Pre-pregnancy obesity has been proposed as a risk factor related to gestational diabetes and hypertensive disorders during pregnancy.
ObjectivesIdentify pregnancy related diseases associated with pre-pregnancy obesity as a risk factor in a high risk pregnancy patient population.
Methods600 patients whose pre-pregnancy obesity had been assessed as a high risk factor were included in the study. The means, standard deviation, median, interquartile intervals, Pearson and Spearman correlation and logistic regression to estimate risk with the odds ratio and 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
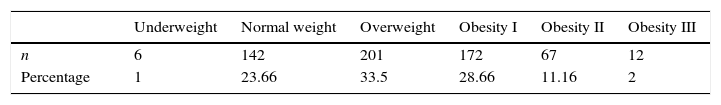
ResultsThe mean pre-pregnancy body mass index was 29.59±6.42kg/m2. The mean for recommended pregnancy weight gain was 2.31±1.03kg, but the mean of real weight gain was 8.91±6.84kg. A significant correlation between pre-pregnancy obesity and family history of diabetes mellitus (p=0.000), systemic hypertension (p=0.003), cardiac diseases (p=0.000), dyslipidemia (p=0.000) and obesity (p=0.000) was identified. Pre-pregnancy obesity was identified as a risk factor for the development of gestational diabetes (OR: 1.95; 95% CI: 1.39–2.76; p=0.000) in this kind of patient.
Discussion and conclusion75% of high risk pregnancy women in a high specialty hospital in West Mexico are overweight or obese when they become pregnant. These are risk factors in the development of gestational diabetes.
La obesidad pregestacional se ha propuesto como factor de riesgo relacionado con la presencia de diabetes y trastornos hipertensivos durante el embarazo.
ObjetivosIdentificar las patologías asociadas con la obesidad pregestacional como factor de riesgo en una población de pacientes que cursan con embarazo del alto riesgo.
MétodosSe estudió a 600 pacientes en quienes se evaluó la presencia de obesidad pregestacional como factor de riesgo. Se calcularon promedios, desviación estándar, mediana, intervalos intercuartilares, correlación de Pearson, Spearman y regresión logística para estimación del riesgo a través de odds ratio (OR) e intervalos de confianza (IC) del 95%.
ResultadosEl índice de masa corporal (IMC) pregestacional fue 29.59±6.42kg/m2. La ganancia ponderal recomendada acorde al IMC pregestacional fue en promedio de 2.31±1.03kg, mientras el peso efectivamente ganado por el grupo de mujeres fue en promedio de 8.91±6.84kg. Se identificó una correlación estadísticamente significativa entre la presencia de obesidad con el antecedente heredofamiliar de diabetes mellitus (p=0.000), hipertensión arterial sistémica (p=0.003), cardiopatía (p=0.000), dislipidemia (p=0.000) y obesidad (p=0.000); se identificó la obesidad pregestacional como factor de riesgo para el desarrollo de diabetes gestacional (OR: 1.95; IC del 95%: 1.39 a 2.76; p=0.000) en esta población de pacientes.
Discusión y conclusionesUn 75% de las mujeres que cursan con embarazo de alto riesgo en un hospital de alta especialidad en el occidente de México llegan al embarazo con sobrepeso u obesidad pregestacional y estas entidades son factores de riesgo para el desarrollo de diabetes gestacional.
The worldwide prevalence of overweight and obesity has reached epidemic proportions and also includes women of reproductive ages,1 who are a vulnerable group and for whom this phenomenon has become more common.2
According to the World Health Organisation,3 the percentage of the population with obesity has doubled since 1980. In 2008, over 1400 million adults over 20 were overweight or obese, which amounts to 35% of the worldwide population being overweight and 11% being obese and of these, over 300 million are women of childbearing age.
At present, 65% of the worldwide population is overweight and the presence of overweight or obesity has been found to be related to a higher number of deaths than low weight. 42 million children under 5 are obese. Obesity is a potentially predictable risk factor.4
Up until 2008, the year in which comparative data became available, 72.3% of the population in the United States of American (U.S.A.) was overweight and 32.2% was obese. In Brazil, the combined prevalence of overweight-obesity was 42.8% and 16.1% of the population was obese (national 2006–2007 data). In Mexico, according to the 2006 National Survey of Health and Nutrition (ENSANUT), the prevalence of overweight-obesity was 66.7%, 42.5% of whom were overweight and 24.2% were obese. This ranked Mexico as the country with the second highest rate of obesity in the continent of America.5
According to 2012 ENSANUT data, from 1999 an epidemic of obesity in adult women was detected. In 2006, overweight and obesity increased its percentages in all age groups, regions and socio-economic groups in Mexico. In 2012, the combined prevalence of overweight and obesity in teenage women was 35.8%, of whom 14.5% were reported as obese. In adult women the combined prevalence was 73%. In childbearing age women, the pattern of combined overweight-obesity is as follows: women aged between 20 and 29: 30.6% overweight, 24% obese; aged between 30 and 39: 38.1% overweight and 37.3% obese, and aged between 40 and 49: 37.6% overweight and 46.1% obese.6 Previous figures show the raised probability that pre-pregnancy overweight and obesity continue to be present during pregnancy in Mexican women.
Maternal overweight and obesity are associated with several obstetric and perinatal complications,7–11 such as gestational diabetes,12 preeclampsia,13–15 foetal macrosomia16 and a higher risk of a non-natural birth through a caesarean section.17,18
Whilst this phenomenon in pre-pregnancy obesity may be observed, so too may excessive weight gain during pregnancy confer a similar risk profile associated with a high-risk of adverse maternal and foetal outcome,19,20 and the birth of babies which are oversized for their gestational age.21–23 The previously described situation coincides with the outcome observed in women of childbearing age who were from Latin or Brazilian backgrounds.24
Pre-pregnancy overweight and obesity increases the probabilities of excessive weight gain during pregnancy and this is associated with perinatal complications in the foetal-maternal interaction, such as obstetric haemorrhaging, macrosomia and hypoglycaemia in the newborn, etc. There are also medical and metabolic complications for the pregnant woman during the postpartum period, such as: gestational diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia–eclampsia, and postpartum overweight or obesity.25,26
Factors associated with pre-pregnancy overweight and obesity have been identified in these women and include: being a mother over 35,27 high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, consumption of alcohol,28 low educational level, African ascendancy, overeating and sedentary lifestyle.29
In 2011, in U.S.A. 23.4% of mothers in one area of 23 states and the District of Columbia (DC) were obese (body mass index [BMI]≥30kg/m2) prior to pregnancy and intervals were 18–28.6%; women over 20 were obese more often and it is of note that those who presented this situation more often were women of Hispanic origin.30
Despite the fact that metabolic changes are relatively uncommon amongst young women, they may increase with obesity. In one study carried out in the Danish population associations between BMI and the risk of diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia were analysed in 292,847 young apparently healthy women, who had given birth between years 2004 and 2009, and who had no history of cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, metabolic changes related to pregnancy, diabetes, hypertension or dyslipidemia. Of those women studied, 2029 patients developed diabetes, 3133 hypertension and 1549 dyslipidemia. The relative risks for (RR) for diabetes were: 0.84 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.62–1.14) if low weight, 2.63 (2.36–2.93) if overweight, 4.83 (4.27–5.47) if obese grade I, 7.17 (6.1–8.48) if obesity grade II and 6.93 (5.47–8.79) if obesity grade III. For hypertension it was 0.86 (0.69–1.09), 1.82 (1.67–1.98), 2.81 (2.52–3.13), 3.92 (3.36–4.56) and 5.69 (4.71–6.89), and for dyslipidemia 1.18 (0.85–1.65), 2.01 (1.75–2.31), 3.11 (2.61–3.70), 4.64 (3.66–5.87) and 3.72 (2.53–5.48), respectively. In this study BMI was strongly associated with an increase in the risk of diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia to 5.5 years after the birth of the babies.31
Our study presents frequency and estimates the risks of metabolic complications of pregnancy related with overweight or obesity in Mexican women who had high risk pregnancies and who were treated in a high specialty obstetric hospital in West Mexico.
ObjectivesTo identify pregnancy pathologies associated with pre-pregnancy obesity as a risk factor in a patient group who had high-risk pregnancies.
MethodsDesignAnalytical transversal study.
Sample populationThe data from 600 women with high-risk pregnancies attended by the Clinical Department of Perinatal Medicine of the Speciality Medical Unit (UMAE) of the Hospital de Gineco-Obstetricia del Centro Médico Nacional de Occidente (CMNO) del Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS) were analysed. All pregnant patients with at least one hospital stay organised by the Clinical Department of Perinatal Medicine were selected. Postpartum patients were not taken into consideration, nor those with cognitive deficit or those in a critical condition. Patients who were unaware of their bodyweight and/or increase in weight during pregnancy were excluded from the study.
Ethical standardsThe project was authorised by the Local Research and Ethics in Health Research Committee 1310 with its head office in the UMAE, Hospital de Gineco-Obstetricia del CMNO (IMSS, with registry number R-2014-1310-35). Patients were assessed nutritionally as part of the standard process of attention and data was treated confidentially.
Statistical methodsStatistical analysis was carried out in 2 stages: analysis with descriptive statistical analysis which included: averages, standard deviation, medians and quantitative variables, as well as proportions and percentages in the case of qualitative variables. The second stage included analysis of Pearson correlation for quantitative variables and Rho de Spearman for ordinal variables, with which the association between variables considered as prognostic factors was determined. Logistic regression was carried out for the calculation of odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals, as risk assessors.
Analysis was complemented with the obtainment of statistical significance (p≤0.05), using the Chi-square test for qualitative variables and the Student's t-test for quantitative variables.
ProceduresHospitalised patients were assessed nutritionally by the Clinical Department of Perinatal Medicine of the Hospital de Gineco-Obstetricia, CMNO, as were their hospital records, during the period between February 2013 and December 2014. All assessments made and data obtained from the patients’ hospital records were the result of standard patient care in the said division. Blood pressure was expressed in terms of mean blood pressure (MBP), which was obtained from registered systolic blood pressure (SBP) values and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) values, in accordance with the following formula: (SBP+2 [DBP])/3.32
ResultsThe cases of high-risk pregnancy women studied were classified according to primary and most common comorbidities in the female Mexican population of women of childbearing age. These included: pregestational diabetes mellitus, type 1 (DM1) and 2 (DM2), hypertension and alterations to kidneys which, due to their risk profile were treated in second and third level hospitals, as was the case of the 600 patients studied, whose mean age was 31, with an interquartile interval (IQI) from 26 to 36.
Out of the total patients assessed 23.6% (142) had an ideal weight and 1% (6) were underweight. However, out of the 75.3% of the remaining patients (452), 201 patients were overweight and 172 suffered from grade I obesity (Table 1).
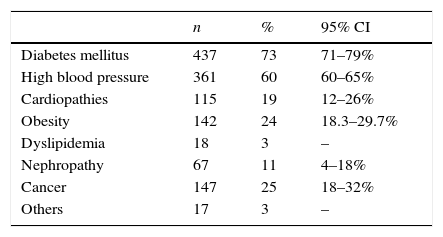
With regard to family history backgrounds, 73% of the patients had a relative with diabetes mellitus and 60% with high blood pressure. Furthermore, 24% of patients presented with a history of obesity in first-degree relatives (Table 2).
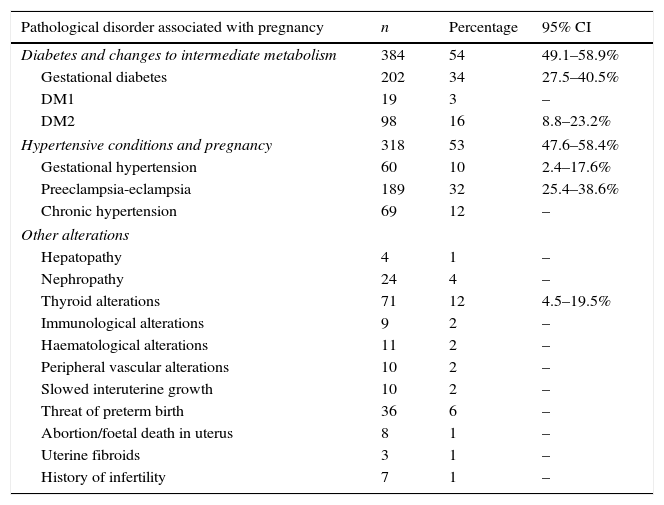
In accordance with the records assessed, 54% of patients (384) had gestational diabetes, DM1 or DM2; hypertensive disorders as a whole represented 53% (n=318) of pathologies in the patient group who had high-risk pregnancies (Table 3), with 2 pathologies coinciding in 202 women.
High risk pathological disorders in pregnancy.
| Pathological disorder associated with pregnancy | n | Percentage | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes and changes to intermediate metabolism | 384 | 54 | 49.1–58.9% |
| Gestational diabetes | 202 | 34 | 27.5–40.5% |
| DM1 | 19 | 3 | – |
| DM2 | 98 | 16 | 8.8–23.2% |
| Hypertensive conditions and pregnancy | 318 | 53 | 47.6–58.4% |
| Gestational hypertension | 60 | 10 | 2.4–17.6% |
| Preeclampsia-eclampsia | 189 | 32 | 25.4–38.6% |
| Chronic hypertension | 69 | 12 | – |
| Other alterations | |||
| Hepatopathy | 4 | 1 | – |
| Nephropathy | 24 | 4 | – |
| Thyroid alterations | 71 | 12 | 4.5–19.5% |
| Immunological alterations | 9 | 2 | – |
| Haematological alterations | 11 | 2 | – |
| Peripheral vascular alterations | 10 | 2 | – |
| Slowed interuterine growth | 10 | 2 | – |
| Threat of preterm birth | 36 | 6 | – |
| Abortion/foetal death in uterus | 8 | 1 | – |
| Uterine fibroids | 3 | 1 | – |
| History of infertility | 7 | 1 | – |
Regarding nutritional and infectious disorders associated with pregnancy, nausea ranked first in frequency, which affected 66% of patients, followed by heartburn (58%), urinary infections (56%) and oedema (55%).
The median of MBP in patients was 86.66 (interquartile interval [IQI]: 66–100)mmHg, fasting blood sugar median of 83.00 (IQI: 66–100)mg/dL and post-meal blood sugar median of 126 (IQI: 105–172).
Pre-pregnancy BMI was at a median level of 28.67 (IQI: 25.15–33.15)kg/m2. The recommended weighted gain for pre-pregnancy BMI was a median of 6 (IQI: 6.00–8.7kg), whilst the median weight effectively gained by the group of women was 9.00kg (IQI: 5.00–13.00kg).
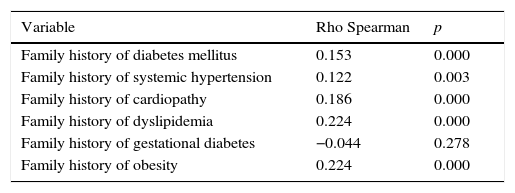
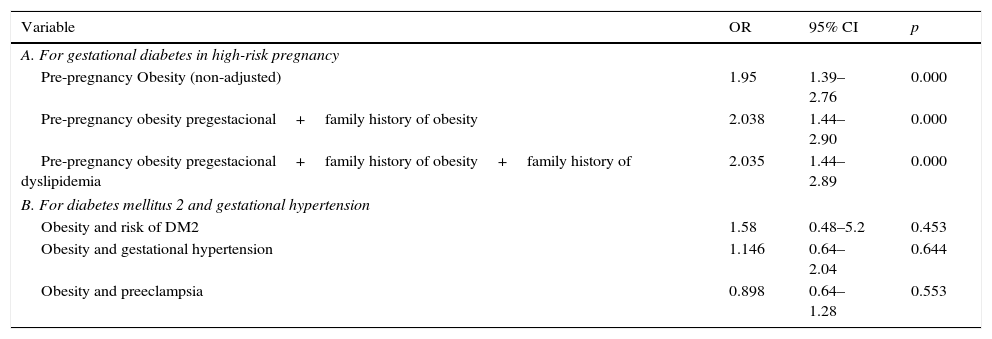
There was a statistically significant correlation between the presence of obesity and a family history of diabetes mellitus (p=0.000), systemic hypertension (p=0.003), cardiopathy (p=0.000), dyslipidemia (p=0.000) and background of obesity (p=0.000). The association of obesity with a pre-pregnancy background of diabetes in previous pregnancies (p=0.278) was not significant (Table 4). Pre-pregnancy obesity was also identified as a risk factor for the development of gestational diabetes (OR: 1.95; 95% CI: 1.39–2.76; p=0.000) in this patient group (Table 5).
Correlation of pre-pregnancy obesity with other variables.
| Variable | Rho Spearman | p |
|---|---|---|
| Family history of diabetes mellitus | 0.153 | 0.000 |
| Family history of systemic hypertension | 0.122 | 0.003 |
| Family history of cardiopathy | 0.186 | 0.000 |
| Family history of dyslipidemia | 0.224 | 0.000 |
| Family history of gestational diabetes | −0.044 | 0.278 |
| Family history of obesity | 0.224 | 0.000 |
Pre-pregnancy obesity as a cardiometabolic risk factor.
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. For gestational diabetes in high-risk pregnancy | |||
| Pre-pregnancy Obesity (non-adjusted) | 1.95 | 1.39–2.76 | 0.000 |
| Pre-pregnancy obesity pregestacional+family history of obesity | 2.038 | 1.44–2.90 | 0.000 |
| Pre-pregnancy obesity pregestacional+family history of obesity+family history of dyslipidemia | 2.035 | 1.44–2.89 | 0.000 |
| B. For diabetes mellitus 2 and gestational hypertension | |||
| Obesity and risk of DM2 | 1.58 | 0.48–5.2 | 0.453 |
| Obesity and gestational hypertension | 1.146 | 0.64–2.04 | 0.644 |
| Obesity and preeclampsia | 0.898 | 0.64–1.28 | 0.553 |
The pre-pregnancy BMI median in women with a high-risk pregnancy was found to be within the parameters considered for overweight (28.67kg/m2SC), which is very close to the obesity limit. When analysing pre-pregnancy BMI in this context we observe that the 25 percentile limit is in a BMI of 25.15kg/m2SC and the 75 percentile limit in 33.15kg/m2SC. This means that at least 75% of the women with a high-risk pregnancy become pregnant when they are overweight or obese at very early ages in their lives, since the average age of the sample population was 30.8±6.31 years. These figures coincide with the findings published as part of the ENSANUT in Mexico from 2012, which only represented the non-pregnant female population.
In accordance with the BMI classification and ideal weight increase, it was found that the suggested average of the weight increase of patients assessed was 7.3±2.5kg, whilst effective weight gain was 8.91±6.8kg. This was more than a 2kg increase over that recommended, but there was a standard deviation of 6.8kg. Total recommended weight gain in 75% of the population was 8.7kg. However, 50% of the population had an increase in total weight over 9kg, including 25% whose weight increase was over 13kg.
These findings coincide with those observed in the U.S.A., a country which, according to reports from the World Health Organisation, ranks first in obesity in its adult population. Mexico also has high rates of overweight and obesity and ranks second worldwide. However, there is an important contrast here where, according to reports of its vital statistics, only 23.4% of its pre-pregnancy population are obese. What is striking is that the women who mostly present with obesity are of Latin origin.30
Weight increase during pregnancy leads to 40% of American women being overweight or obese when they give birth. In our study this was surpassed, as 63% of the women were classified as overweight and grade I obese.32
In Mexico the study published in 2012 by the Reyes et al. group assessed the impact of pre-pregnancy weight gain in an urban population of pregnant Mexican women who presented with pre-pregnancy overweight or obesity. A cohort of 546 women underwent an intensive obstetric and nutritional programme, 201 (36.81%) of whom presented with normal pre-pregnancy weight, 171 (31.32%) with overweight and 174 (31.87%) with obesity.33
These preliminary findings show us that there is a combined prevalence of overweight-obesity in the population of Mexico City of 63.19%, compared with that of 75.32% in the sample population with high-risk pregnancy in West Mexico. This accounts for a difference of 12.13 percentage points more between the 2 Mexican regions.33
Current figures of metabolic diseases associated with pre-pregnancy overweight and obesity and overweight and obesity during pregnancy in women with high-risk pregnancy in West Mexico exceed the figures given in the national and worldwide literature. We should thus enhance preconception consultations with educational interventions aimed at achieving a healthy lifestyle prior to conception with a programme of appropriate detection and nutritional advice for our obstetric population who present with cardiometabolic risk factors.
Activities should focus on the identification of cardiometabolic risk factors in pre-conception consultation with measurement of waist circumference, determination of blood pressure and baseline blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, and triglycerides. Measures should be taken during this period to reduce insulin resistance through improving levels of physical activity, elasticity, strength and resistance through an exercise programme, with emphasis on self-care. Specific objectives prior to pregnancy should be aimed at.33
Conclusions75.32% of the 600 patients in the study who had high-risk pregnancies in the specialised hospital in West Mexico presented with overweight or obesity when they became pregnant.
The women who presented with overweight or obesity developed associated metabolic conditions including diabetes mellitus (pregestational, types 1 and 2), systemic hypertension, cardiopathies and kidney changes. As a result of this there is an urgent need to implement epidemiological measures, to make women of childbearing ages more aware about the importance of having a healthy lifestyle and weight, prior to, during and also after pregnancy.
These changes should be established in the population of childbearing ages and at the pre-pregnant stage, with strategies designed to modify dietary habits, together with changes in physical activity. As a result, the short and midterm impact of them may be assessed with regards to metabolic diseases and other changes to health during pregnancy.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments in human beings or animals were performed for this research.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they followed the protocols of their centre of work regarding the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this paper.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
The authors would like to thank the women with high-risk pregnancies for their collaboration in nutritional evaluation and also the nutrition graduate interns, Martha Uribe Manzano, Sandra Patricia Orozco López, Laura Lizeth Escobedo Sánchez, and Laura Noemí Patiño Rodríguez.
Please cite this article as: Hernández-Higareda S, Pérez-Pérez OA, Balderas-Peña LA, Martínez-Herrera BE, Salcedo-Rocha AL, Ramírez-Conchas RE. Enfermedades metabólicas maternas asociadas a sobrepeso y obesidad pregestacional en mujeres mexicanas que cursan con embarazo de alto riesgo. Cir Cir. 2017;85:292–298.