This study aims to examine the relationship between birth length and stunting in 18–23 months old infants in Indonesia.
MethodsThis study was a cohort study after supplementing pregnant and lactating women with Moringa oleiver, iron folic acid. Several factors have been measured previously including the family characteristics, maternal conditions, breastfeeding complementary foods. Infant body weight and length were measured at age of 18–23 months (n=344). All measurements were evaluated by trained field workers using standard questionnaire. Data were analyzed using bivariate and multiple logistic regression analysis.
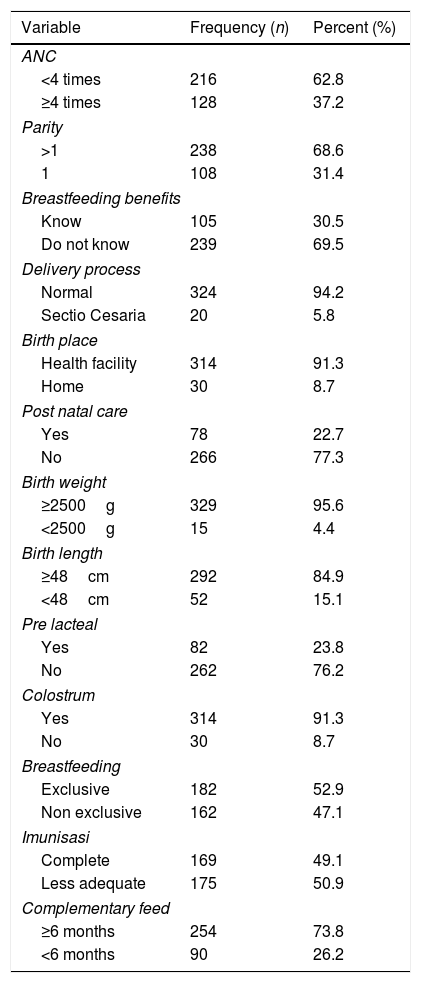
ResultsThe majority of mothers aged 20–35 years, education level was<12 years, working as housewife, infants born with normal body weight, normal length, born in health facility, fed with exclusive breast milk. Stunting prevalence was 44.2%. Bivariate analysis indicated a threshold significant relationship to stunting for family income (0.079), breastfeeding complementary feed (0.073), whereas the birth length had a significant relationship to stunting (0.048). After controlling for all potential confounding variables, birth length was the online variable to correlate with stunting (p=0.0233).
ConclusionStunting prevalence is high at the period of 18–23 months and significantly related to birth length.