This study aims to determine the description of prediabetes events in children based on socio-demographic, anthropometric, and lifestyle characteristics.
MethodThis cross-sectional study involved 110 school-aged children and their parents. Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children (PAQ-C) was used to examine children's physical activity, HbA1c measured to evaluate diabetes status, and feeding behavior questionnaire is given to students and through interviews.
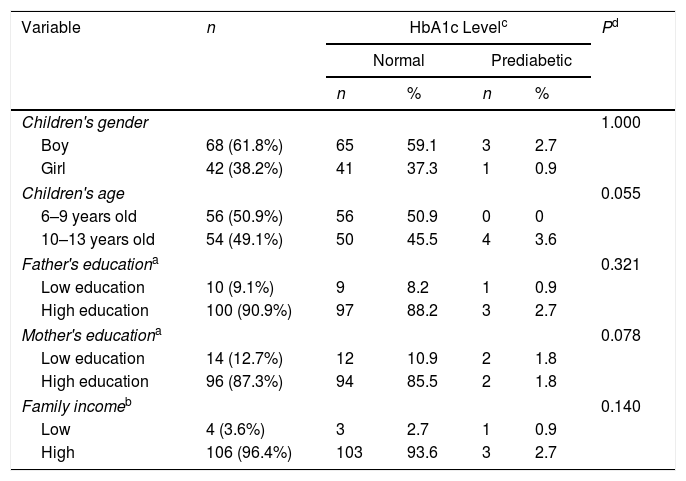
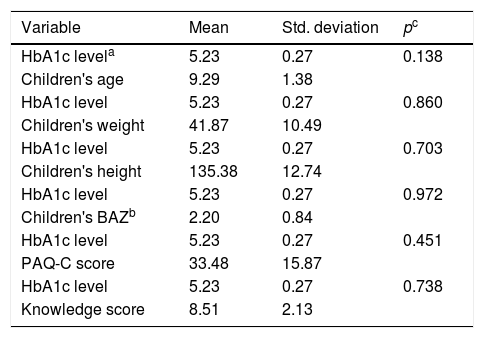
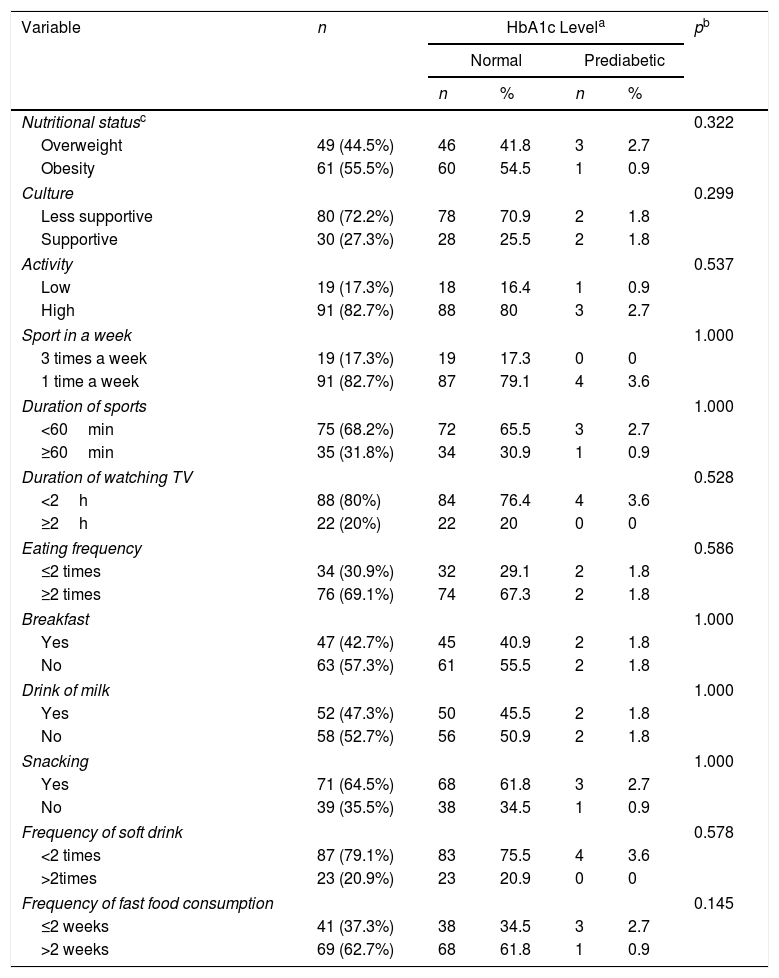
ResultsPrevalence of overweight and obese children who have an HbA1c level between 5.2% and 5.6% was 62.7%. Obese and overweight children are less support from family 72.2%, exercise once a week 82.7% with duration less than 60min 68.2%, the habit of snacking 64.5%, and consumption of fast food≥two times a week 62.7%.
ConclusionSocio-demographic, cultural family, and lifestyle play a role in increasing the risk of incident prediabetes in overweight and obese children of school age.