Audits for monitoring the quality of antimicrobial prescribing are a main tool in antimicrobial stewardship programs; however, interobserver reliability has not been conclusively assessed. Our objective was to measure the level of agreement between pharmacists and physicians on the appropriateness of antimicrobials prescribing in hospitals.
MethodsA national multicenter, cross-sectional study was conducted of patients who were receiving antimicrobials one day of April 2021. Hospital participation was voluntary, and the study population was randomly selected. Pharmacists and physicians performed a simultaneous, independent assessment of the quality of antimicrobial prescriptions. The observers used an assessment method by which all indicators of the quality of antimicrobial use were considered. Finally, an algorithm was used to rate overall antimicrobial prescribing as appropriate, suboptimal, inappropriate, or not assessable. Gwet's AC1 coefficient was used to assess interobserver agreement.
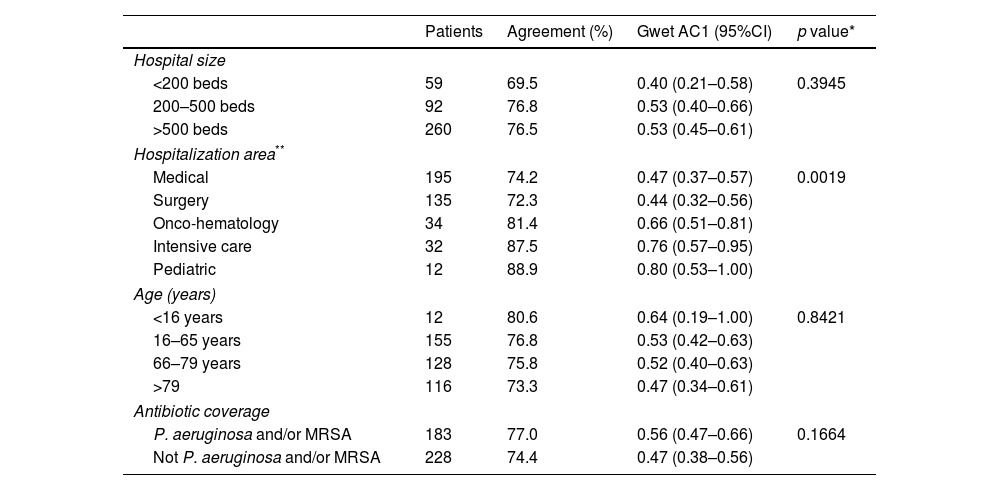
ResultsIn total, 101 hospitals participated, and 411 hospital antimicrobial prescriptions were reviewed. The strength of agreement was moderate regarding the overall quality of prescribing (AC1=0.51; 95%CI=[0.44–0.58]). A very good level of agreement (AC1>0.80) was observed between pharmacists and physicians in all indicators of the quality, except for duration of treatment, rated as good (AC1=0.79; 95%CI=[0.75–0.83]), and registration on the medical record, rated as fair (AC1=0.34; 95%CI=[0.26–0.43]). The agreement was greater in critical care, onco-hematology, and pediatric units than in medical and surgery units.
ConclusionsIn this point prevalence study, a moderate level of agreement was observed between pharmacists and physicians in the evaluation of the appropriateness of antimicrobials prescribing in hospitals.
Las auditorías para evaluar la calidad de las prescripciones antibióticas son una herramienta fundamental en los Programas de Optimización del Uso de Antimicrobianos, sin embargo, la concordancia entre evaluadores no ha sido valorada de forma concluyente. El objetivo fue medir el nivel de acuerdo entre farmacéuticos y médicos en la evaluación de la adecuación de las prescripciones antibióticas en hospitales.
MétodosEstudio multicéntrico, transversal en pacientes hospitalizados que recibieron antibióticos un día de abril de 2021. La participación de los hospitales fue voluntaria, y los pacientes seleccionados aleatoriamente. Farmacéuticos y médicos evaluaron la adecuación de las prescripciones de forma simultánea e independiente utilizando una metódica de evaluación que consideraba indicadores implicados en la calidad del uso de los antibióticos. Finalmente se usó un algoritmo para calificar la prescripción como adecuada, mejorable, inadecuada y no valorable. Se utilizó el coeficiente Gwet's AC1 para valorar la concordancia entre evaluadores.
ResultadosParticiparon 101 hospitales y se revisaron 411 prescripciones antibióticas. El acuerdo fue moderado en la calificación global de la prescripción (AC1=0,51; 95%CI=[0,44-0,58]). Se alcanzó un nivel de acuerdo muy bueno (AC1>0,80) en todos los indicadores de calidad, excepto la duración del tratamiento, valorado como bueno (AC1=0,79; 95%CI=[0,75-0,83]), y el registro en la historia clínica, valorado como moderado (AC1=0,34; 95%CI=[0,26-0,43]). El acuerdo fue mayor en unidades de críticos, oncohematología y pediatría que en unidades médicas y quirúrgicas.
ConclusionesEste estudio de prevalencia registró un nivel de acuerdo moderado entre farmacéuticos y médicos en la evaluación de la adecuación de prescripciones antibióticas en hospitales.
Article
Socio de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica

Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la SEIMC, clique aquí