Las enfermedades neuromusculares y las lesiones medulares comprometen los músculos respiratorios y función pulmonar ocasionando complicaciones respiratorias. La insuficiencia respiratoria aguda y el compromiso respiratorio crónico ocasionan alto riesgo de morbilidad y mortalidad. Se ha descrito el uso de la respiración glosofaríngea para mejorar variables de función pulmonar y muscular respiratoria que promueven la tos más efectiva y aumento del tiempo libre de ventilación mecánica.
ObjetivoDescribir y presentar la evidencia actual de la efectividad de la respiración glosofaríngea en mejorar la función pulmonar y muscular respiratoria en pacientes adultos y pediátricos con enfermedades neuromusculares o lesión medular con o sin ventilación mecánica.
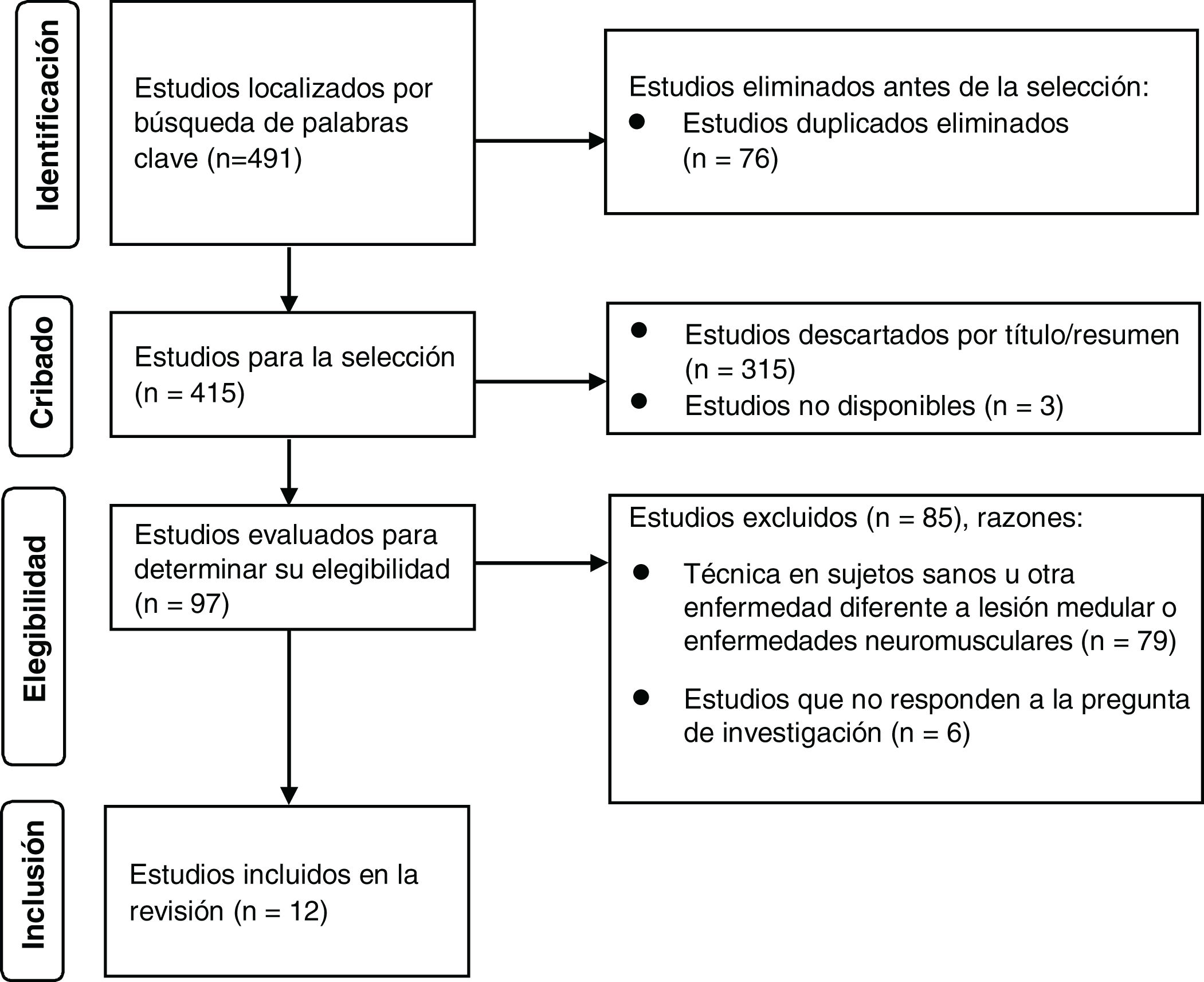
DiseñoRevisión exploratoria con la metodología PRISMA-ScR. Se realizó una búsqueda en las bases de datos PEDro, Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, ScienceDirect, Springer, Medline, Cochrane, SciELO, Lilacs, Google Académico, se usaron palabras claves y términos MeSH en idiomas español, inglés y portugués, entre los años 2000-2020. Los resultados se presentan de forma descriptiva.
ResultadosSe identificaron 491 estudios y fueron incluidos 12. El 58,3% fueron realizados en países europeos. El 41,6% de los estudios fueron valorados y ninguno cumplió totalmente los criterios de calidad. La efectividad de la respiración glosofaríngea en la función pulmonar y muscular respiratoria estuvo relacionada con mejoría de capacidad vital en 66,6% y pico flujo de tos en 33,3% de los estudios. Se reportó mejoría en expansión torácica en 66,6% de los estudios y complicaciones como síncope, mareo en 33,3%.
ConclusiónLa efectividad de respiración glosofaríngea en pacientes con enfermedades neuromusculares y lesión medular está relacionada con aumento de capacidad vital y pico flujo de tos. Se recomienda la realización de estudios con más rigurosidad científica para soportar la validez de estos resultados.
Neuromuscular diseases and spinal cord injuries compromise respiratory muscles and lung function, causing respiratory complications. Acute respiratory failure and chronic respiratory compromise cause high risk of morbidity and mortality. The use of glossopharyngeal respiration has been described to improve pulmonary and respiratory muscle function variables that promote more effective coughing and increased time off mechanical ventilation.
ObjectiveDescribe and present the current evidence of the effectiveness of glossopharyngeal respiration in improving lung and respiratory muscle function in adult and pediatric patients with neuromuscular diseases or spinal cord injury with or without mechanical ventilation.
DesignExploratory review with the PRISMA-ScR methodology. A search was carried out in the PEDro, Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, ScienceDirect, Springer, Medline, Cochrane, SciELO, Lilacs, Google Academic databases, keywords and MeSH terms were used in Spanish, English and Portuguese languages, among the years 2000–2020. The results are presented in a descriptive way.
Results491 studies were identified and 12 were included. 58.3% were conducted in European countries. 41.6% of the studies were critically appraised and none fully met the quality criteria. The effectiveness of glossopharyngeal breathing in lung and respiratory muscle function was related to an improvement in vital capacity in 66.6% and peak cough flow in 33.3% of the studies. Improvement in thoracic expansion was reported in 66.6% of the studies and complications such as syncope, dizziness in 33.3%.
ConclusionThe effectiveness of glossopharyngeal respiration in patients with neuromuscular diseases and spinal cord injury is related to increased vital capacity and peak flow of cough. Studies with more scientific rigor are recommended to support the validity of these results.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".