Diseño y consenso de los ítems de un cuestionario sobre el proceso de información del tratamiento sustitutivo renal y el grado de información y promoción del trasplante renal de donante vivo que realizan las enfermeras de nefrología con perspectiva de género.
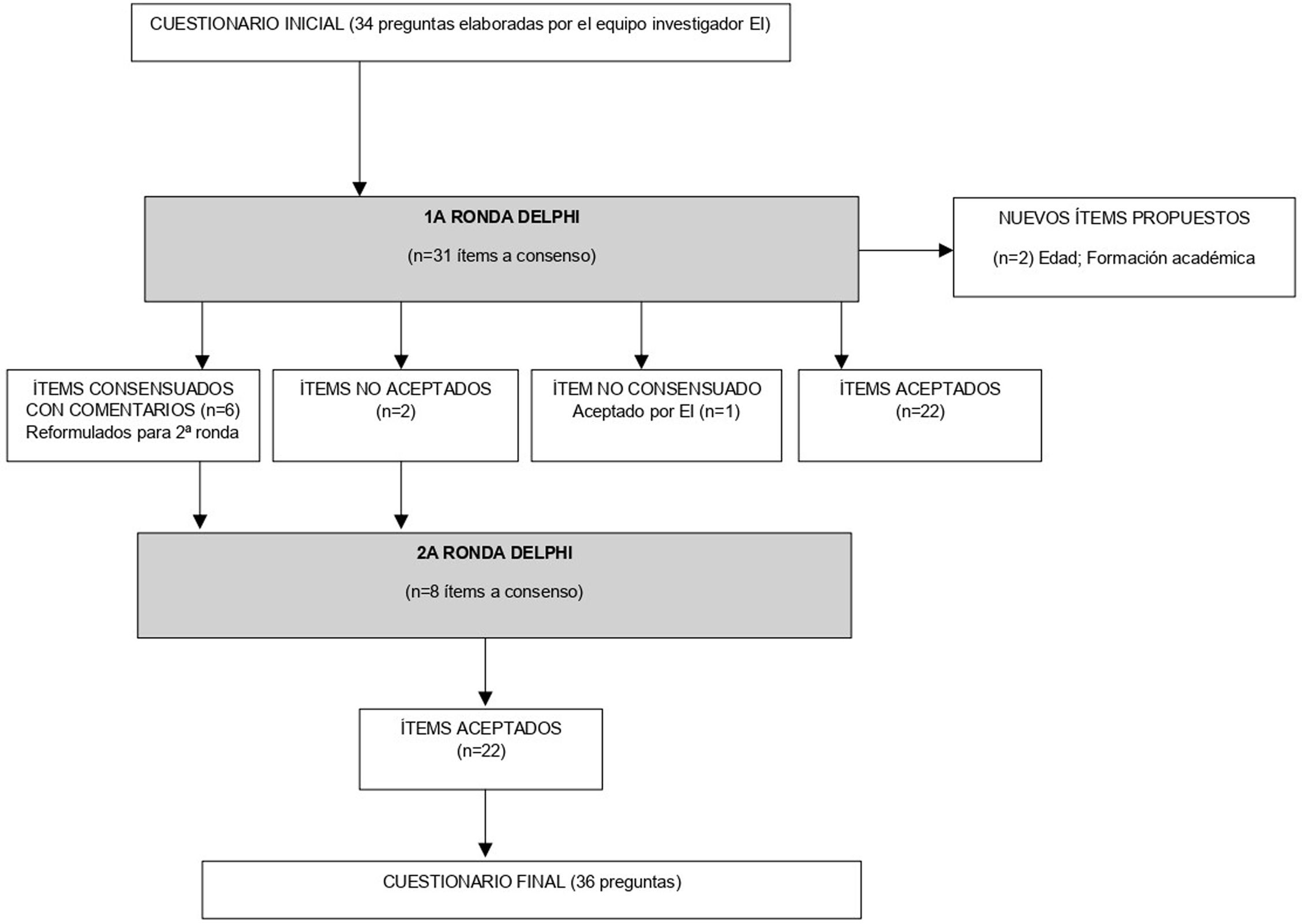
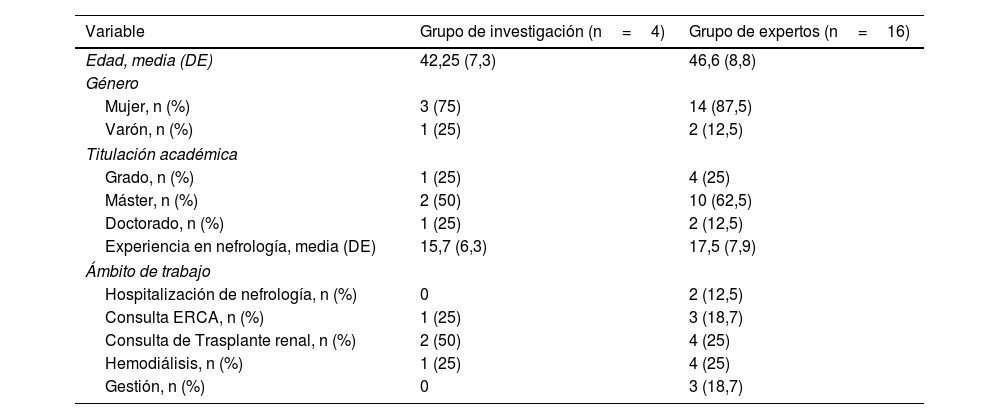
MétodoEste estudio se desarrolló en 2 fases: 1) elaboración de un cuestionario inicial por parte del equipo investigador formado por 4 enfermeras y 2) realización de 2 rondas de consenso mediante la técnica o el método Delphi.
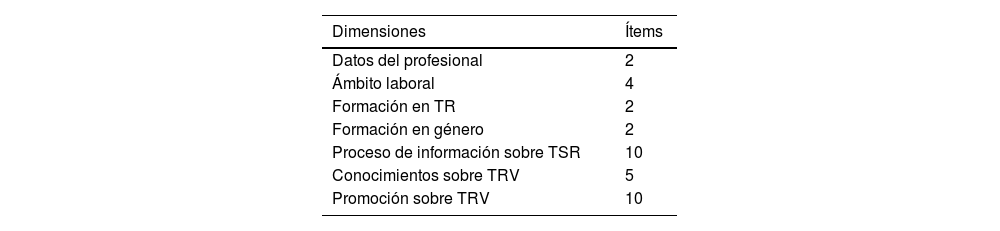
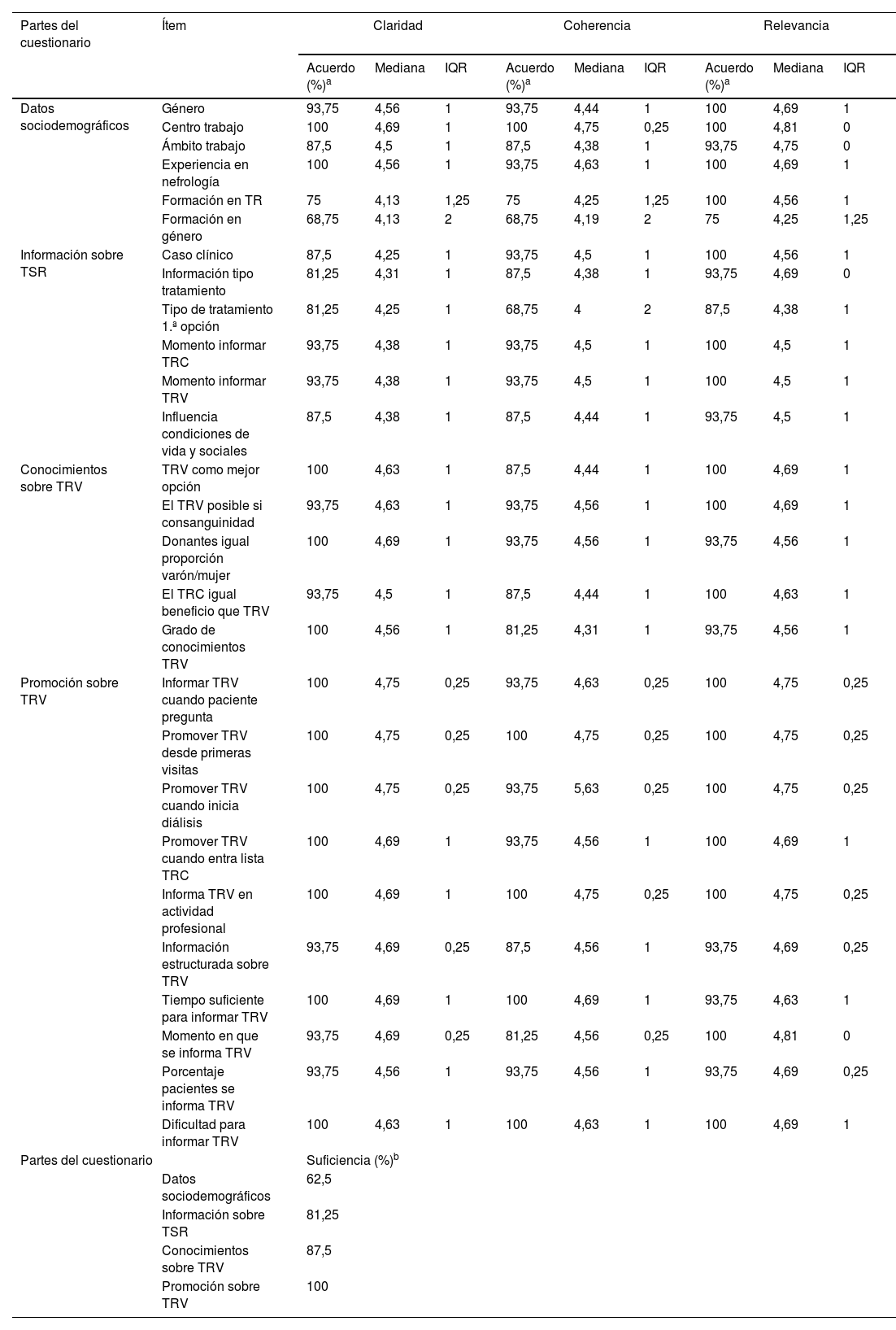
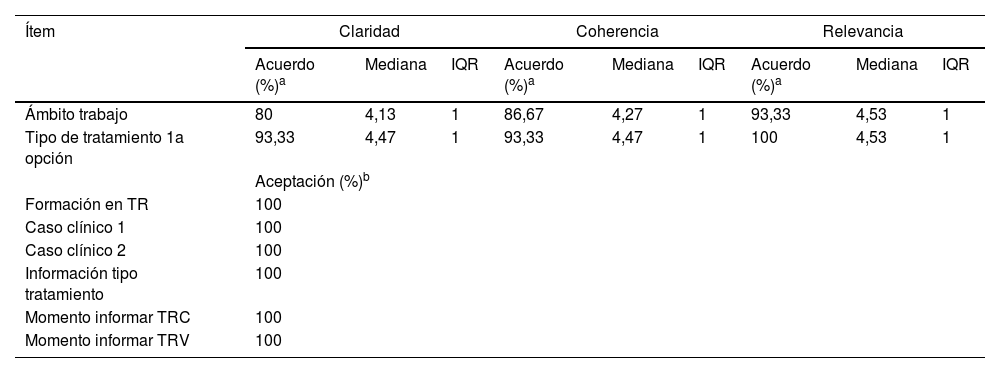
ResultadosParticiparon 16 enfermeras expertas de todas las áreas de la enfermería nefrológica. Del cuestionario inicial de 35 preguntas se valoraron 31 ítems. Después de las 2 rondas Delphi se consensuaron todos los ítems y se incluyó un nuevo ítem aportado por los panelistas. El consenso permitió identificar 7 dimensiones que se estructuraron en 4 temas: perfil del profesional, tipo de información sobre tratamiento sustitutivo renal, conocimientos y promoción sobre trasplante renal de vivo.
ConclusionesEsta investigación ha permitido disponer de un cuestionario consensuado por expertos para detectar el tipo de información que dan las enfermeras de nefrología a las personas con enfermedad renal, y conocer como la perspectiva de género influye en el proceso de información. Al mismo tiempo, esta herramienta facilitará la detección del grado de conocimientos que las enfermeras tienen sobre el trasplante renal de donante vivo y qué tipo de promoción hacen de este tratamiento renal a las personas a las que atienden.
To match the items of a questionnaire on the information process of renal replacement therapy and the degree of information and promotion of living donor kidney transplantation by nephrology nurses, taking into account the gender perspective.
MethodsThis study was developed in 2 phases: 1) elaboration of an initial questionnaire by the research team, which consisted of 4 nurses, and 2) completion of two rounds of the Delphi method to agree on the research team's proposal.
Results16 specialist nurses from all areas of nephrology nursing participated. Of the original questionnaire with 35 questions, 31 items were agreed upon. After the two Delphi rounds, consensus was reached on all questions and a new question was included, which was introduced by the panelists. The consensus made it possible to identify 7 dimensions, which were grouped into 4 themes: Profile of professionals, type of information on renal replacement therapy, knowledge and promotion of kidney transplantation in vivo.
ConclusionsThis research has made it possible to create a questionnaire agreed by experts to identify the type of information that nephrology nurses give to people with kidney disease and how the gender perspective influences the information process. At the same time, this tool will facilitate the identification of nurses’ level of knowledge about living donor kidney transplantation and the way they promote this renal treatment to the people they care for.