Various polymorphisms in the beta-2 adrenergic receptor (ADRB2) gene have been associated with cardiometabolic risk factors, such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity contributing to the physiopathology of these chronic conditions. However, the association of the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs12654778 at the ADRB2 gene with metabolic changes has been poorly studied and there is no information on the Chilean adult population.
ObjectiveTo investigate the association between the rs12654778 SNP at the ADRB2 gene with cardiometabolic risk markers in a Chilean adult population.
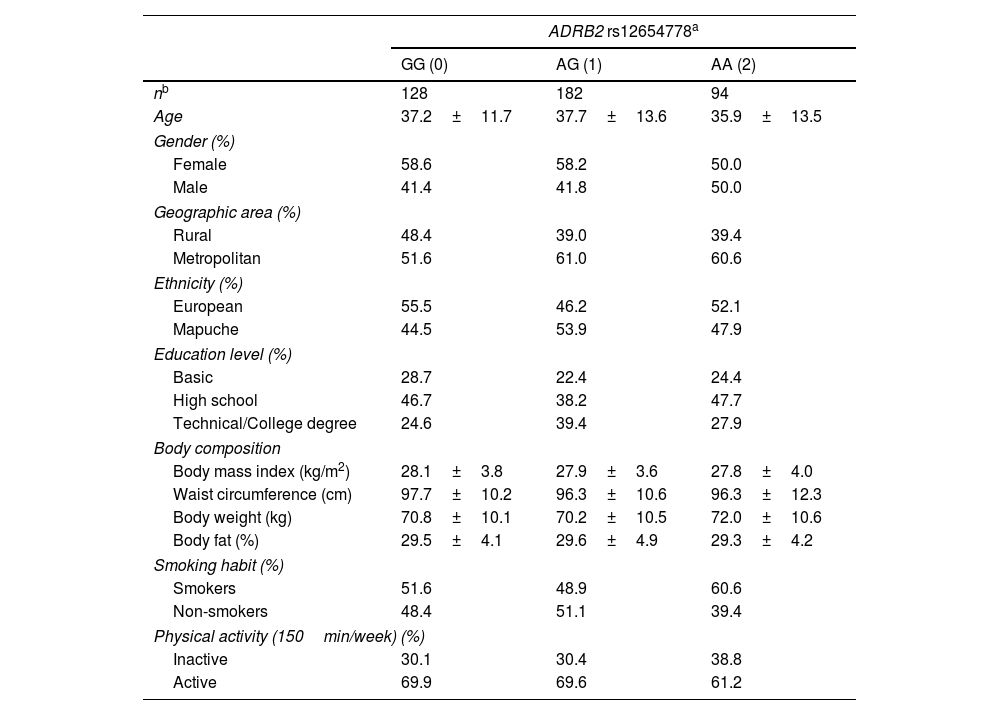
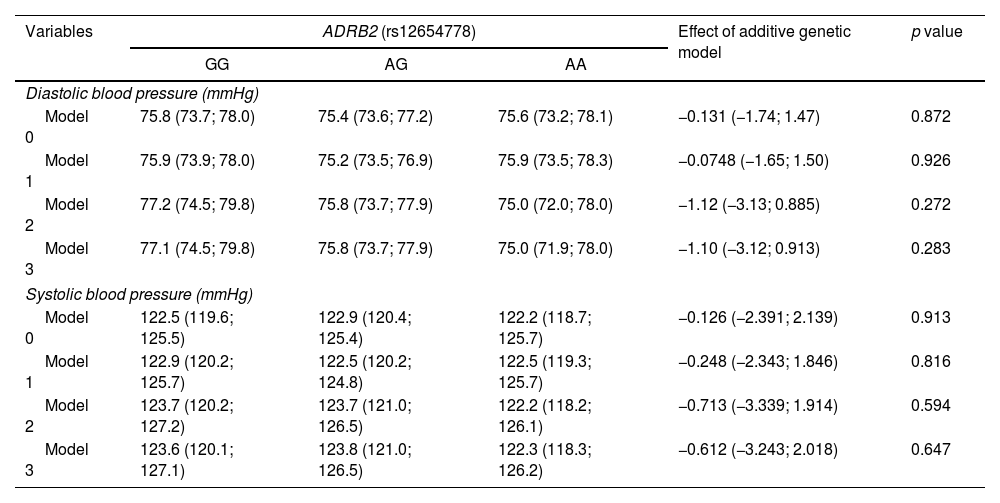
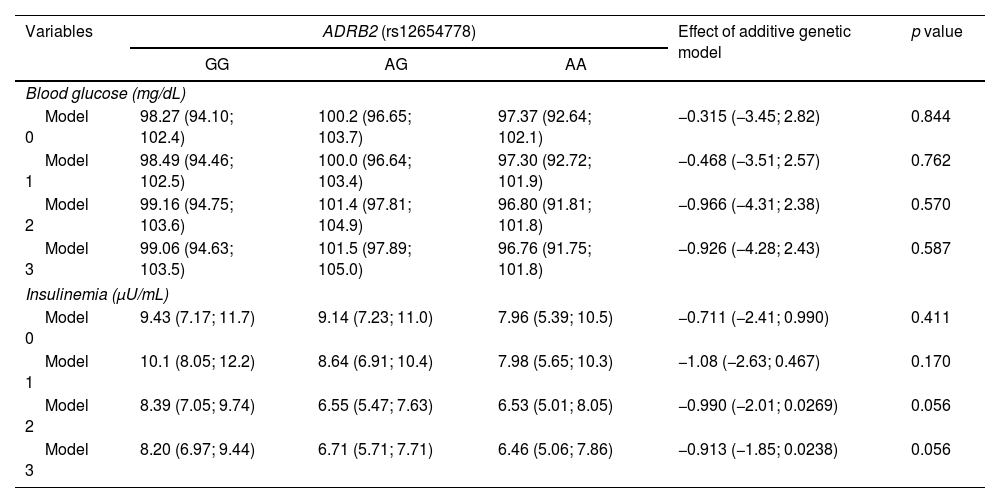
MethodsWe conducted a cross-sectional study including 404 participants from the GENADIO study whom were genotyped for rs12654778 and categorized into GG, AG, and AA genotypes. Associations with cardiometabolic risk markers, such as blood pressure, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, blood glucose and insulin were examined using multivariate regression analysis, while statistical models were adjusted for sociodemographic and lifestyle variables.
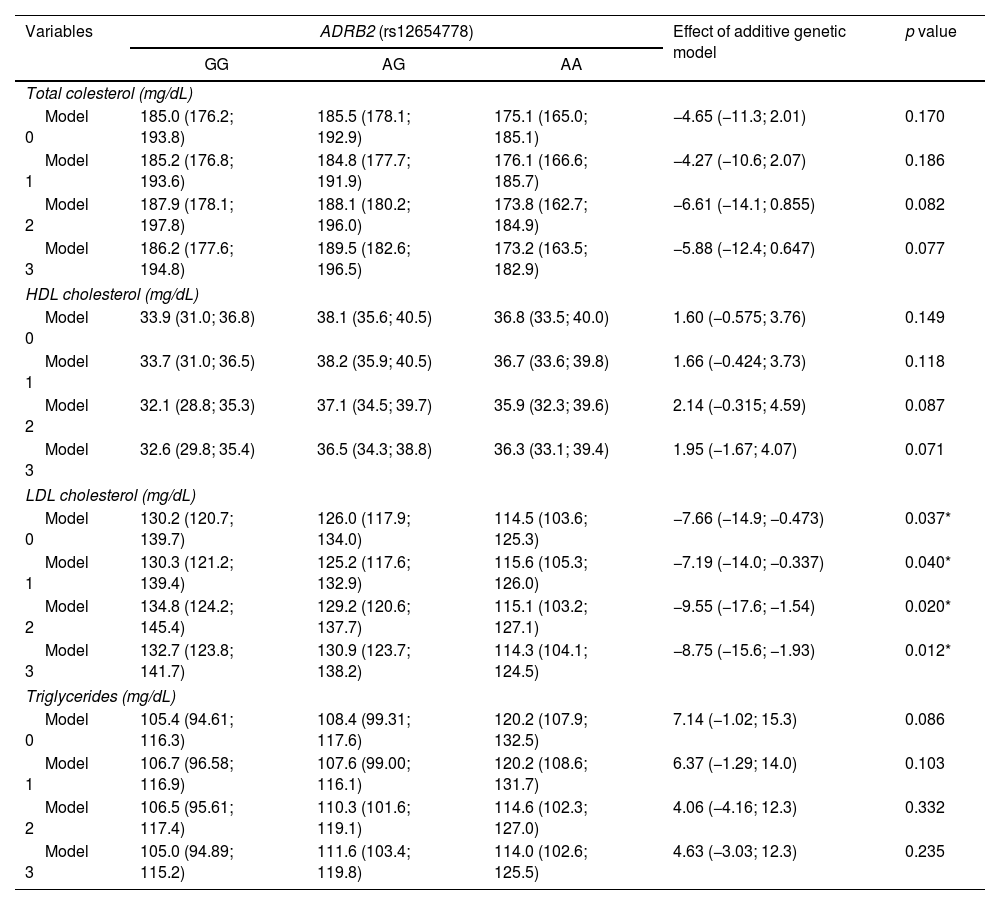
ResultsOur findings indicate a significant association between the presence of the protective genotype (AA) of the rs12654778 polymorphism and lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels corresponding to 8.75mg/dL per each copy of the protective allele (maximally adjusted model). No significant associations were seen for the remaining variables.
ConclusionThe AA genotype of the rs12654778 SNP at the ADRB2 gene had a protective effect specifically against low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. This is the first study ever conducted in Chile on this SNP of ADRB2 and one of the few conducted worldwide to establish an association between the rs12654778 SNP at the ADRB2 gene and LDL cholesterol.
Varios polimorfismos en el gen del receptor the beta-2 adrenérgico (ADRB2) han sido asociados a factores cardiometabólicos, como hipertensión, dislipidemia, diabetes tipo 2 y obesidad, contribuyendo a la fisiopatología de dichas condiciones crónicas. Sin embargo, la asociación del polimorfismo de un nucleótido (SNP) rs12654778 del gen ADRB2 con alteraciones metabólicas ha sido pobremente estudiada, sin información en población chilena.
ObjetivoInvestigar la asociación del SNP rs12654778 del gen ADRB2 con marcadores de riesgo cardiometabólico en una población chilena adulta.
MétodosSe trata de un estudio de corte transversal con 404 participantes del estudio GENADIO. Los individuos fueron genotipificados para rs12654778 y categorizados en genotipos GG, AG y AA. Se analizó su asociación con marcadores de riesgo cardiometabólico como presión arterial total, colesterol total, colesterol en lipoproteína de alta densidad, colesterol en lipoproteína de baja densidad, triglicéridos, glucosa e insulina mediante análisis de regresión multivariado, usando modelos estadísticos ajustados por variables sociodemográficas y de estilo de vida.
ResultadosNuestros resultados indican una asociación significativa entre la presencia del genotipo protector (AA) del polimorfismo rs12654778 y los niveles de colesterol en lipoproteína de baja densidad, correspondiente a 8,75mg/dl menos por cada copia del alelo protector (modelo máximamente ajustado). No se observaron asociaciones significativas para las otras variables.
ConclusiónEl genotipo AA del SNP rs12654778 del gen ADRB2 presenta efecto protector específicamente sobre los niveles de colesterol en lipoproteína de baja densidad. Este es el primer estudio en Chile que incluye este SNP del gen ADRB2 y uno de los pocos realizados a nivel mundial que establece asociación entre el SNP rs12654778 del gen ADRB2 y colesterol LDL.