Proper breastfeeding practice is the most effective way to meet the nutritional adequacy of children. Breast milk has a nutrient composition that matches the nutritional needs of children and is believed to be able to have a positive influence on the infant's growth. The purpose of this study was to analyses the effect of breastfeeding on the prevention of stunting in poor families.
MethodThis study is cross-sectional. Samples were taken systematically randomly from all mothers who had children aged 0–36 months in Pangkep. This location was chosen because it is included in the height prevalence of stunting (41.9%) in South Sulawesi, Indonesia1. The sample size was 1038 mother–child pairs. The percent distribution of children, according to weight for age, height/length for age, and weight for height/length as per the standard deviation (SD) classification by World Health Organization (WHO), 2006 was carried out.
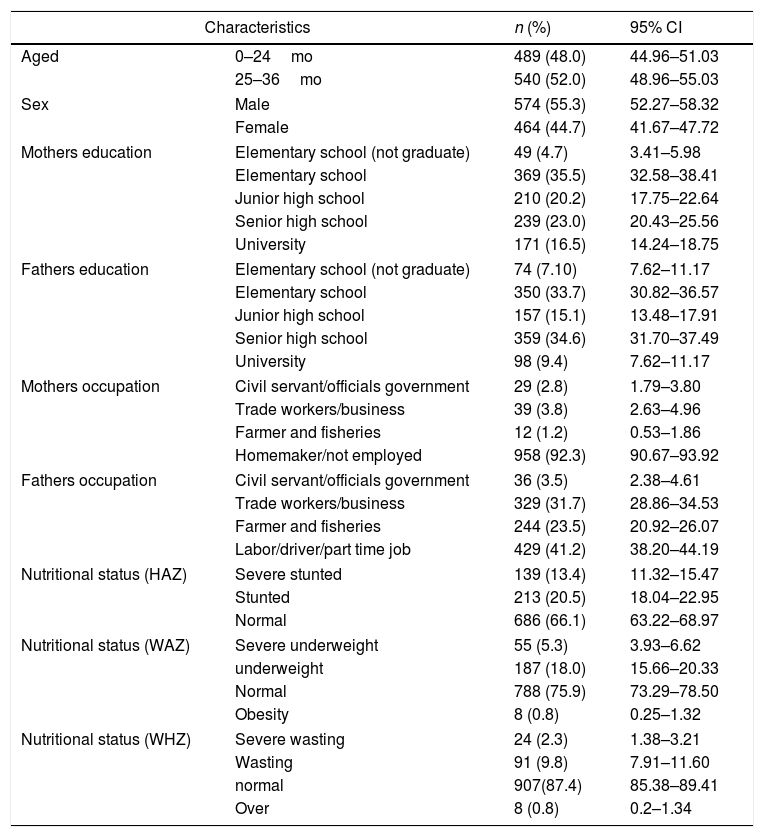
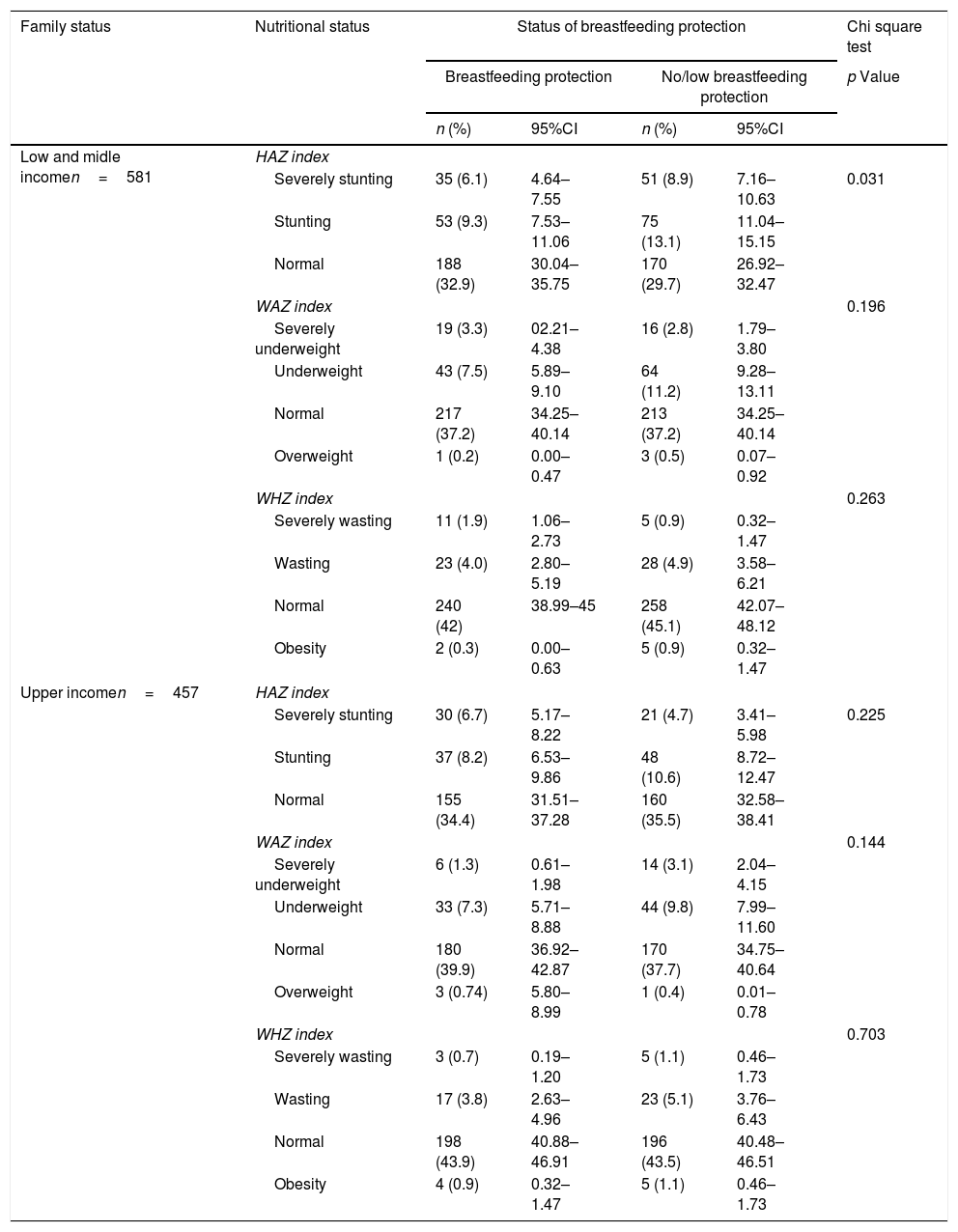
Resultsshort stature (stunting) and normal status about 33.9% and 66.1%. As many as 56% of them occur outside the age period of breastfeeding. On the contrary, it was known that 63.5% of those who were still in the period of breastfeeding. The statistical analyses show that breastfeeding can prevent stunting (p=0.039).
ConclusionBreastfeeding practice was effective in preventing stunting in poor family children.