Evaluar la evolución de la musculatura perineal en mujeres primigestas afectas de obesidad (índice de masa corporal [IMC]≥30) y comparar dicha evolución con mujeres primigestas con un IMC en rango de normopeso.
MétodoSe realizó un estudio cohorte longitudinal prospectivo donde se estudió a las gestantes en 3 momentos: en semana 12 de gestación, la semana 34 de gestación y a las 12 semanas tras el parto. En estas consultas se realizó medición mediante perinometría para determinar el tono basal (TB), la fuerza máxima contráctil (FMax); y la fuerza ejercida (FE). Además, se utilizó el test de Oxford modificado (MOS). Para el estudio estadístico se utilizaron modelos estadísticos generales mixtos.
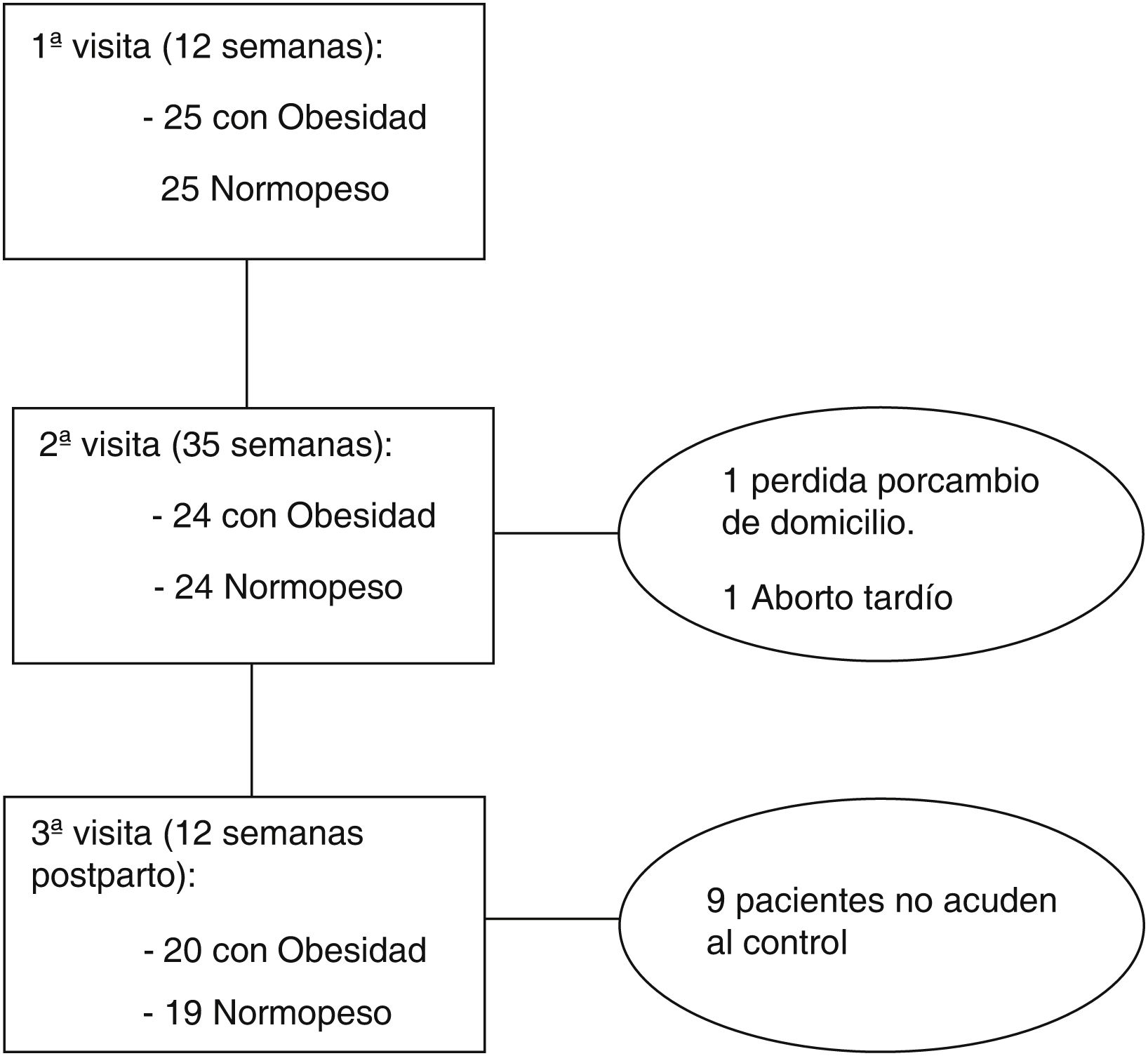
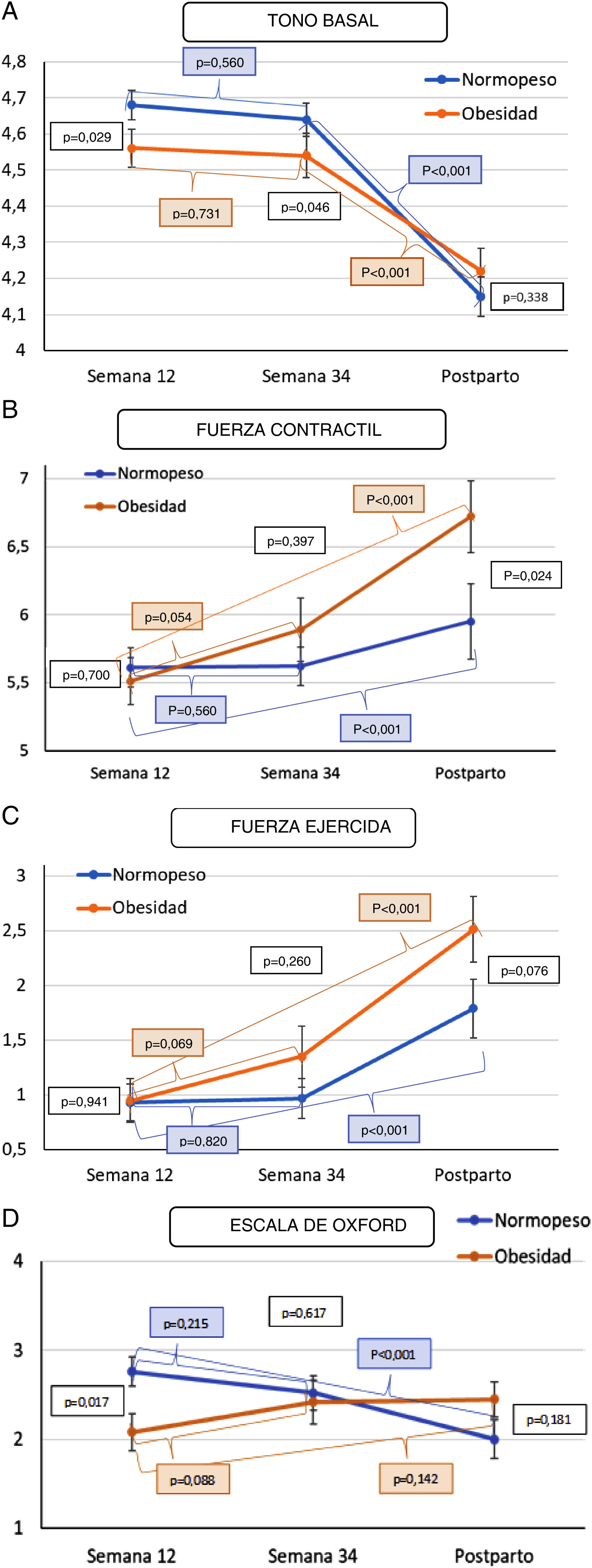
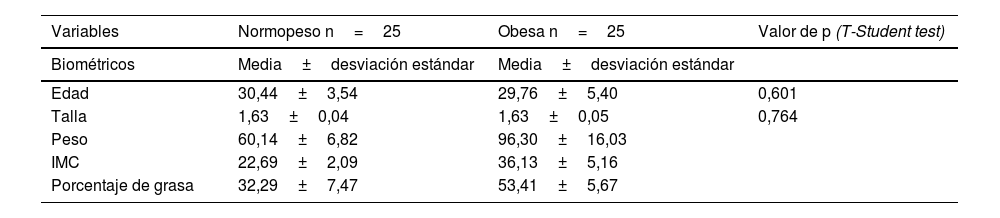
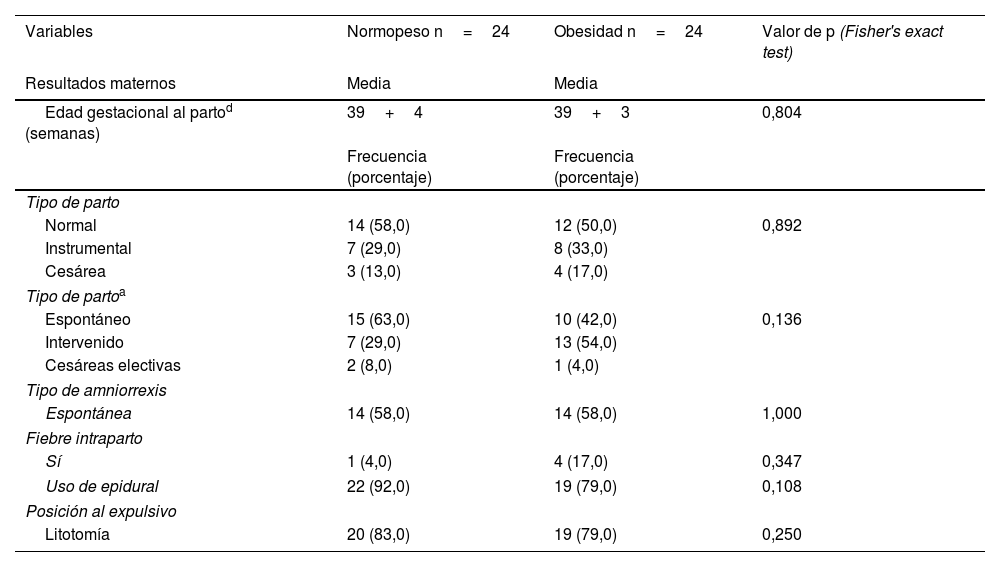
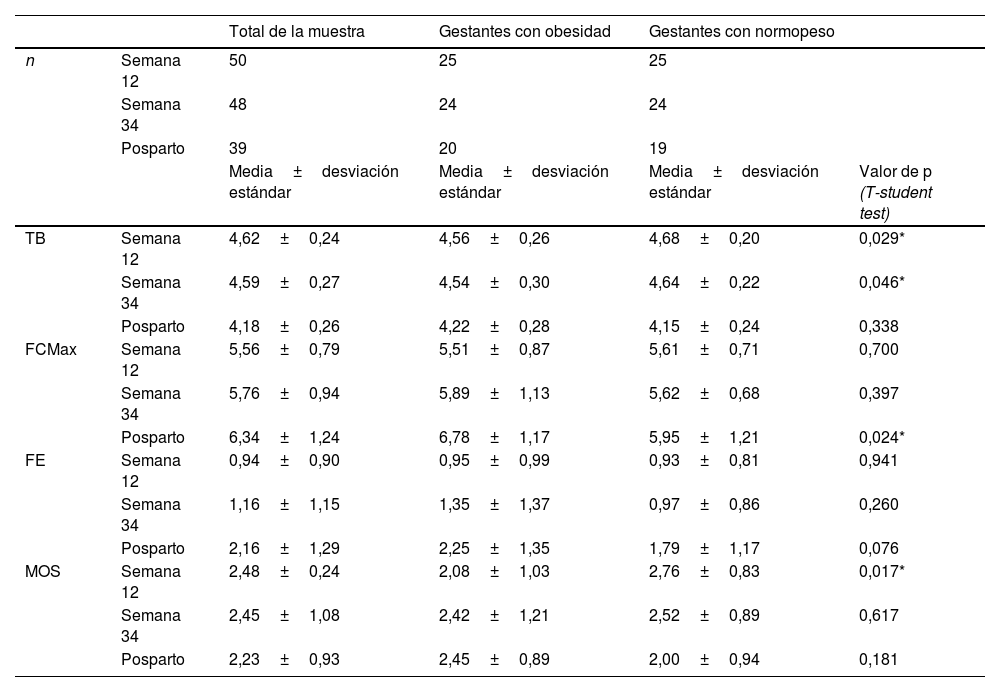
ResultadosSe reclutaron al inicio 50 gestantes nulíparas (25 con IMC≥30 y 25 con IMC<25), concluyendo el estudio completo 39. Al inicio del embarazo el tono perineal basal fue de 4,62±0,24Newton (Nw) y descendió a 4,18±0,26Nw tras el parto. La capacidad contráctil fue de 5,56±0,79Nw en la semana 12 y aumento a 6,34±1,24Nw tras el parto. Al comparar la FCMax en la semana 12 en gestantes obesas vs. Normopeso se observan valores de 5,51±87Nw vs. 5,61±0,71Nw (p=0,941). Se observaron valores posparto 6,72±1,17Nw vs. 5,95±1,21Nw (p=0,024), superiores en la población con obesidad.
ConclusionesExiste una disminución significativa del tono basal que es contrarrestada con un aumento de la fuerza contráctil objetivable a las 12 semanas posparto. El organismo dispone de mecanismos compensadores que permiten la recuperación a partir de los 3 meses posparto existiendo una mayor fuerza muscular dentro de las pacientes con obesidad.
Evaluating the changes of the perineal muscles in primigravid women with obesity (BMI≥30) and to compare the progress with primigravid women in normal BMI range.
MethodsA prospective longitudinal cohort study was carried out. The pregnant women were studied at three moments: at 12 weeks’ gestation, at 34 weeks’ gestation and at 12 weeks after delivery. During the ckeck-up, perinometric measurements were taken to determine basal tone (BT), maximum contractile force (FMax) and applied forced (AF). In addition, the Oxford test (MOS) was used. General statistical mixed models were used for the statistical study.
ResultsFifty nulliparous pregnant women (25 with BMI≥30 and 25 with BMI<25) were recruited at the beginning of the study and 39 completed the entire study. Basal tone (BT) was 4.62±0.24 Nw at the beginning of pregnancy and decreased to 4.18±0.26 Nw after delivery. Contractile capacity was 5.56±0.79 Nw at week 12 and increased to 6.34±1.24 Nw after delivery. When comparing the FCMax at week 12 in obese vs. normal weight pregnant women, values of 5.51±87 Nw vs. 5.61±0.71 Nw were observed (P=.941). Postpartum values were 6.72±1.17 Nw vs. 5.95±1.21 Nw (P=.024), higher in the obese population.
ConclusionsThere is an increase in contractile strength (Fmax) at 12 weeks postpartum in order to counteract the significant decrease in basal tone (BT). The body has compensatory mechanisms that allow recovery after 3 months postpartum, with greater muscle strength in obese patients.