This study aims to describe the hematological profile of severe preeclampsia.
MethodThe study design was cross-sectional with observational analytic. Data is taken from the medical records of pregnant women and childbirth at the Central General Hospital Dr. Wahidin Sudirohusodo Makassar City, State Higher Education Hospital Hasanuddin University Makassar City, Special Region of Mother and Child Hospital Pertiwi Makassar City, Mother and Child Hospital Sitti Khadijah 1 Makassar City, Mother and Child Hospital Children Sitti Khadijah 3 Makassar City from June to August 2019. The hematological profile assessed is white blood cell, red blood cell, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelet, procalcitonin, lymphocyte, and monocyte.
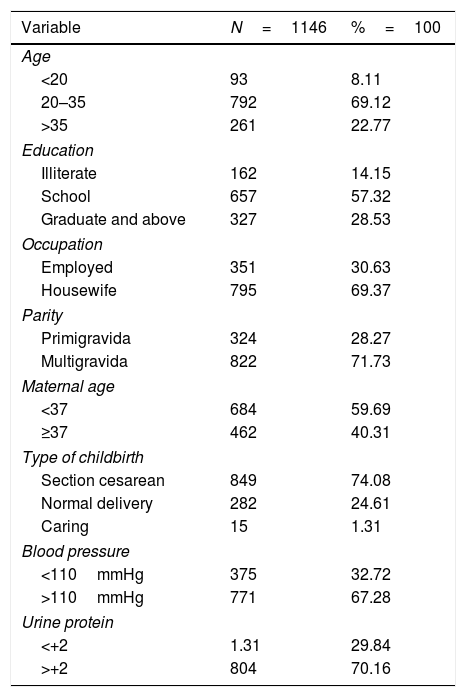
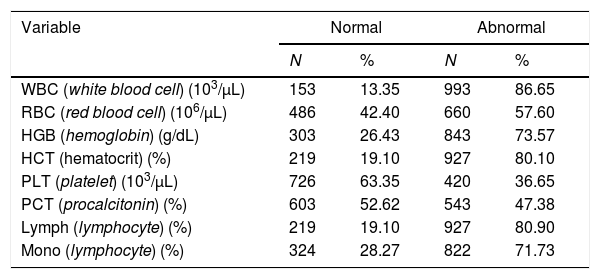
ResultsThere were 1146 patients with severe preeclampsia. White blood cells, red blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, lymphocytes, monocytes have abnormal results in mothers with severe preeclampsia and tend to be significant.
ConclusionWhite blood cells in patients with severe preeclampsia tend to be higher than normotensive pregnancies. Whereas red blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, lymphocyte, and monocyte in severe preeclampsia tend to be lower than normotensive pregnancies. There was no difference between platelets and procalcitonin in pregnant women with severe preeclampsia and normotension.