4th International Conference for Global Health (ICGH) in conjunction with the 7th Asian International Conference in Humanized Health Care (AIC-HHC)
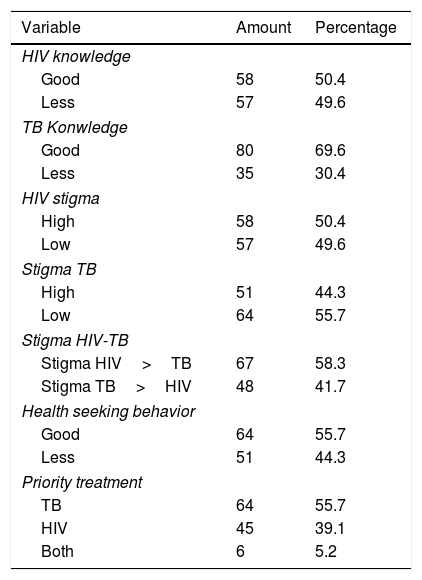
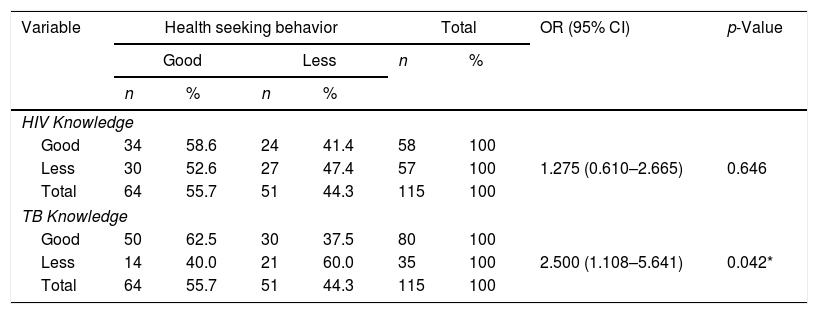
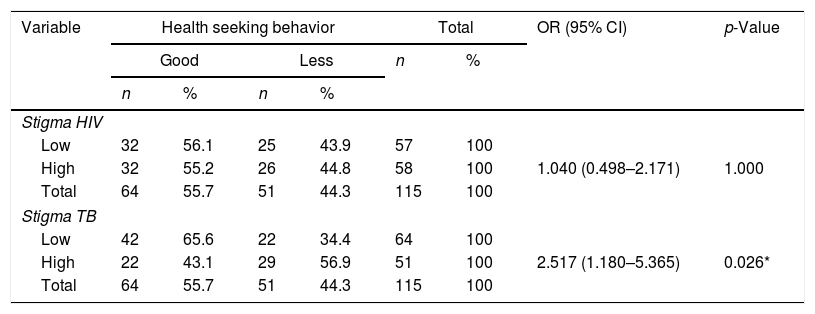
More infoThe purpose was to identify knowledge and TB stigma, as well as its relationship with health-seeking behavior in HIV and TB co-infection patients. A cross-sectional study was conducted with 115 HIV and TB co-infection patients who visited the VCT Polyclinic in five hospitals in Jakarta. This study was using instruments: Brief HIV-Knowledge Questionnaire (HIV-KQ-18), Knowledge TB survey Questionnaire, Berger HIV stigma Scale, Tuberculosis-Related Stigma Scale. This study showed that respondents had good knowledge of TB (69.6%) and had a low stigma of TB (55.7%), and had a health-seeking behavior that did not delay consultation (55.7%). There was a significant relationship between TB knowledge (p-value: 0.042) and TB stigma (p-value: 0.026) with health-seeking behavior. The results of this study can be used as guidelines to improve education and counseling about TB knowledge and TB stigma in HIV and TB co-infection patients.