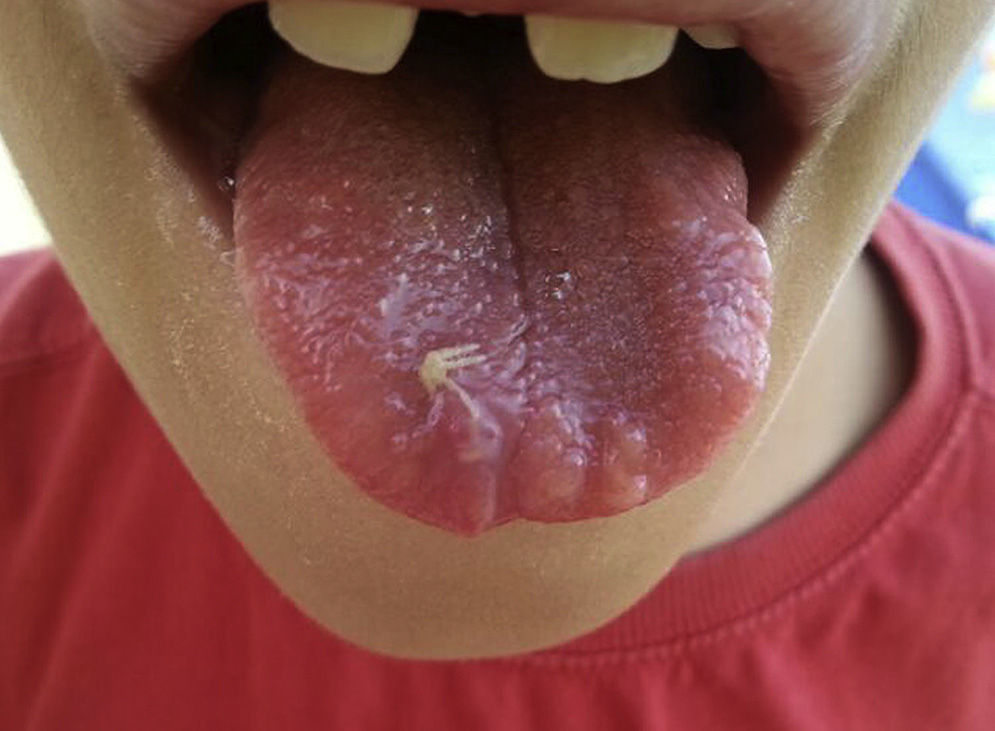
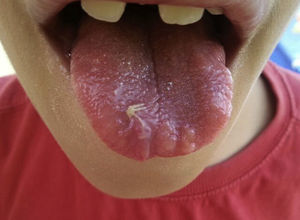
A 10-year-old boy was referred to our consultation due to tongue lesions. Examination revealed enlarged lips and tongue nodules. Biopsy established the diagnosis of neuroma of the tongue (Fig. 1). Lab work showed calcitonin 91pg/ml (0–20), and cervical ultrasound identified a hypoechoic thyroid nodule with microcalcifications and anarchical peripheral vascularization.
MEN 2B syndrome is a rare clinical entity that is aggressive and difficult to diagnose. It demonstrates a characteristic phenotype: marfanoid habitus and bulging lips, with the occasional presence of neuromas of the tongue. In patients with this phenotype, clinical suspicion should be confirmed with a thyroid ultrasound and serum calcitonin determination, providing early diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis: Multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 2B (MEN 2B).
Please cite this article as: Febrero B, Rodríguez JM, Amate E, Ríos A. Neuromas linguales en la infancia como indicador en el diagnóstico del síndrome MEN 2B. Cir Esp. 2015;93:e31.