La enfermedad pulmonar intersticial difusa (EPID) es un grupo de enfermedades que causan un trastorno de la capacidad aeróbica y calidad de vida, además ocasionan una gran tasa de morbimortalidad para esta población. El uso de oxigenoterapia domiciliaria tiene beneficios que aún no se comparan en programas de rehabilitación pulmonar.
ObjetivoDeterminar los efectos de un programa de rehabilitación pulmonar en la capacidad funcional y calidad de vida relacionada con la salud en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar intersticial difusa con y sin uso de oxígeno domiciliario.
Materiales y métodosEstudio cuasiexperimental en el que todos los pacientes, por conveniencia, firmaron el consentimiento informado. Se dividieron en 2 grupos: con y sin oxígeno domiciliario, evaluados antes y después de la rehabilitación pulmonar en variables clínicas, capacidad funcional y calidad de vida.
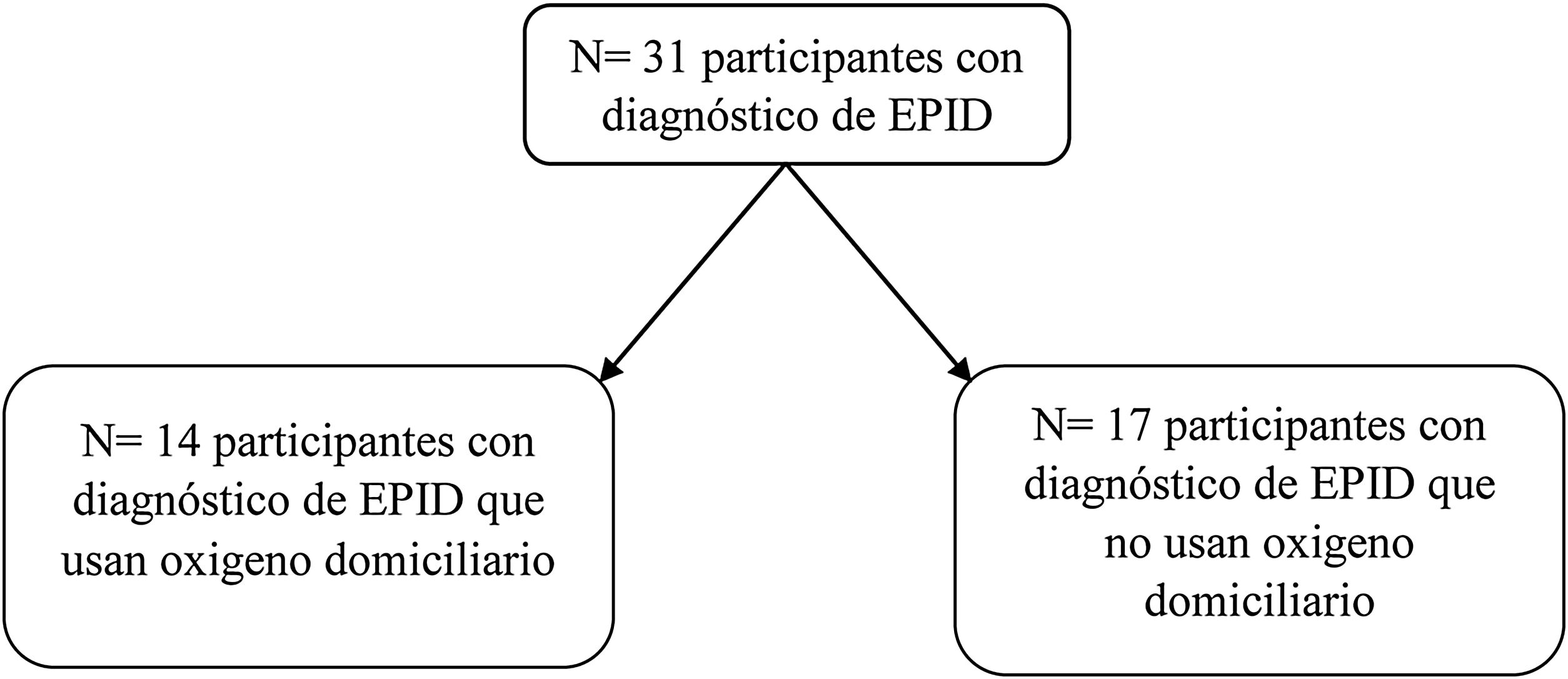
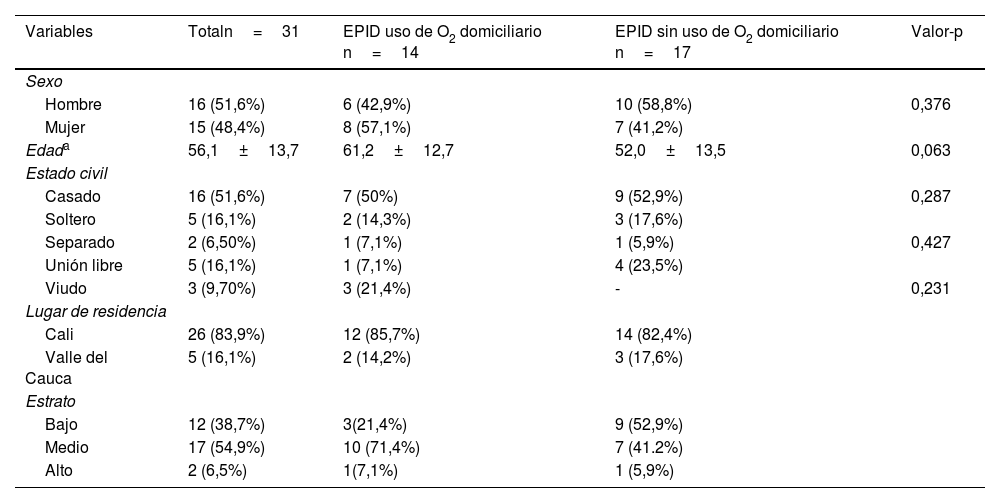
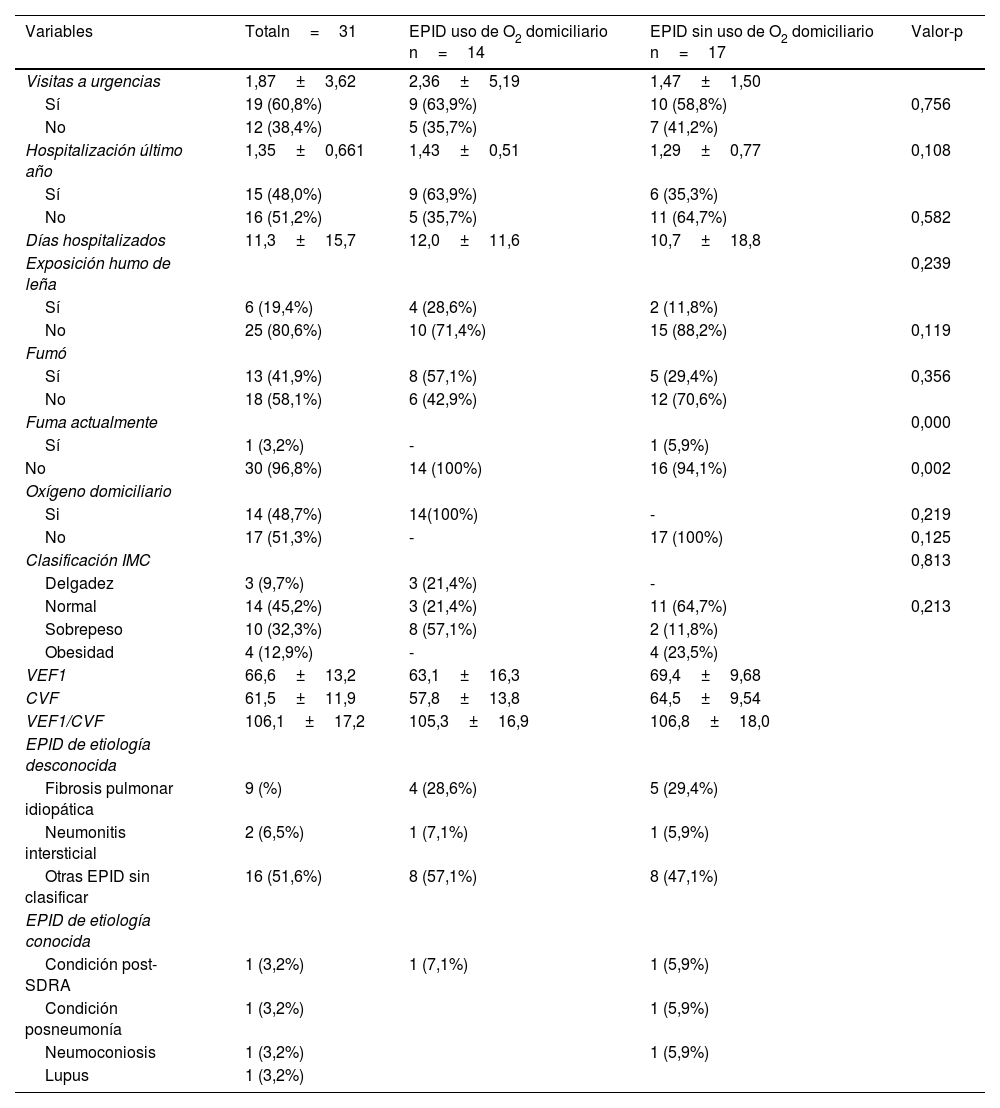
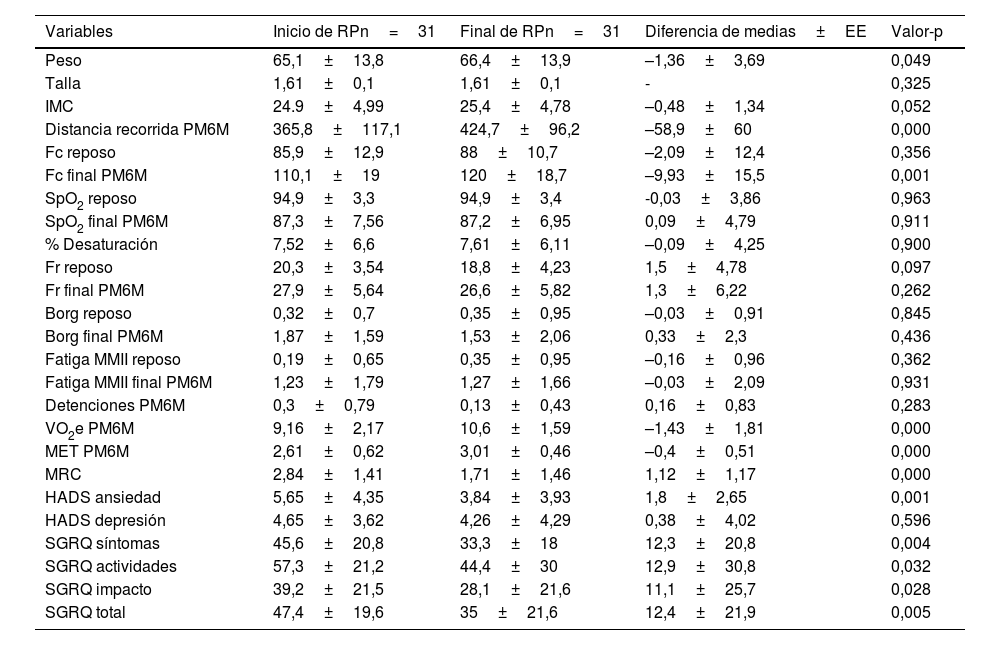
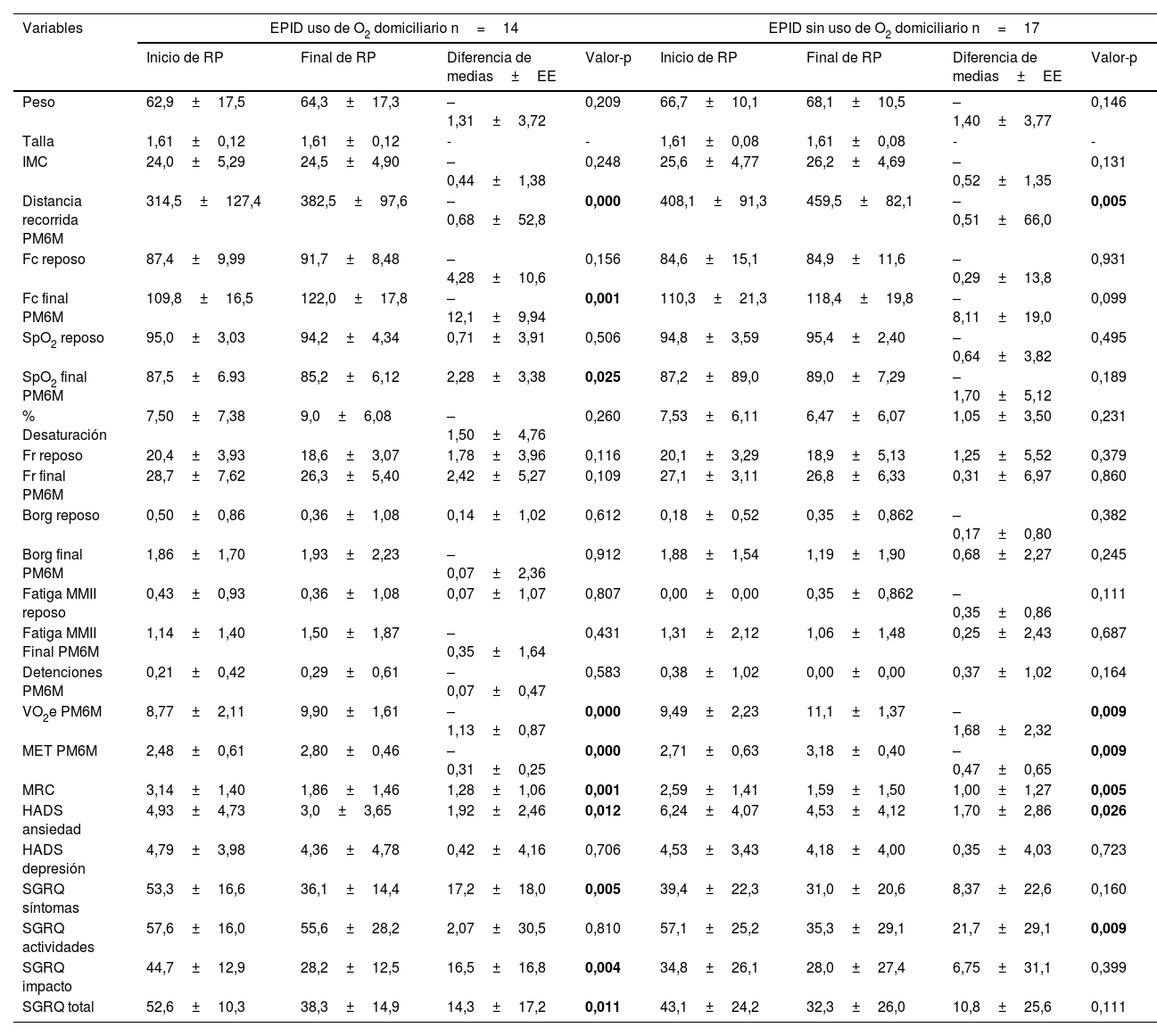
ResultadosSe vincularon 31 pacientes que se dividieron en 2 grupos con oxígeno y sin oxígeno domiciliario, la mayor participación fue de hombres, edad promedio de 56 años, y se obtuvo que la mayoría había acudido a urgencias. Ambos grupos presentaron mejorías en la distancia recorrida y en la ansiedad: valor-p<0,05. La calidad de vida presentó mejorías significativas por dominio en ambos grupos: valor-p<0,05.
ConclusiónEl grupo de EPID con uso de oxígeno domiciliario presenta mayores cambios en la capacidad funcional. En cuanto a la calidad de vida el grupo EPID sin uso de oxígeno domiciliario mejoró significativamente el dominio actividades del SGRQ, y el grupo EPID con uso de oxígeno domiciliario presentó mejoría en los dominios síntomas e impacto.
Diffuse Interstitial Pulmonary Disease is a group of diseases that cause a disorder of aerobic capacity and quality of life, also cause a high rate of morbidity and mortality for this population. The use of home oxygen therapy has benefits that have not yet been compared in pulmonary rehabilitation programs.
ObjectiveTo determine the effects of a pulmonary rehabilitation program on functional capacity and health-related quality of life in patients with diffuse interstitial lung disease with and without the use of home oxygen.
Materials and methodsQuasi-experimental study, all patients for convenience who signed the informed consent. They were divided into two groups: with and without home oxygen, evaluated before and after pulmonary rehabilitation in clinical variables, functional capacity and quality of life.
Results31 patients were linked, divided into two groups with oxygen and without home oxygen, the largest participation was men, average age 56 years, it was obtained that the majority had gone to the emergency room. Both groups presented improvements in the distance traveled and in anxiety p-value≤0.05. The quality of life presented significant improvements by domain in both groups p-value≤0.05.
ConclusionThe ILD group with home oxygen use presents greater changes in functional capacity. Regarding quality of life, the ILD group without home oxygen use significantly improved the activities domain of the SGRQ and the ILD group with home oxygen use showed improvement in the symptoms and impact domains.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".