La medición de la fuerza muscular respiratoria y la movilidad torácica tienen importancia en la evaluación clínica del sistema respiratorio en población pediátrica, sin embargo, sus valores pueden cambiar por las características de la población de cada país. El objetivo del estudio fue describir la fuerza muscular respiratoria y movilidad torácica en niños sanos de Cali, Colombia y analizar la correlación con medidas antropométricas.
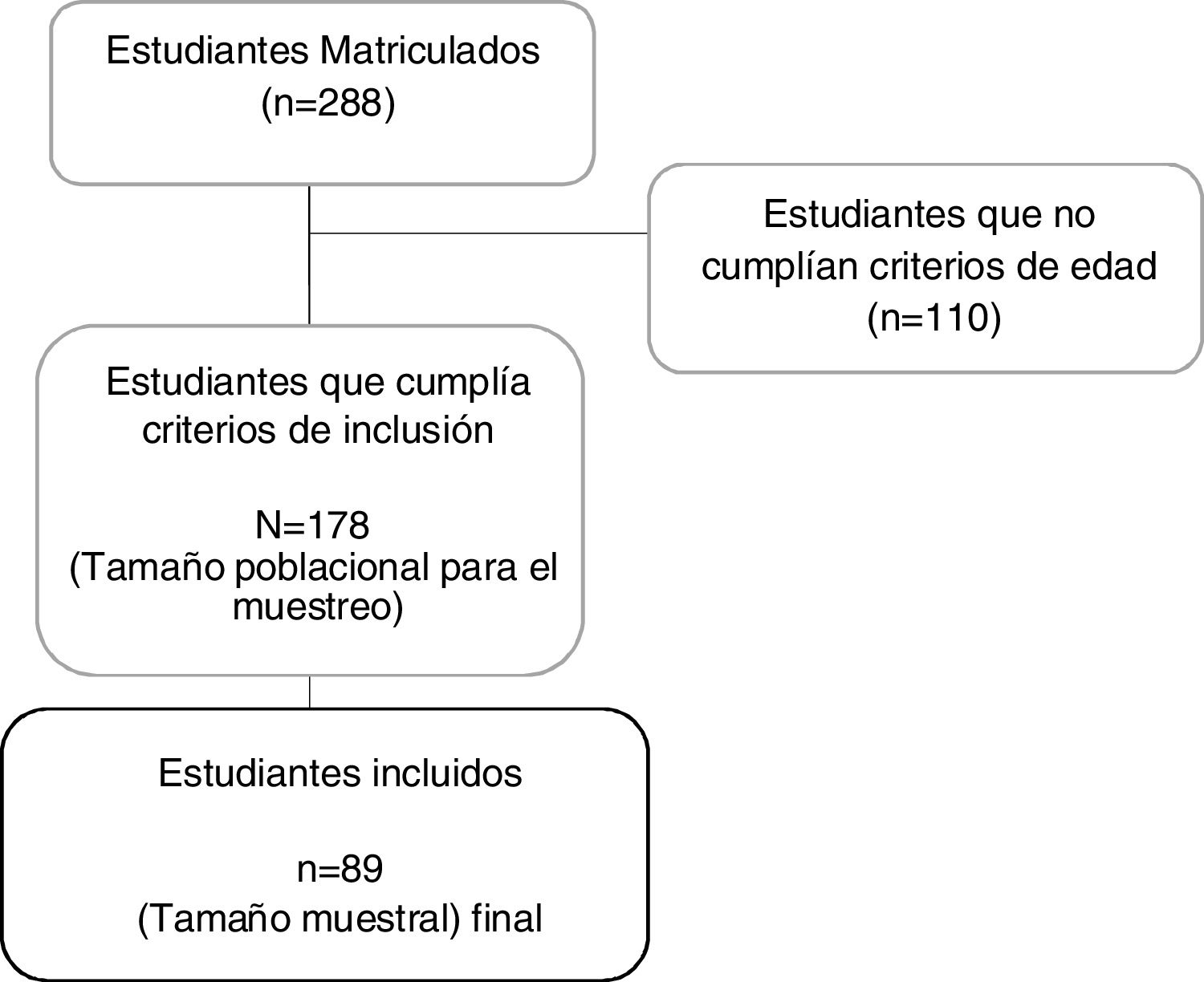
Materiales y métodosEstudio transversal. Se incluyeron niños sanos entre 8 y 11 años de un colegio de Cali, Colombia a quienes se les midió la fuerza muscular respiratoria con la Presión Inspiratoria Máxima (PIM) y Presión Espiratoria Máxima (PEM) y la movilidad torácica con la cirtometría axilar y xifoidea. También se tomaron las medidas antropométricas peso, talla e IMC para la edad.
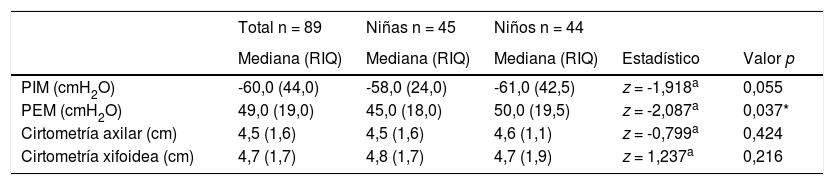
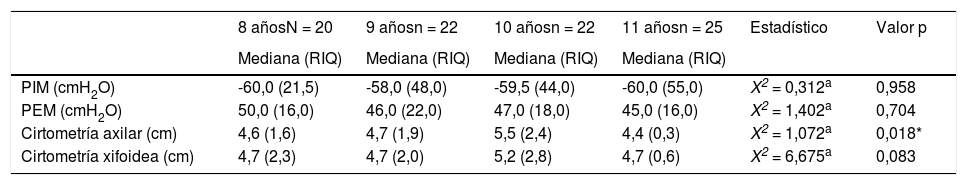
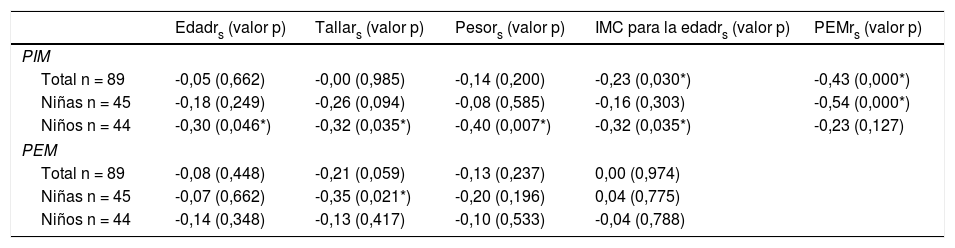
ResultadosSe admitieron 89 niños, un 50,6% de sexo femenino y con IMC en normopeso para la edad del 62,9%. Mediana de PIM -60,0 cmH2O (Rango Intercuartílico [RIQ] 44,0) y PEM 49,0 cmH2O (RIQ 19,0). Mediana de cirtometría axilar 4,5 cm (RIQ 1,6) y xifoidea 4,7 cm (RIQ 1,7). La PIM tuvo correlación con el índice de masa corporal (IMC) para la edad (rs = 0,23 p = 0,030), la cirtometría axilar con el peso (rs = 0,35; p = 0,001) y el IMC para la edad (rs = 0,31; p = 0,003), la cirtometría xifoidea con el peso (rs = 0,24; p = 0,027) y la talla (rs = 0,22; p = 0,037). No hubo correlación entre la PIM-PEM y cirtometría.
DiscusiónLa fuerza muscular respiratoria y la movilidad torácica dependen de los cambios experimentados en el crecimiento del infante y de características diferenciales entre niños y niñas durante la pubertad.
The measurement of respiratory muscle strength and thoracic mobility are important in clinical assessment of the respiratory system in the paediatric population, however, their values can change according to the characteristics of the population of each country. The objective of the study was to describe respiratory muscle strength and thoracic mobility in healthy children from Cali, Colombia, and analyse their correlation with anthropometric measurements.
Materials and MethodsA cross-sectional study. We included healthy children between 8 and 11 years old, from a school in Cali, Colombia, whose respiratory muscle strength was measured with Maximum Inspiratory Pressure (MIP) and Maximum Expiratory Pressure (MEP) and thoracic mobility with axillary and xiphoid cirtometry. Anthropometric measurements were taken, such as weight, height and BMI-for-age.
Results89 children were admitted, most were female (50.6%) and with normal BMI-for-age (62.9%). Median MIP -60.0 cmH2O (IQR 44.0) and MEP 49.0 cmH2O (IQR 19.0). Median axillary cirtometry 4.5 cm (IQR 1.6) and xiphoid cirtometry 4.7 cm (IQR 1.7). MIP correlated with BMI-for-age (rs = 0.23 p = 0.030), axillary cirtometry with weight (rs = 0.35 p = 0.001) and BMI-for-age (rs = 0.31 p = 0.003), xiphoid cirtometry with weight (rs = 0.24 p = 0.027) and height (rs = 0.22 p = 0.037). There was no correlation between MIP-MEP and cirtometry.
DiscussionRespiratory muscle strength and thoracic mobility depend on changes in the growth of the infant and differential characteristics between boys and girls during puberty.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".