like the case reported by Shashi et al.,2 endovascular coil extraction must be the first line approach. In 2018, Leon et al.1 reported a case of symptomatic coil NTPE treated only with anticoagulation that had symptoms improvement during the clinical follow up. A case report published by D’ Amato et al.3 in 2016, presented a patient with an incidental radiological finding of a nodular image of metal density in the left hemithorax. Chest CT scan showed a foreign body consistent with a coil in the left lower lobe segmental branch. The patient was asymptomatic, so she was treated conservatively with clinical and image follow up.3 Cases of coil migration have been described in men as well. In 1993 Moriel et al.4 published a case report of a man with an asymptomatic pulmonary migration of a coil after a pelvic embolization due to the treatment of erectile dysfunction.4 There are no reported cases of patients with coil NTPE that needed an open surgical approach.
In conclusion, the non-thrombotic coils pulmonary embolism after the endovascular treatment of congestive pelvic syndrome is a rare complication. However, it should be considered as a differential diagnosis in patients with acute onset dyspnea after pelvic varicose vein embolization. Large studies are needed to define the real incidence the best treatment approach to this entity. This brief report contributes to the world literature on the presentation, management and outcome of this complication, which is a rare occurrence.
Ethical considerationsThe ethics committee of the Hospital Militar Central approved this case report. Constant of the use of medical data is obtained verbally and in written form from the patient.
Financial disclosuresNone.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
None.