El sistema miofascial es una red tridimensional ininterrumpida. Para efectos de este estudio, el abordaje del tejido fascial se realizó a la luz de la técnica de Inducción Miofascial (IMF®), propuesta por Andrzej Pilat. Dentro de las técnicas profundas resalta la técnica de manos cruzadas. Sin embargo, a la fecha, no se cuenta con parámetros estandarizables que permitan la reproducibilidad de la técnica. El objetivo fue describir los grados de flexión de los miembros superiores y su relación con la fuerza ejercida por el fisioterapeuta durante la ejecución de la técnica manos cruzadas en la región toracolumbar.
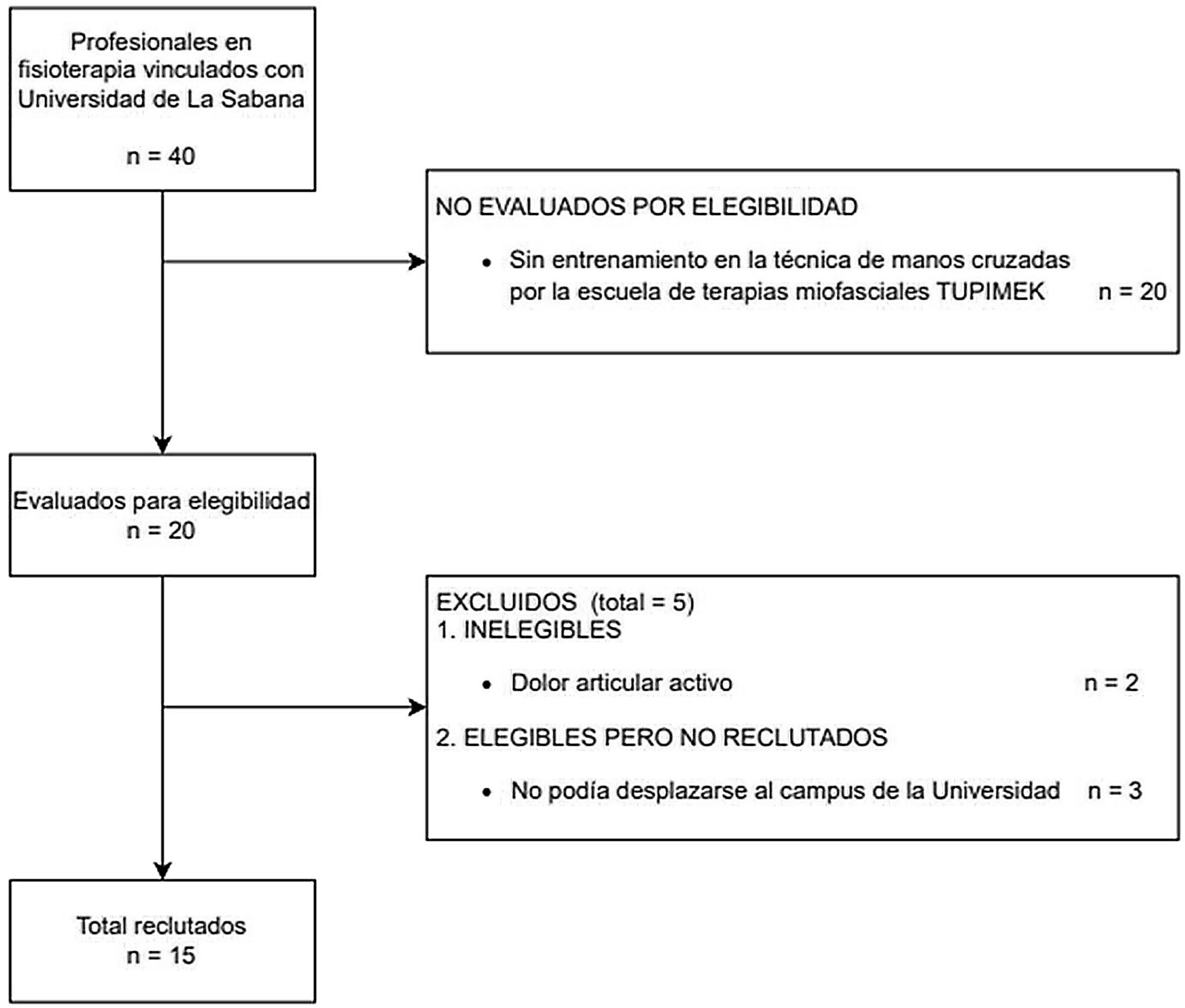
Materiales y métodosEstudio cuantitativo, descriptivo, transversal, que evaluó el comportamiento de las variables entre un grupo de 15 fisioterapeutas entrenados en IMF® que realizaron la técnica de manos cruzadas durante 5 minutos ininterrumpidos. Se generó un análisis estadístico y gráfico en el software R Studio versión 4.2.1, calculando medidas de tendencia central junto con el análisis de correlación de Spearman.
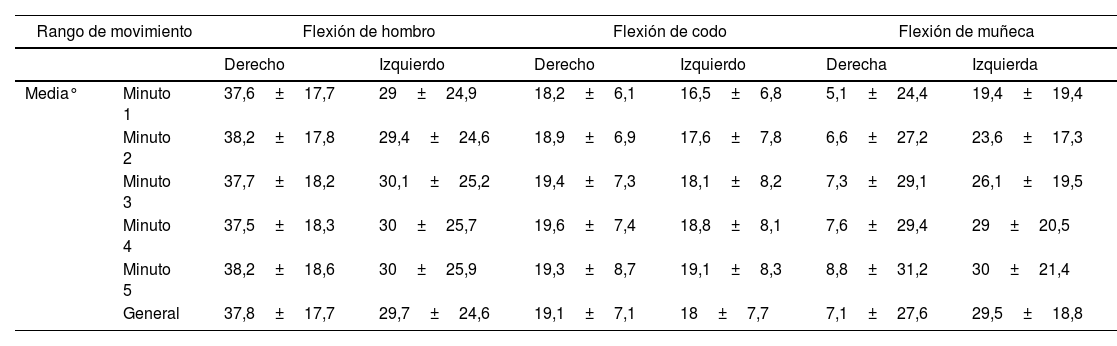
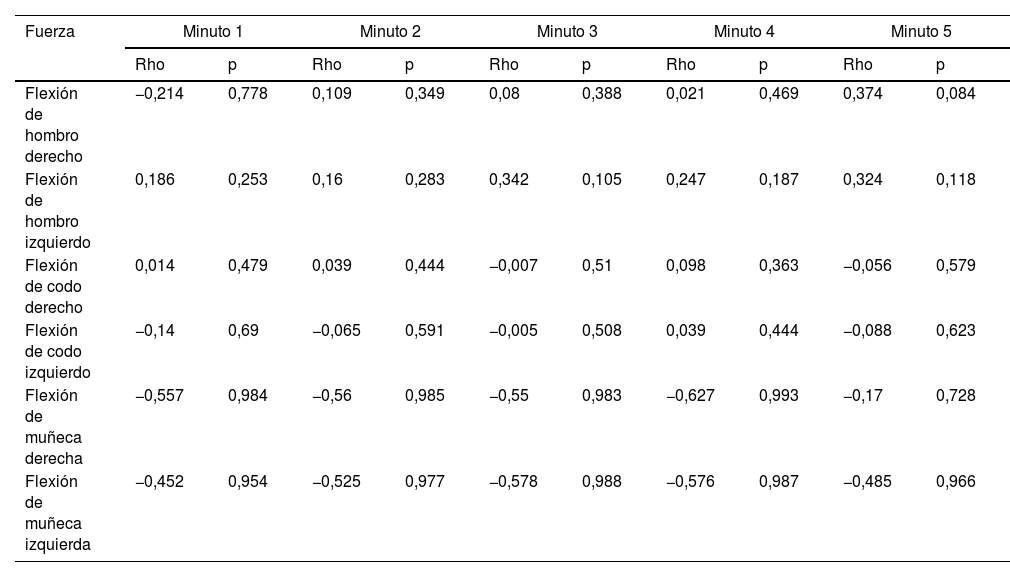
ResultadosEl coeficiente de correlación Spearman (Rho) entre variables fue predominantemente negativo débil o moderado al pasar los 5 minutos. Si bien no se encontró una correlación positiva, se cree que pueden existir más variables influyentes que no fueron analizadas en el estudio.
ConclusionesLa cinemática de miembros superiores no presenta relación significativa estadísticamente con la fuerza ejercida en la ejecución de la técnica de manos cruzadas en la zona fascial dorsolumbar. Este es un estudio inicial que permitirá a investigadores seguir generando práctica basada en la evidencia.
The myofascial system is an uninterrupted three-dimensional network. For the purposes of this study, the approach to the fascial tissue was carried out in light of the Myofascial Induction (MIF®) technique, proposed by Andrzej Pilat. Among the deep techniques, the crossed hands technique stands out. However, to date, there are no standardizable parameters that allow the reproducibility of the technique. The objective was to describe the degrees of flexion of the upper limbs and its relationship with the force exerted by the physiotherapist during the execution of the crossed hands technique in the thoracolumbar region.
Materials and methodsQuantitative, descriptive, cross-sectional study that evaluated the behavior of the variables among a group of 15 physiotherapists trained in IMF® who performed the crossed hands technique for 5 uninterrupted minutes. A statistical and graphical analysis was generated in R Studio Software version 4.2.1, calculating measures of central tendency along with Spearman correlation analysis.
ResultsThe Spearman correlation coefficient (Rho) between variables was predominantly weak or moderately negative after 5minutes. Although a positive correlation was not found, it is believed that there may be more influential variables that were not analyzed in the study.
ConclusionsThe kinematics of the upper limbs does not present a statistically significant relationship with the force exerted in the execution of the crossed hands technique in the thoracolumbar fascial area. This is an initial study that will allow researchers to continue generating evidence-based practice.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".