In breast cancer surgery, there are techniques for sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) that do not require Nuclear Medicine, such SentiMag®, which uses ferromagnetic particles. The main purpose of this analysis is to study the degree of concordance in SLNB between SentiMag® and the standard method (Tc99 radiotracer). The secondary objective is to identify factors that impact in sentinel node detection rate and matching detection rate between both probes.
MethodsObservational and retrospective study performed from January to December 2021 focused on patients undergoing breast surgery and SLNB who were injected with both tracers, the ferromagnetic SentiMag® and Tc99 radiotracer. Once the diagnostic accuracy tests were performed, a further evaluation of the detection rate for each probe and the concordance between probes were accomplished. After those results, a deeper analysis of differences in detection rates for each probe and concordance between probes were assessed for various factors: neoadjuvant therapy, BMI, mitotic index, and triple-negative immunohistochemical profile.
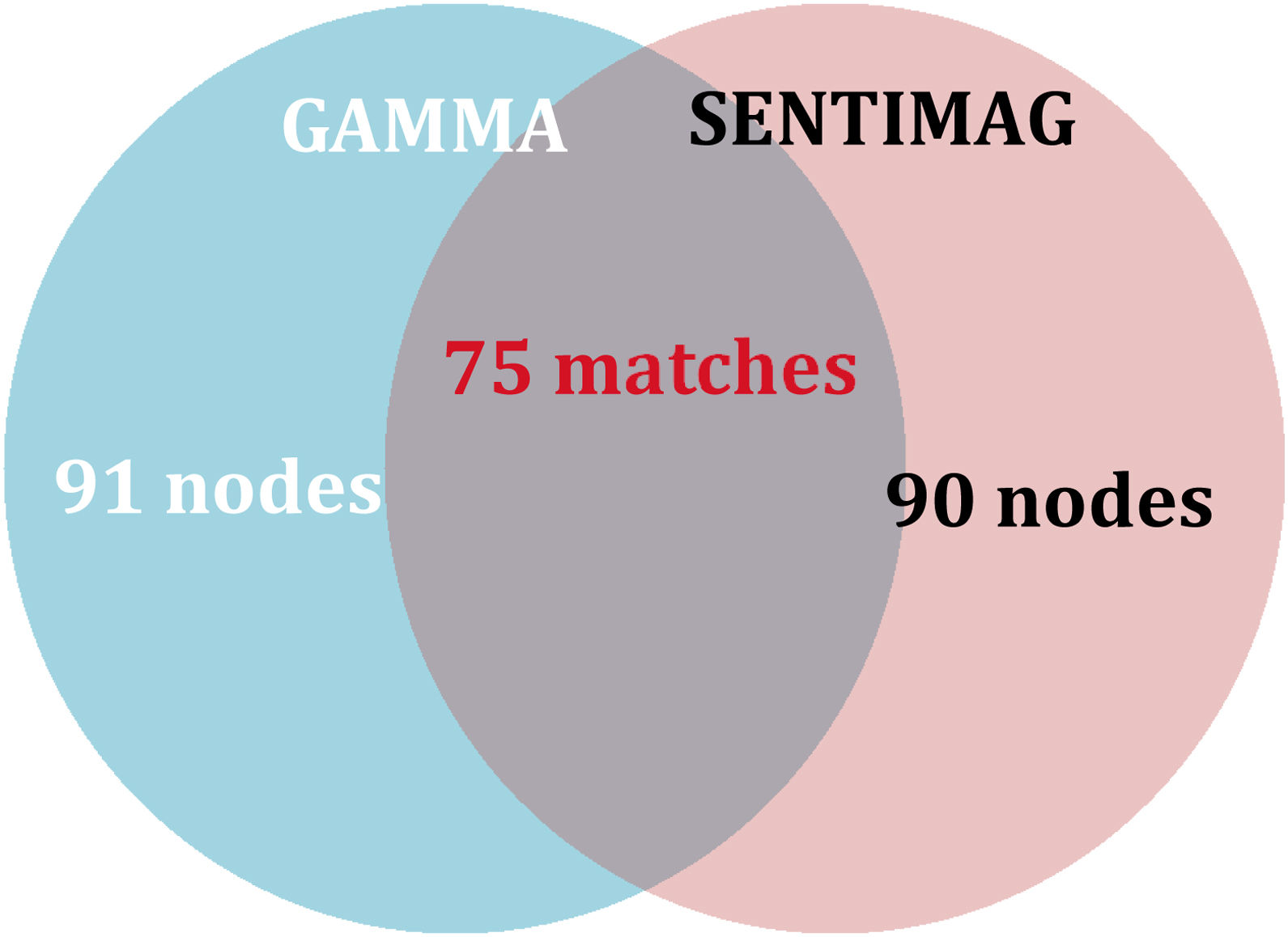
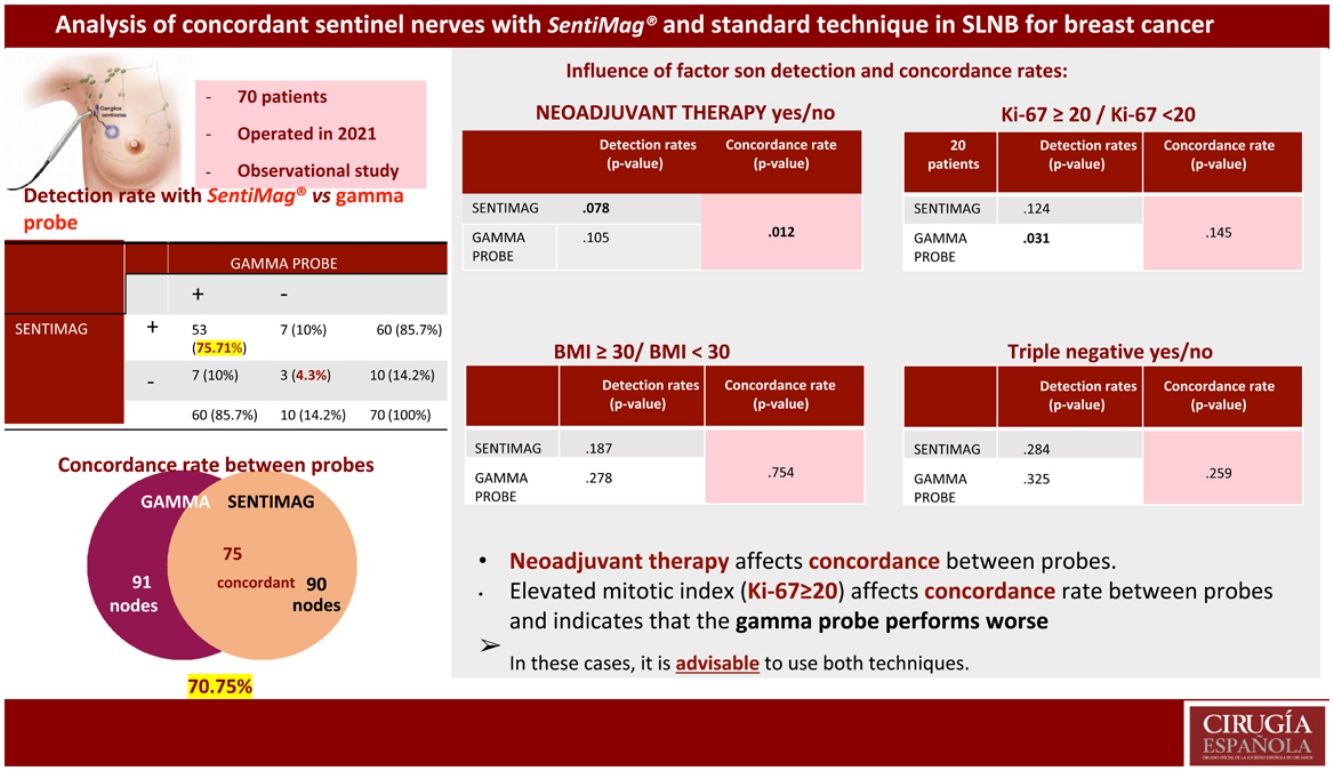
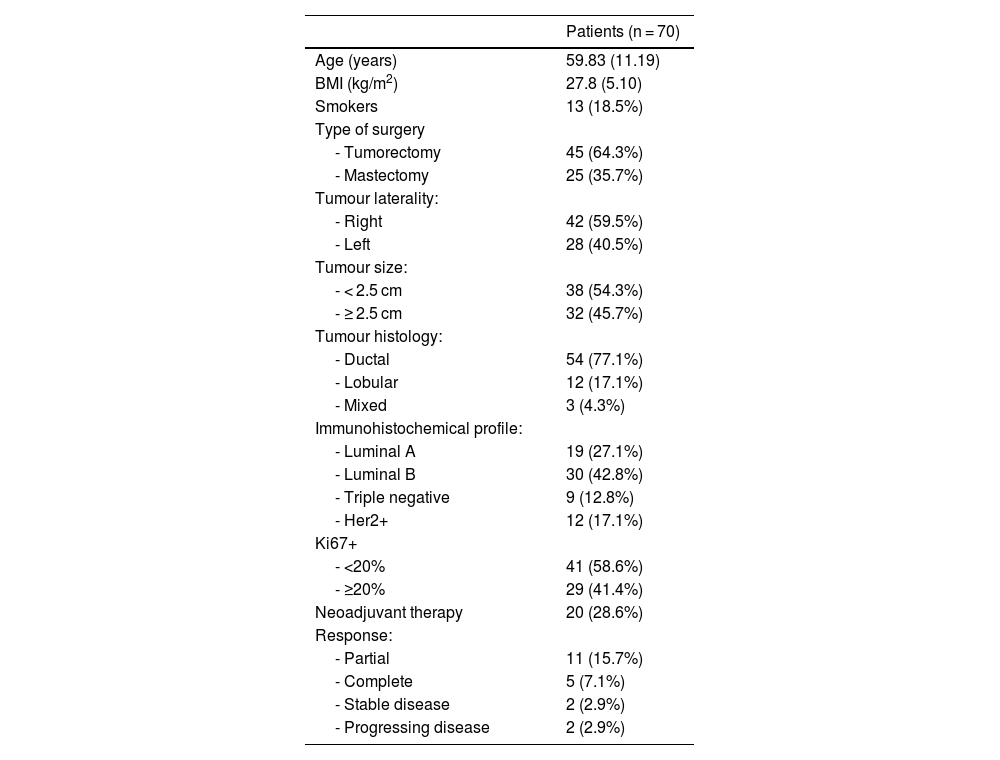
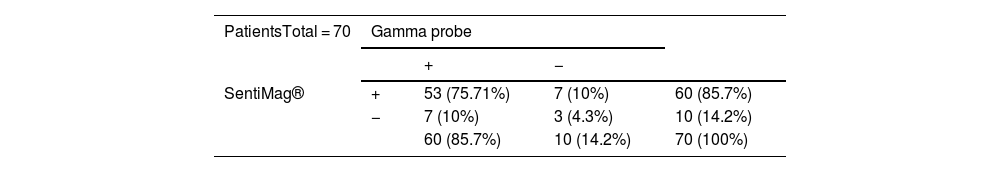
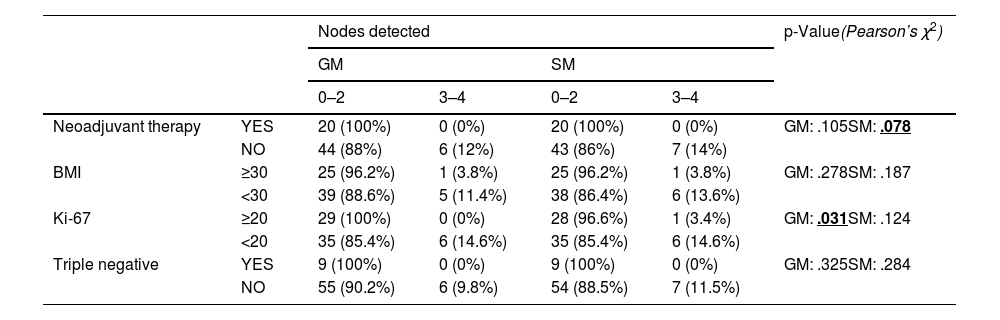
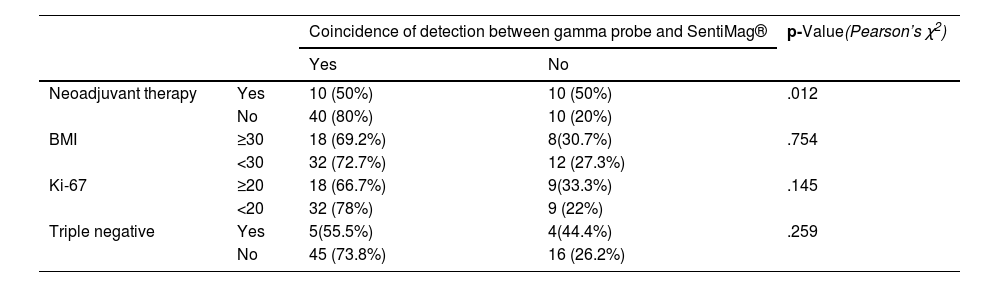
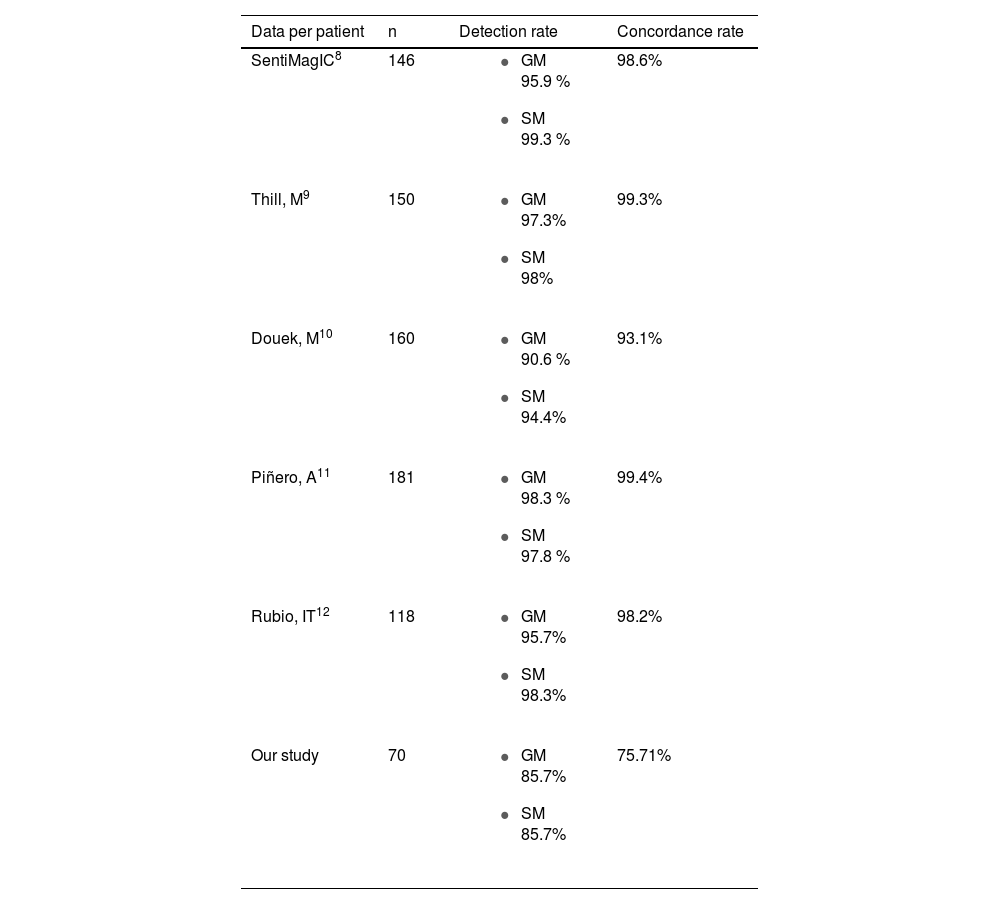
ResultsThe clinical study had a sample size of 70 patients. The overall false-negative rate (FNR) was 4.3%. The detection rate was the same for each technique (85.7%). A total of 106 nodes were biopsied, with a concordance rate of 70.75%. Significant differences were found in concordant nodes according to neoadjuvant therapy (p-value 0.012). For the Ki-67 factor (<20 or ≥20), significant differences were found in detected nodes (p-value 0.031 gamma probe; p-value 0.124 SentiMag®).
ConclusionsThe detection rates of SentiMag® and the gamma probe are equivalent. The application of the dual technique minimizes the FNR. A high mitotic index affects the detection rate of the gamma probe, and neoadjuvant therapy negatively impacts the concordance rate.
Existen técnicas para la biopsia selectiva del ganglio centinela (BSGC) en cáncer de mama que no precisan Medicina Nuclear como SentiMag® que emplea partículas ferromagnéticas. El objetivo principal es estudiar el grado de concordancia en la BSGC con SentiMag® y con el método estándar (radiotrazador Tc99). Los objetivos secundarios son identificar factores que repercutan en la detección y la concordancia entre sondas.
MétodosEstudio observacional y retrospectivo desde enero hasta diciembre de 2021. Se incluyeron pacientes sometidas a cirugía mamaria y BSGC a las que se les inyectó el radiotrazador y trazador ferromagnético. Se realizó un análisis de pruebas diagnósticas y se analizó la tasa de detección por cada sonda y la tasa de concordancia entre sondas. Además, se evaluaron las diferencias en tasas de detección por cada sonda y en concordancia entre sondas para diferentes factores: neoadyuvancia, IMC, índice mitótico y perfil inmunohistoquímico triple negativo.
Resultados70 pacientes fueron incluidas. La tasa de falsos negativos (TFN) global fue 4,3%. La detección para cada técnica fue equivalente (85,7%). Fueron biopsiados 106 ganglios con una tasa de concordancia del 70,75%. Al analizar la tasa de concordancia de los ganglios centinela en pacientes con y sin neoadyuvancia, se hallaron diferencias significativas (p-valor 0,012). Para el factor Ki-67 (<20 o ≥20) se obtuvieron diferencias significativas en la tasa de detección de ganglios centinela (p-valor 0,031 sonda gamma; p-valor 0,124 SentiMag®).
ConclusionesLa tasa de detección de SentiMag® y sonda gamma es equivalente. La aplicación de la doble técnica minimiza la TFN. La neoadyuvancia repercute negativamente en la tasa de concordancia. El índice mitótico elevado (Ki-67 ≥ 20) afecta a la tasa de concordancia entre sondas y apunta un peor desempeño de sonda gamma.