This study was to determine the risk factors for HIV incidence in MSM (Men Sex with Men) communities at the HIV/AIDS Advocacy Institute in Southeast Sulawesi.
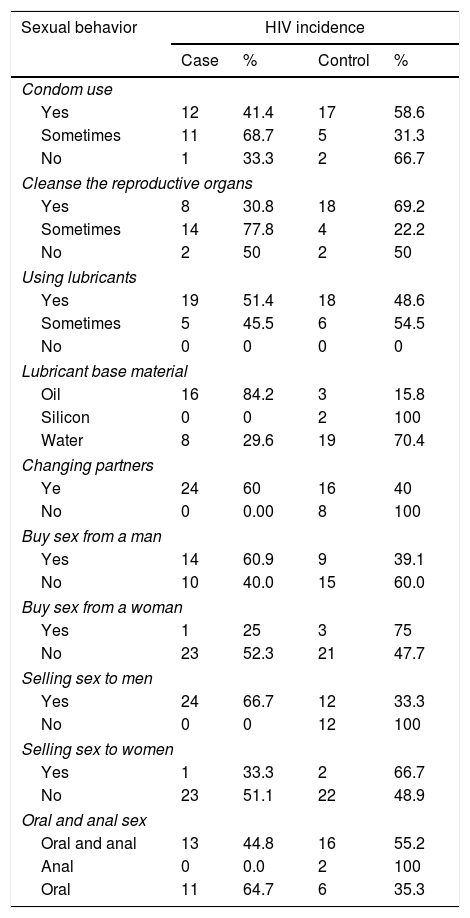
MethodsIt was an analytic survey and case–control. Data collected includes age, education level, occupation, gender, and sexual behavior including (condom use, cleaning reproductive organs, using basic materials (lubricants, silicon, water), changing partners, buying sex from men, buying sex from women, sell sex to men, sell sex to women, oral and anal sex. Data used secondary and primary data and collected in two months with the team. The number of samples in this study was 40 respondents consisting of 24 cases and 24 controls.
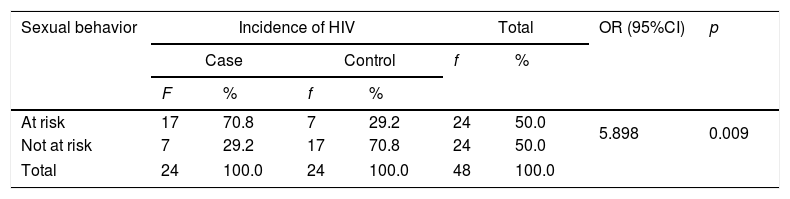
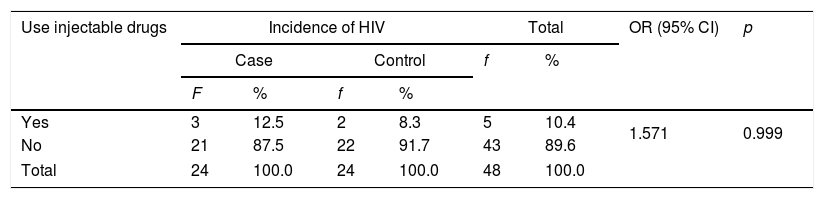
ResultsThe results showed that the risk factors for HIV incidence in MSM communities were sexual behavior (p=0.009, OR=5.898 and 95% CI 1.609–20.479), while injecting drug use factors were not a risk factor for HIV incidence in MSM communities (p=1.000, OR=1.571 and 95% CI 0.238–10.365).
ConclusionRisk factor for HIV incidence in MSM communities was sexual behavior.