Schwannomas are benign peripheral nerve sheath tumours whose intramuscular localisation is exceptional.1,2 Approximately 15 cases of schwannomas in the psoas muscle have been published in the international literature.1,3,4 We present a new case and review the limited literature about this type of lesions and the “ancient schwannoma” variety that our patient presented.
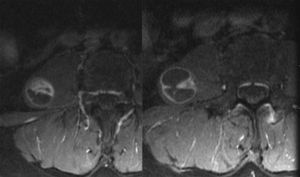
The patient is a 62-year-old woman with no medical history of interest except having undergone surgery on three different occasions for a right inguinal hernia. She currently reported having severe post-hernioplasty pain in the entire inguinal region that did not radiate to the right leg. Abdominal-pelvic MRI revealed a well-defined, oval, cystic mass located in the outer portion of the right psoas muscle that measured 2.6cm×2.5cm×3.5cm. The mass was hypointense in T1 and hyperintense in T2, with a solid pole at the lower margin and internal septa that were enhanced with injected contrast material (Fig. 1). Lab work-up and tumour marker studies (CEA, CA19-9) were normal. We proceeded with surgical exeresis through an abdominal approach with the suspected diagnosis of a malignant nerve tumour (Fig. 2). We performed a Cattell manoeuvre to access the retroperitoneum and locate the ureter, right renal vein and kidney, and inferior vena cava. A 3cm lesion was observed in the psoas at the cited location, which was resected with free margins (R0). The postoperative period transpired without incident. The histology study showed an encapsulated lesion with expansive edges comprised of cells with elongated nuclei, without atypia and with eosinophil cytoplasm presenting areas of Antoni A with Verocay bodies and other Antoni B areas. Occasionally, pleomorphic nuclei were seen with myxoid and cystic changes, as in evolved forms (“ancient schwannomas”). The immunohistochemistry study was positive for S-100, vimentin and neuron-specific enolase, and negative for smooth muscle actin (SMA) and CD117. The free surgical margins were comprised of muscle tissue. At later follow-up visits, (6 months) the patient presented no functional loss; the pain in the inguinal region continued, but the patient refused triple neurectomy. There have been no signs of recurrence.
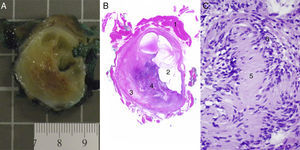
(A) Macroscopic appearance of the nodular lesion that is outlined from the muscle by a capsule; the interior has alternating myxoid-looking solid and cystic areas. (B) Microscope image confirming delimitation from the muscle,1 cystic areas2 and more solid eosinophil–myxoid areas3 and even more cellular areas.4 (C) In these, at higher magnification, the Verocay bodies of the schwannomas are identified, which are comprised by groups of filaments5 surrounded by rows of nuclei in the form of palisades.6
Schwannomas are tumours formed by the Schwann cells of peripheral nerve sheaths. They are usually benign, although on rare occasions they may undergo malignant transformation; nonetheless, there are no available data about their rate of malignisation or related clinical characteristics.4–6 Associations have been described with neurofibromatosis.6 Schwannomas are solid, encapsulated, slow-growing lesions most frequently located in the head, neck and trunk.1,2,5,6 Histologically, they present two alternating areas: one with dense cellularity, known as Antoni A; and, other areas of myxoid matrix, known as Antoni B.4,5 Immunohistochemically, schwannomas are positive for S-100, vimentin and neuron-specific enolase, and negative for SMA and CD117.5
There is a variety of schwannoma with solid-cystic characteristics and degenerative histological changes that is known in the English literature as “ancient schwannoma”, which was first described by Ackerman and Taylor in 1951.1,5,7 The typical histological characteristics of this variety are attributed to the progressive growth and age of the lesion.1,5,7 The existence of nuclear atypia and hyperchromatosis in this variety can cause an erroneous diagnosis of malignancy. The prognosis and rate of malignant transformation are identical to those of typical schwannomas.5 The case that we present in this report would be of the “ancient” variety.
Schwannomas are usually asymptomatic. When they cause symptoms, they are due to compression or infiltration of neighbouring organs, with no specificity.1,2,4–6 Diagnoses are habitually incidental, as in our case.2,4 We believe that the pain experienced by our patient was related to the hernioplasty and not with the mass in the psoas.
Abdominal MRI and CT scan show no pathognomonic characteristics that would be able to confirm the diagnosis of schwannoma preoperatively.3–6 Therefore, the definitive diagnosis is obtained in many patients during the histology study after surgical resection.1,4,6 Imaging tests usually show defined, well-encapsulated, homogenous solid lesions with peripheral uptake after the administration of contrast material.3,5,6 “Ancient schwannomas” can present a degenerative pattern of cystic areas, calcifications and hyalinisation that make the radiological diagnosis even more difficult.2,5 MRI seems to be superior to CT in “ancient schwannomas” due to its diagnostic capabilities in cystic masses.5 The use of PET to determine the malignant potential of schwannomas has yet to be determined.8
Some authors recommend CT-guided needle aspiration, although this has the important disadvantage of possible tumour dissemination if the diagnosis of schwannoma is incorrect.1,4,6 The differential diagnosis includes other muscle tumours, chronic abscesses, hydatid cysts, haematomas and muscle lesions with central necrosis.1
Treatment of schwannomas is surgical excision with free margins.1–6 Surgery can be done with an abdominal or retroperitoneal approach. The abdominal approach is recommended for lesions located in the lower portion of the psoas, and the retroperitoneal approach is recommended for the more proximal portion.3 A few isolated cases have also been treated by laparoscopy.1 Due to the benign nature of schwannomas, extreme caution must be taken with the ureter and functionality of the lower limbs.3,5 If exeresis is complete, the prognosis of the schwannoma is excellent, and recurrences are quite rare.4,5
Please cite this article as: Ramia JM, de la Plaza R, Alonso S, Gijón L, Valenzuela J. «Ancient» schwannoma localizado en el músculo psoas. Cir Esp. 2016;94:e37–e39.