La fuerza de agarre es aquella que se ejerce con la mano para apretar o soltar cualquier objeto, y es considerada un indicador de salud. Autores han concluido que la fuerza de agarre varía dependiendo de la edad, el sexo, la estatura, el peso, hábitos, factores genéticos, entre otros.
ObjetivosEstablecer un modelo matemático para la predicción de la fuerza de agarre de un grupo de trabajadores de oficina de la ciudad de Bogotá.
MétodosCon el apoyo de un dinamómetro hidráulico marca Jamar se midió la fuerza de agarre de la mano dominante y no dominante a 293 trabajadores de oficina sanos de una entidad pública de la ciudad de Bogotá. Se siguió el protocolo de la Sociedad Americana de Terapistas de la Mano. La edad, el sexo, la talla, el peso y el IMC fueron registrados para cada participante. Se aplicó la regresión lineal Stepwise para establecer los modelos de predicción para la mano dominante y no dominante, con el software R-Studio.
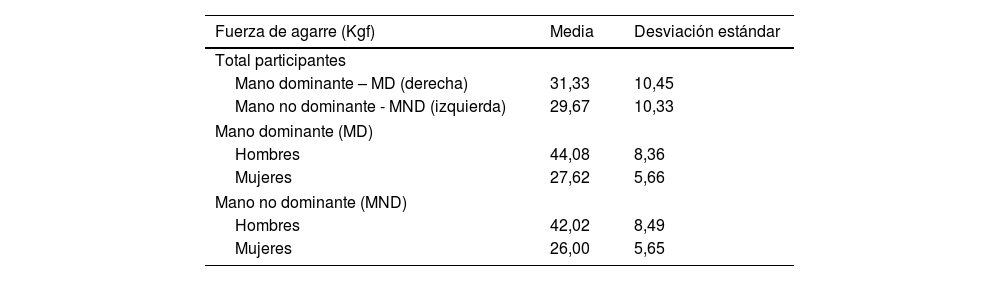
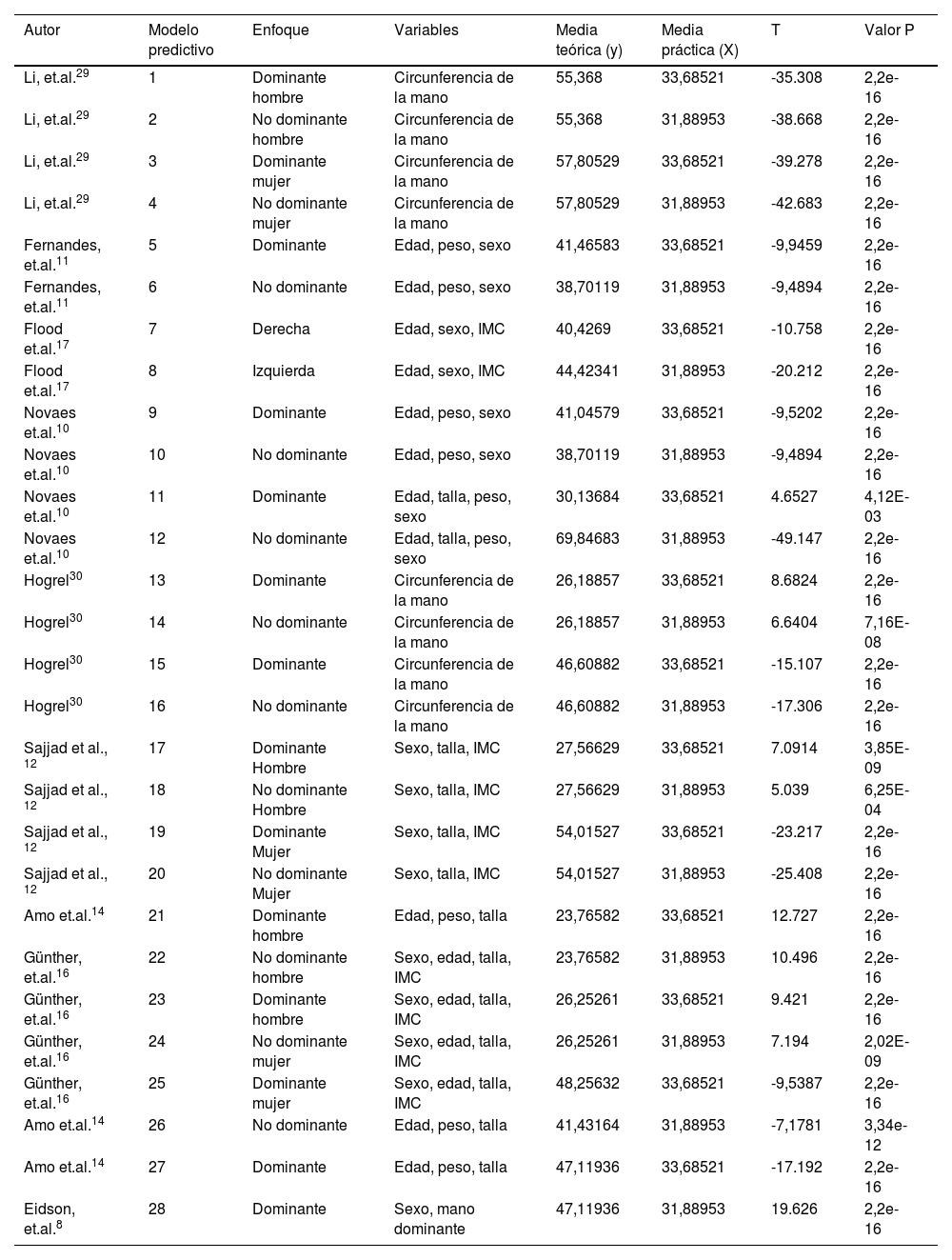
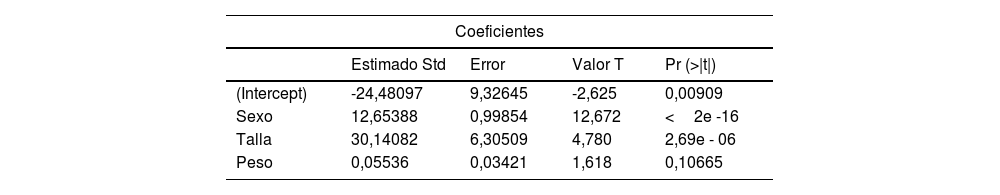
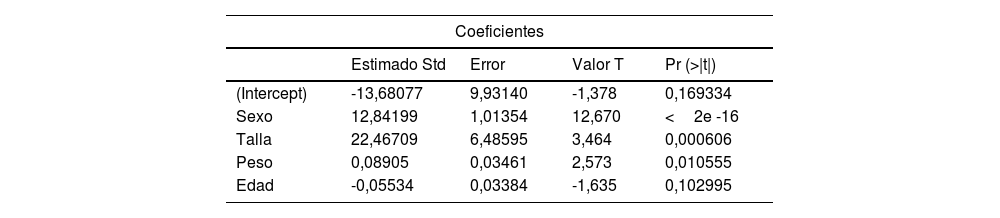
ResultadosLos participantes fueron 185 hombres y 108 mujeres, todos con dominancia derecha. En general, los hombres registraron valores más altos de fuerza de agarre respecto a las mujeres. La fuerza de la mano dominante fue superior a la de la mano no dominante. Los modelos matemáticos resultantes permiten estimar la fuerza de agarre de la mano dominante y la mano no dominante con una predictibilidad del 64,52% y el 63,23% respectivamente.
ConclusionesLos modelos predictivos propuestos consideraron las variables sexo, talla y peso para la estimación de la fuerza de agarre de la mano dominante, y las variables sexo, talla, peso y edad para la fuerza de agarre de la mano no dominante.
Grip strength is the force that is exerted with the hand to squeeze or release any object and it is considered an indicator of health. Authors have concluded that grip strength varies depending on age, sex, height, weight, habits, genetic factors, among others.
ObjectivesTo establish a mathematical model for the prediction of grip strength in a group of office workers in the city of Bogotá.
MethodsThe grip strength of the dominant and non-dominant hand was measured with a Jamar hydraulic dynamometer in 293 healthy office workers of a public entity in the city of Bogota. The protocol of the American Society of Hand Therapists was followed. Age, sex, height, weight, and BMI were recorded for each participant. Stepwise linear regression was applied to establish prediction models for the dominant and non-dominant hand, using R-studio software.
ResultsThe participants were 185 men and 108 women, all with right dominance. In general, men recorded higher values of grip strength than women. The strength of the dominant hand was higher than that of the non-dominant hand. The proposed mathematical models allow estimating the grip strength of the dominant hand and the non-dominant hand with a predictability of 64.52% and 63.23%, respectively.
ConclusionsThe proposed predictive models included the variables sex, height, and weight for the estimation of the grip strength of the dominant hand, and the variables sex, height, weight and age for the grip strength of the non-dominant hand.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".