Los pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES) enfrentan barreras que limitan su actividad física (AF) y pueden afectar su salud física y mental. Este estudio investigó el impacto de una intervención telemática educativa en la AF y factores relacionados entre adolescentes y jóvenes con LES.
MétodoSe utilizó un diseño pretest-postest en un grupo con 12 participantes. Se evaluaron múltiples aspectos, como la frecuencia, intensidad y duración de la AF, intención de realizar AF, calidad de vida y creencias de salud.
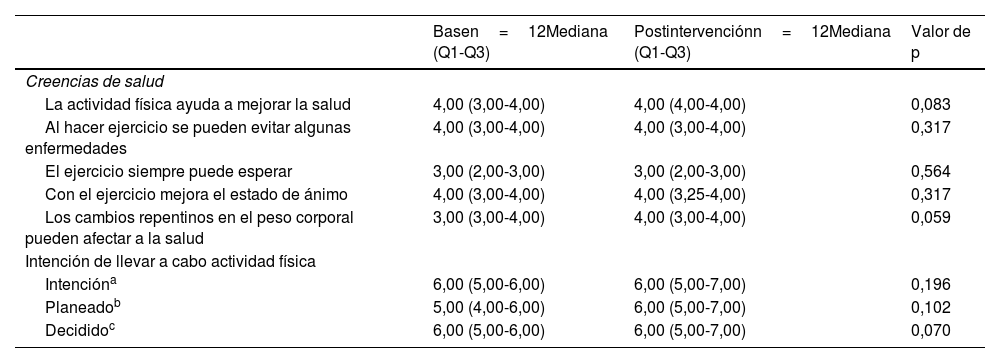
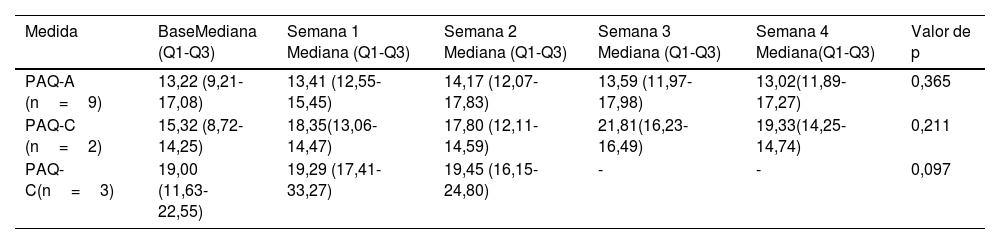
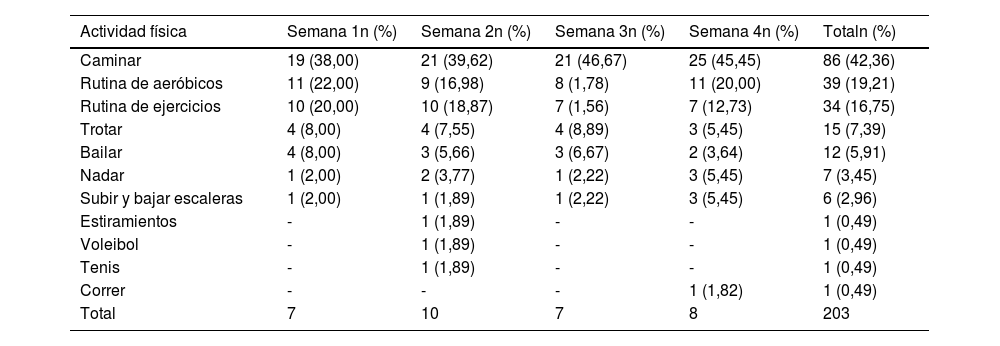
ResultadosDoce adolescentes de género femenino, entre 13 a 20 años (x̅=17,08) participaron del estudio. Se identificaron 12 afecciones concurrentes, como ansiedad (19,44%), artritis (13,89%) e hipertensión (13,89%). Hubo un aumento significativo en la calidad de vida evaluada mediante el Peds-QL-RM desde el inicio hasta la cuarta semana de seguimiento, con un aumento en la mediana de 45,39 (p=0,008). No se identificaron cambios significativos en el nivel de AF (PAQ-A y PAQ-C) ni en la intención de realizar AF. Las actividades físicas más frecuentemente reportadas tras 4 semanas post-intervención fueron caminar (42,36%), rutina de aeróbicos (19,21%) y rutina de ejercicios (16,75%).
ConclusiónLa intervención educativa de múltiples componentes, con un enfoque informativo y socioconductual, implementada en un entorno comunitario, mejoró la calidad de vida en adolescentes y jóvenes con LES. Estos hallazgos respaldan la importancia de abordar la falta de AF en esta población y subrayan la necesidad de desarrollar programas de intervención específicos para mejorar la salud y el bienestar de los pacientes con LES.
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) face barriers that limit their physical activity (PA) and can affect their physical and mental health. This study investigated the impact of a telematic educational intervention on PA and related factors, among adolescents and young people with SLE.
MethodA pretest–posttest design was used in a group with 12 participants. Multiple aspects were evaluated, such as the frequency, intensity and duration of PA, intention to perform PA, quality of life and health beliefs.
ResultsTwelve female adolescents between 13 and 20 years old (x̅=17.08) participated in the study. Twelve concurrent conditions were identified, including anxiety (19.44%), arthritis (13.89%), and hypertension (13.89%). There was a significant increase in quality of life assessed by the Peds-QL-RM from baseline to the fourth week of follow-up, with an increase in median of 45.39 (p=0.008). No significant changes were identified in the level of PA (PAQ-A and PAQ-C) or in the intention to perform PA. The most frequently reported physical activities after four weeks post-intervention were walking (42.36%), aerobics routine (19.21%) and exercise routine (16.75%).
ConclusionThe multi-component educational intervention, with an informational and socio-behavioral approach, implemented in a community setting improved the quality of life in adolescents and young people with SLE. These findings support the importance of addressing the lack of PA in this population and underscore the need to develop specific intervention programs to improve the health and well-being of patients with SLE.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".