The study aimed to determine body image and levels after surgery in cornea transplant patients.
Materials and methodsThe population of this cross-sectional study was composed of 383 patients presented to the Eye Bank unit of a University Hospital after corneal transplantation. Sample size of 193 patients was calculated with 0.5 power, a margin of error of 5%, representing 95% of the universe. The data were collected through face-to-face interviews with the patients by the researcher and the study was completed with 178 patients in September–November 2022. The data were collected using a Patient Information Form, the Body Image Scale, and the General Self-Efficacy Scale. Parametric tests, Pearson Correlation, Student’s t-test, and One-Way Analysis of Variance tests were performed were used in the data analysis.
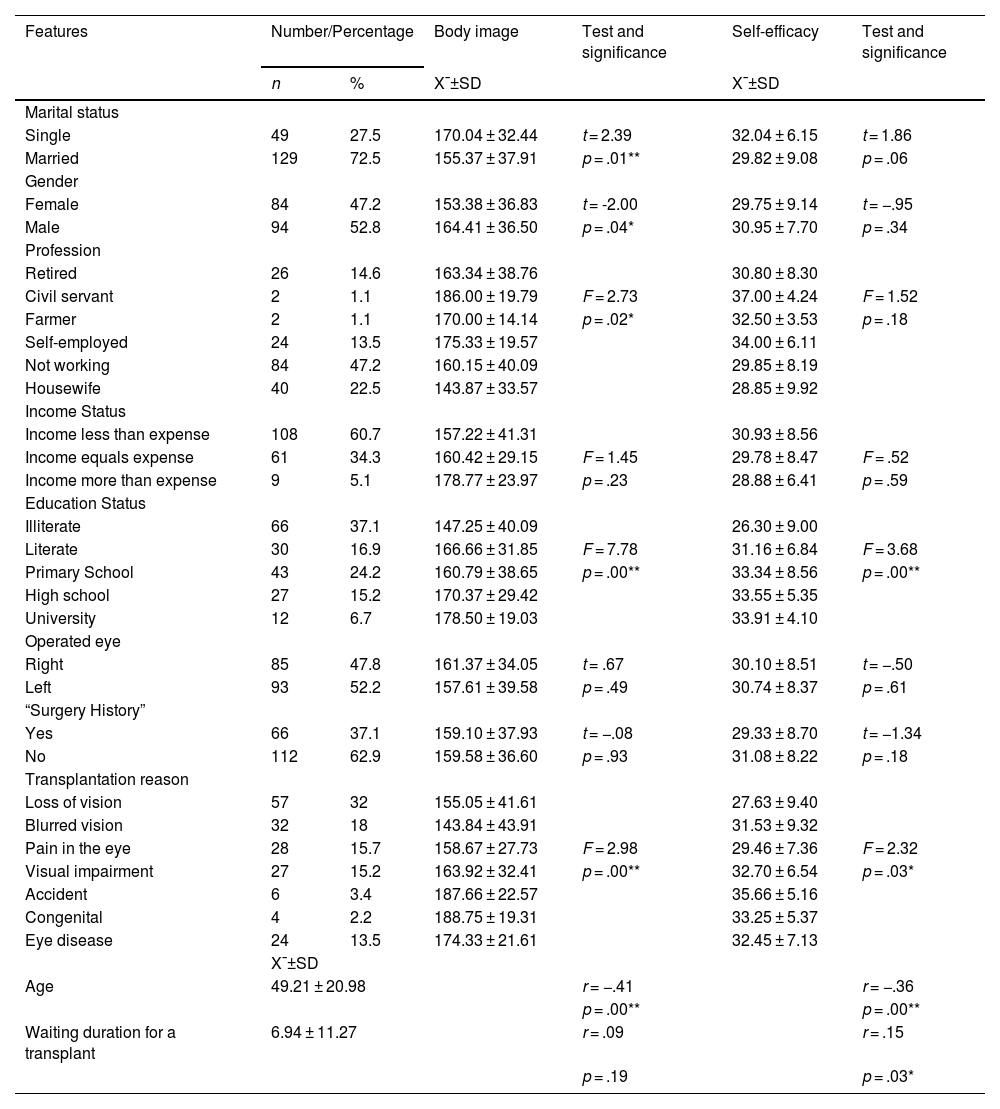
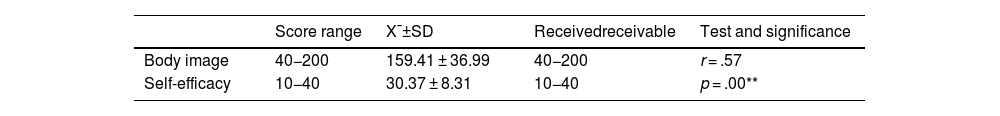
ResultsIt was determined that the mean Body Image Scale score of the transplant patients participating in the study was 159.41 ± 36.99 and the mean Self-Efficacy Scale score was 30.37 ± 8.31. When the comparison of the mean scores was examined, the difference between the mean scores of gender, marital status, occupation, and body image scale was statistically significant (p < .05), while the difference between the self-efficacy mean scores was not statistically significant (p > .05). There was a positive, moderately strong significant relationship between body image and the self-efficacy of the patients (p < .01) (r = .57).
ConclusionIt was found that the patient's body image and self-efficacy levels were high, and self-efficacy increased as the body image increased.
El estudio tuvo como objetivo determinar la imagen corporal y los niveles de autoeficacia después de la cirugía en pacientes con trasplante de córnea.
Materiales y métodosLa población de este estudio descriptivo estuvo compuesta por 383 pacientes que acudieron a la unidad del Banco de ojos de un Hospital Universitario tras un trasplante de córnea. El tamaño de la muestra de 193 pacientes se calculó con una potencia de 0,5 y un margen de error del 5%, lo cual representa el 95% del universo. Los datos fueron recopilados a través de entrevistas presenciales con los pacientes por parte del investigador, y el estudio se completó con 178 pacientes en septiembre - noviembre de 2022. Los datos fueron recolectados utilizando un Formulario de información al Paciente, la Escala de imagen corporal y la Escala de autoeficacia general. En el análisis de datos se utilizaron la distribución porcentual, la media aritmética y el análisis de correlación.
ResultadosSe determinó que la puntuación media de la Escala de imagen corporal de los pacientes trasplantados participantes en el estudio fue de 159,41 ± 36,99 y la puntuación media de la Escala de autoeficacia fue de 30,37 ± 8,31. Cuando se examinó la comparación de las puntuaciones medias, la diferencia entre las puntuaciones medias de la escala de género, estado civil, ocupación y de imagen corporal fue estadísticamente significativa (p < 0,05), mientras que la diferencia entre las puntuaciones medias de autoeficacia no fue estadísticamente significativa (p < 0,05). Existió una relación significativa positiva moderadamente fuerte entre la imagen corporal y la autoeficacia de los pacientes (p < 0,01) (r = 0,57).
ConclusiónSe constató que la imagen corporal y los niveles de autoeficacia de la paciente eran elevados, y la autoeficacia aumentaba a medida que aumentaba la imagen corporal.