Robot-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) is a rapidly expanding technique. In our study, we aimed to analyze the results of the process to adopt robotic surgery in our Department of Thoracic Surgery.
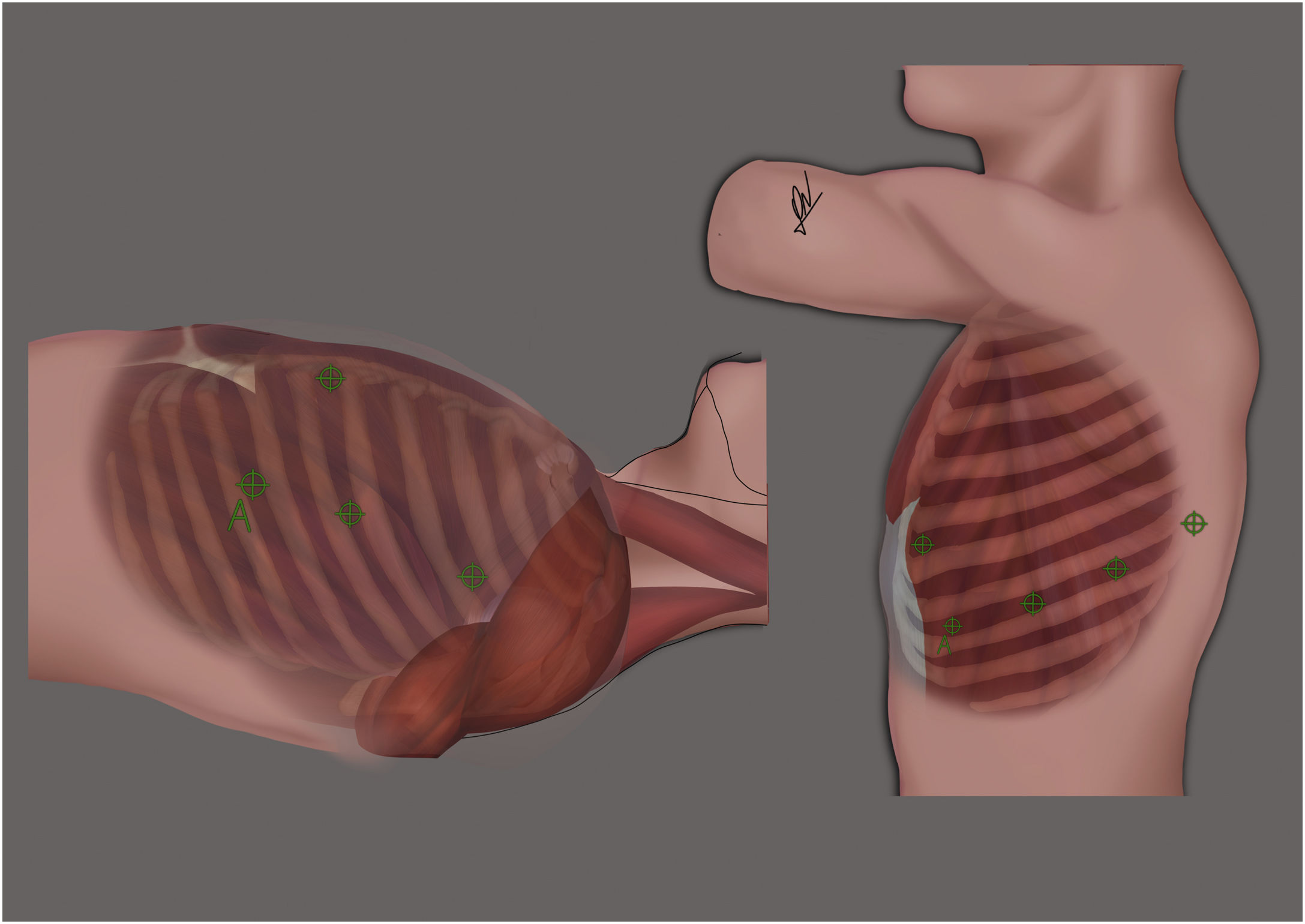
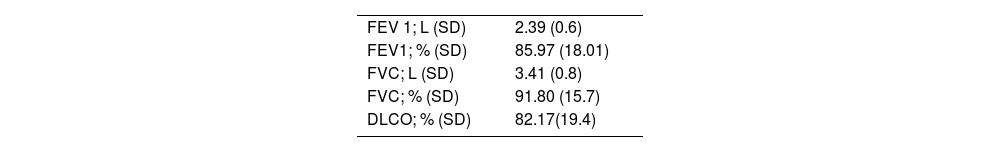
MethodsThis is an intention-to-treat analysis of a series of consecutive patients operated on using the RATS approach in our hospital from January 2021 to March 2022. Data were registered for patient characteristics, type of surgery, operative times, conversion rate, chest tube duration, length of hospital stay and complications.
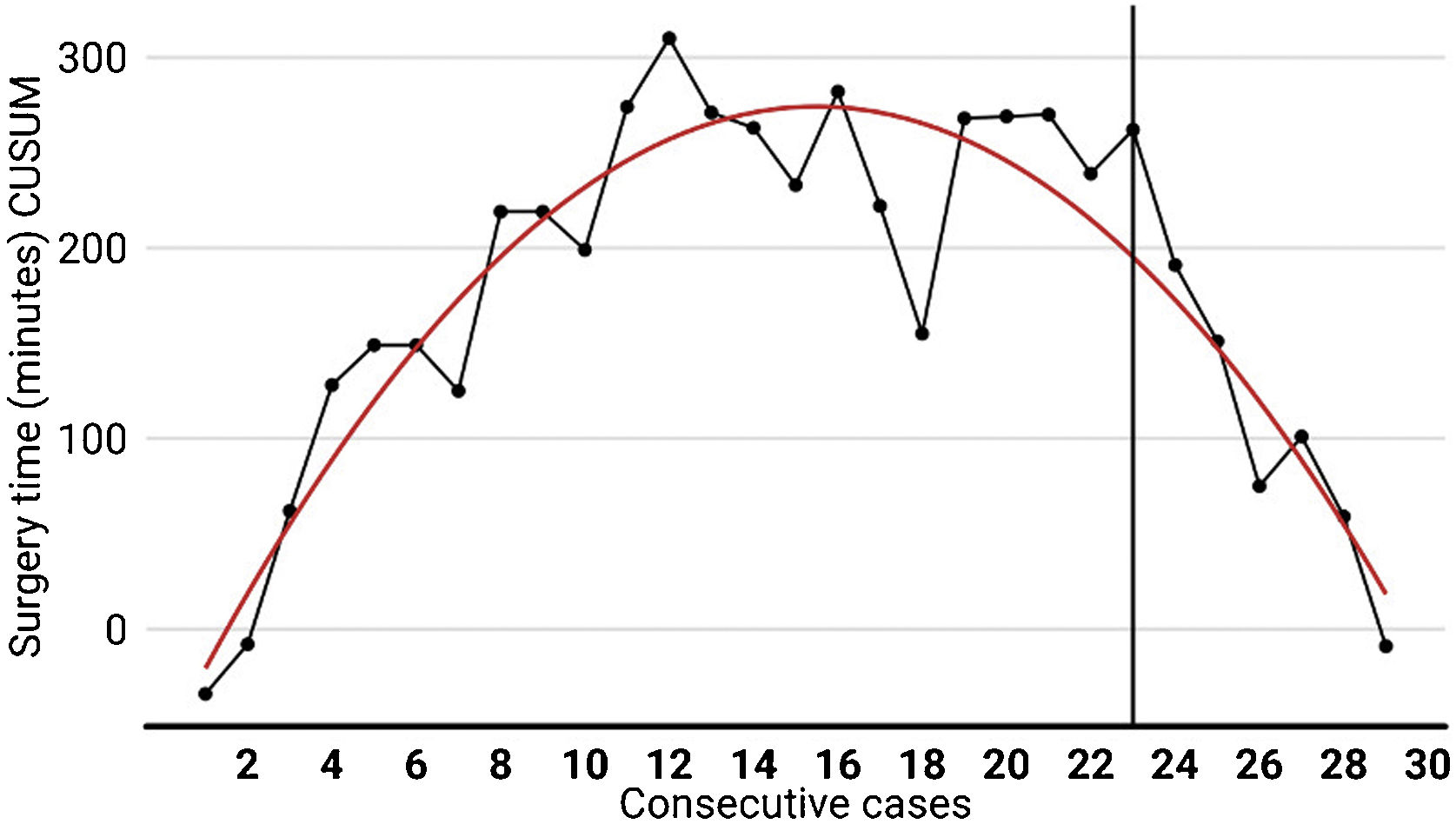
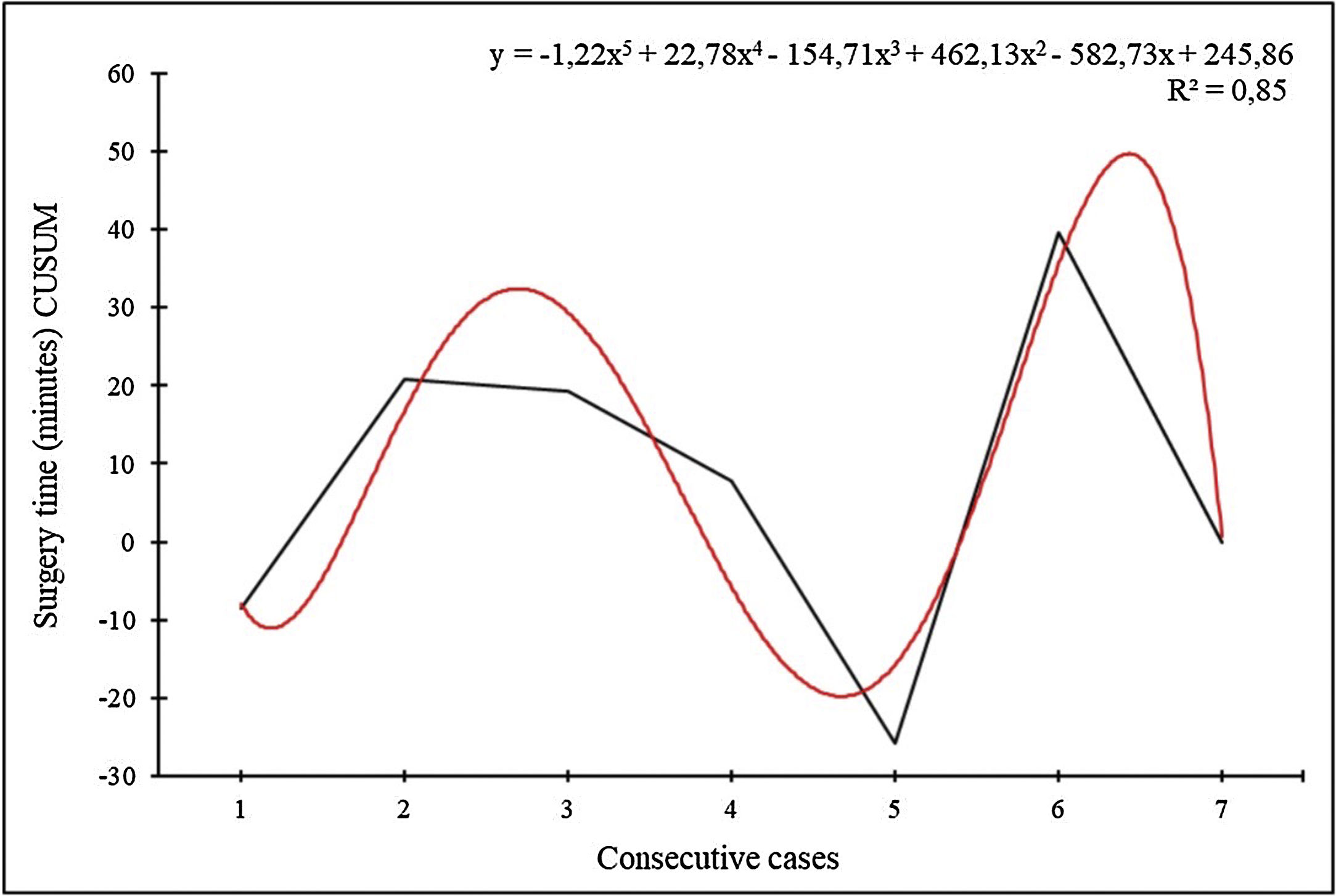
The IBM SPSS® statistical software was used for the statistical analysis. A cumulative sum analysis of the operating time was performed to define the learning curve.
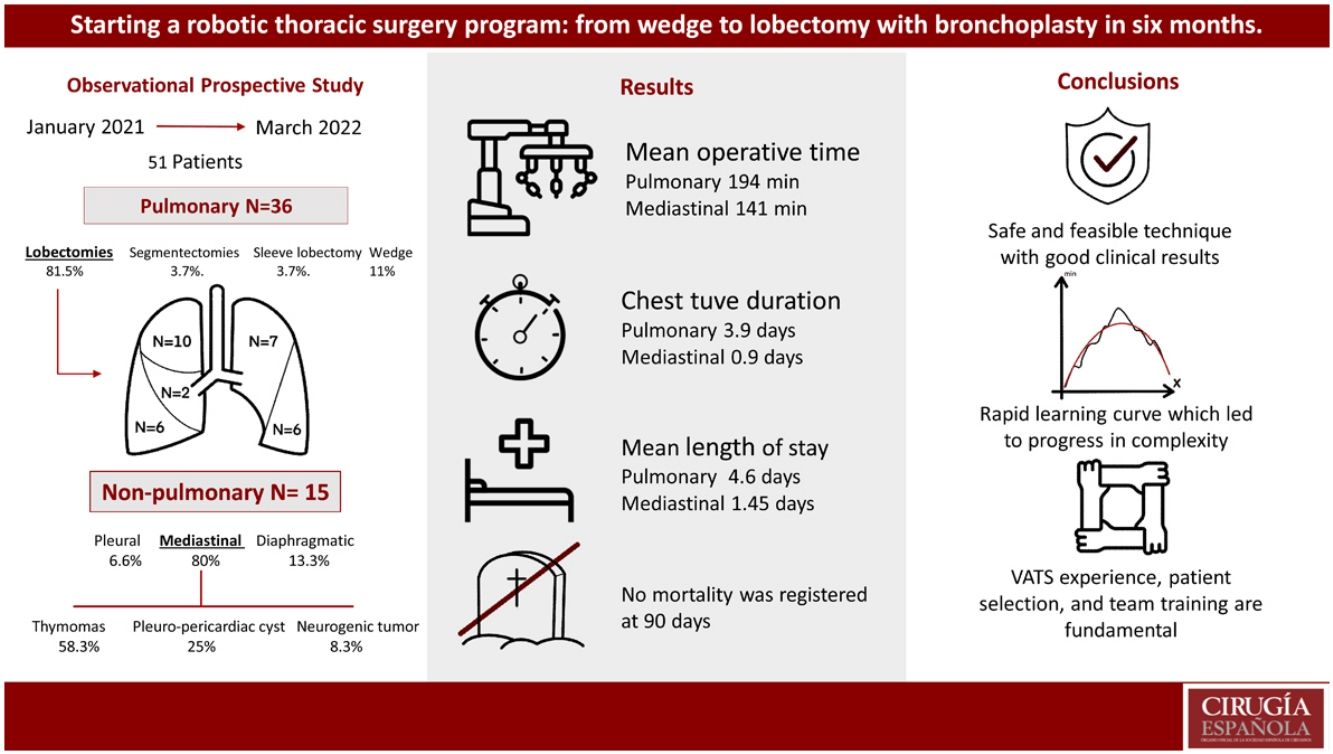
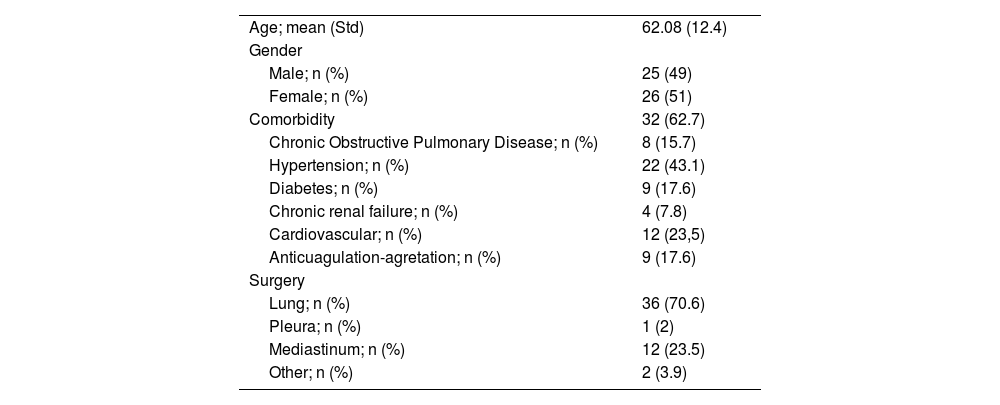
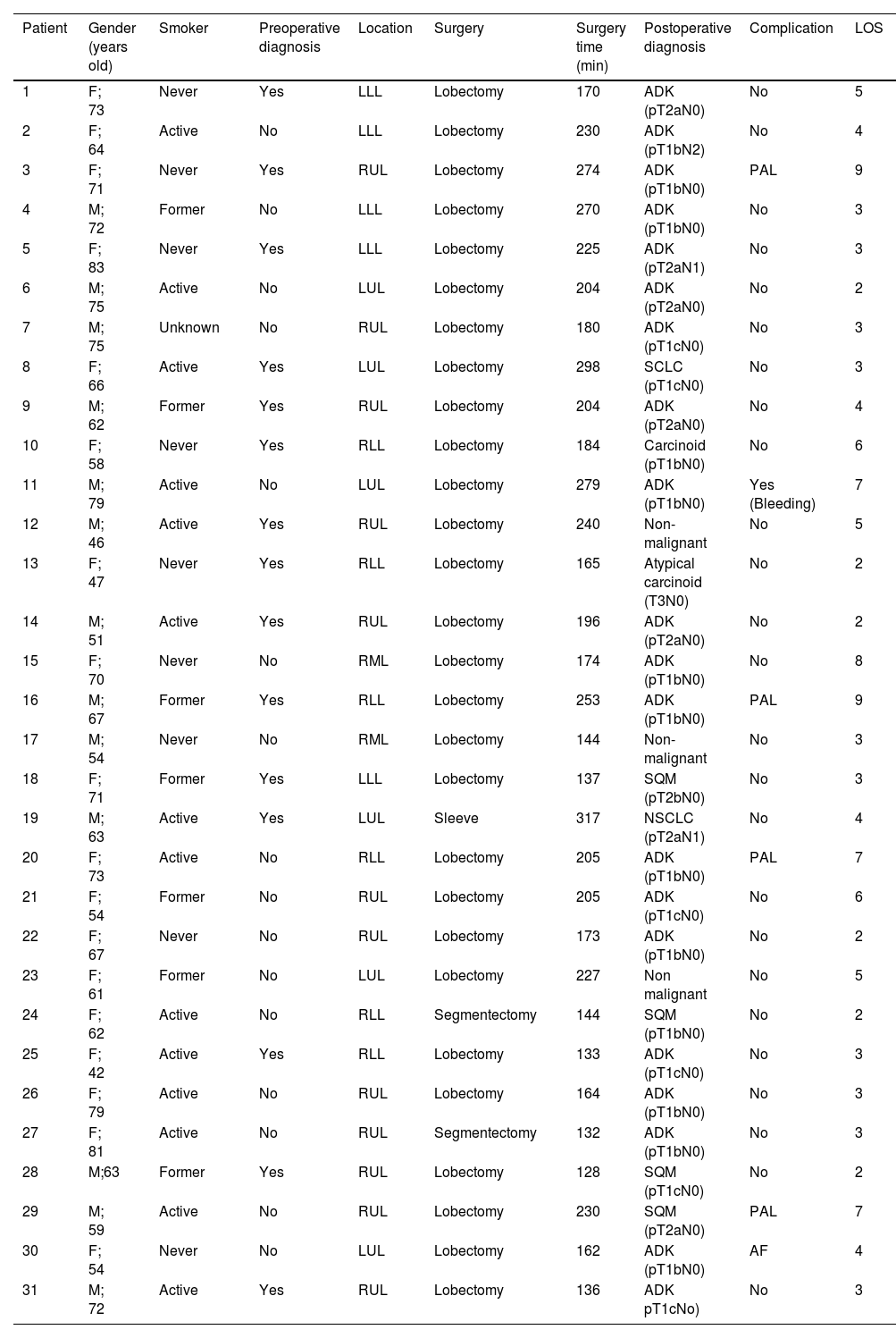
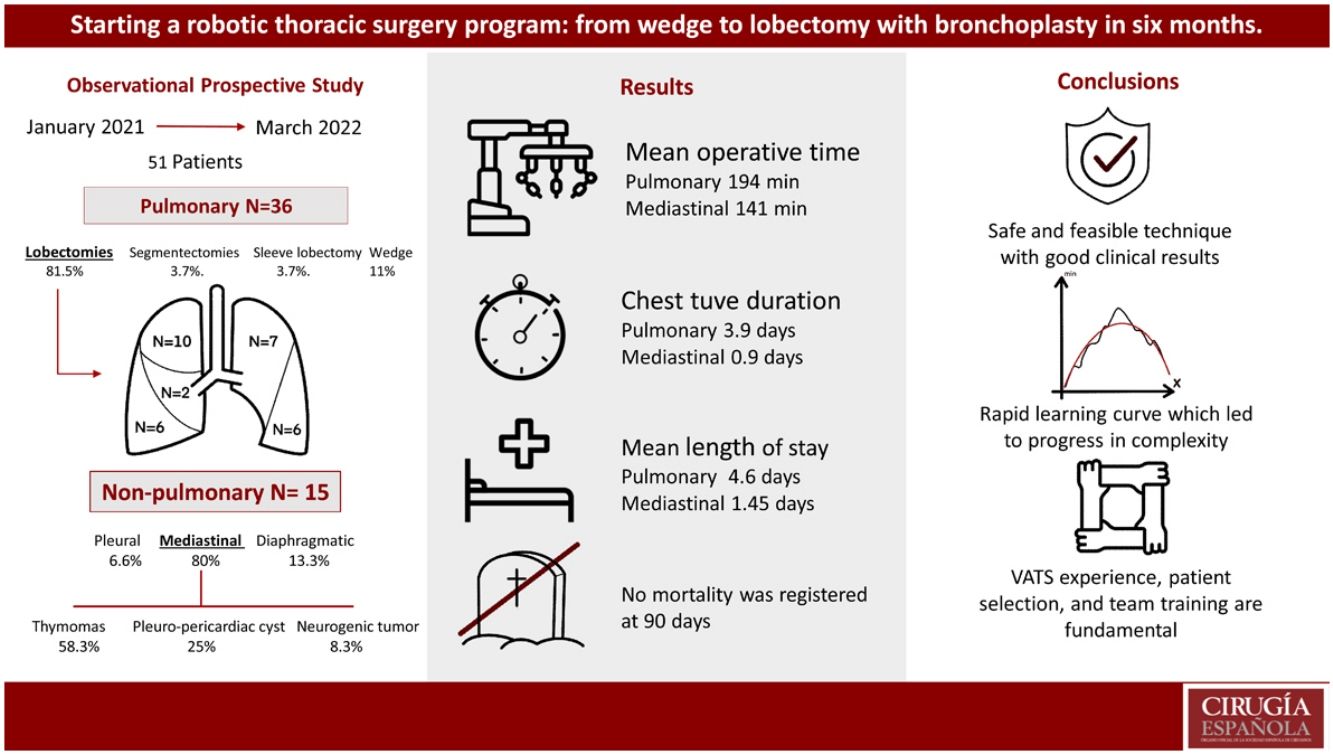
ResultsDuring the study period, 51 patients underwent robotic surgery, including pulmonary and non-pulmonary interventions. In addition, 15 patients (29.4%) underwent non-pulmonary interventions: one pleural (2%), 2 diaphragmatic (3.9%), and 12 mediastinal (23.5%). Among the mediastinal surgeries, one conversion was necessary (8.3%) for a complex vascular malformation, and 11 were completed by RATS, including 7 (58.3%) thymomas, 3 (25%) pleuro-pericardial cysts, and one (8.3%) neurogenic tumor. Mean operative time was 141 min (104–178), mean chest tube duration was 0.9 days (0–2), and mean length of stay was 1.45 days (1–2).
Thirty-six patients underwent lung surgery (70.6%). The complete RATS resections (34; 94.4%) included: 3 wedge resections (11.1%), 2 segmentectomies (3.7%), 28 lobectomies (81.5%), and one sleeve lobectomy (3.7%). Mean surgery time was 194.56 min (141–247), chest tube duration was 3.92 days (1–8), and length of stay was 4.6 days (1–8). Complications occurred in 4 patients (11.1%). No 90-day mortalities were registered.
ConclusionsThe implementation of RATS was achieved with good clinical results and operative times for all indications. A rapid learning curve was accomplished in short time. Previous VATS experience, patient selection, team training and program continuity are fundamental to successfully develop a RATS program.
La cirugía torácica asistida por robot (RATS) es una técnica en rápida expansión. Nuestro objetivo fue analizar el resultado del proceso de adopción de la cirugía robótica en nuestro Departamento de Cirugía Torácica.
MétodosEste es un análisis por intención de tratamiento de una serie de pacientes consecutivos operados mediante el método RATS en nuestro centro desde enero de 2021 a marzo de 2022. Se registraron las características de los pacientes, tipo de cirugía, tiempos operatorios, tasa de conversión, duración del drenaje torácico, estancia hospitalaria y complicaciones. Para el análisis estadístico se utilizó el software IBM SPSS®. Se realizó un análisis de suma acumulada del tiempo de operación para definir la curva de aprendizaje.
ResultadosDurante el periodo de estudio, 51 pacientes fueron sometidos a cirugía robótica.15 pacientes (29,4%) fueron sometidos a intervenciones no pulmonares: 1 pleural (2%), 2 diafragmáticas (3,9%) y 12 mediastínicas (23,5%). Entre las cirugías mediastínicas, fue necesaria una conversión (8,3%) por malformación vascular compleja y 11 fueron completadas por RATS, incluidos 7 (58,3%) timomas, 3 (25%) quistes pleuro-pericárdicos y 1 (8,3%) tumores neurogénicos. El tiempo operatorio medio fue de 141 minutos [104–178], la duración media del tubo torácico fue de 0,9 días [0–2] y la estancia media fue de 1,45 días [1–2].
36 pacientes tuvieron cirugías pulmonares (70,6%). Las resecciones RATS completas (34; 94,4%) incluyeron: 3 resecciones en cuña (11,1%), 2 segmentectomías (3,7%), 28 lobectomías (81,5%) y 1 lobectomía con broncoplastia (3,7%). El tiempo medio de cirugía fue de 194,56 minutos [141–247], la duración del tubo torácico fue de 3,92 días [1–8] y la estancia hospitalaria fue de 4,6 días [1–8]. No se registró mortalidad a los 90 días.
ConclusionesLa implementación de RATS se logró con buenos resultados clínicos y tiempos operatorios en todas las indicaciones. Se completó una rápida curva de aprendizaje en poco tiempo.
La experiencia previa en VATS, la selección de pacientes, la capacitación del equipo y la continuidad del programa son fundamentales para desarrollar con éxito un programa RATS.