4th International Conference for Global Health (ICGH) in conjunction with the 7th Asian International Conference in Humanized Health Care (AIC-HHC)
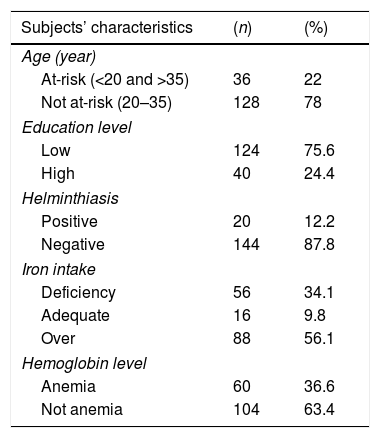
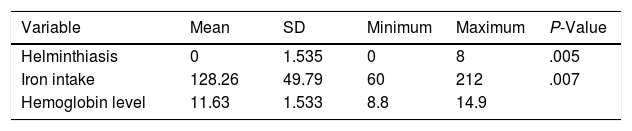
More infoThe study aims to analyze the correlation of helminthiasis, iron intake, and hemoglobin levels in pregnant women in the Public Health Center of Kemusu 2 Boyolali, Central Java, Indonesia. A cross-sectional research design was applied to 164 pregnant women who are in the second-third trimester and selected using simple random sampling. The Cyanmethemoglobin tool was utilized to measure the respondents’ hemoglobin levels. The iron intake was obtained using the Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire (SQ-FFQ). Data analysis applied the Pearson's correlation test. This study discovered that 12.2% of subjects are infected by Ascaris lumbricoides; 34.1% and 36.6% of the subjects suffer from iron intake deficiency and anemia. There is a correlation between helminthiasis, iron intake, and hemoglobin levels in pregnant women (p=.005 and p=.007). Nutrition program is still needed to prevent the helminthiasis, reduce the prevalence of anemia in pregnant women, and improve their iron intake through supplementation and nutrition education.