The gut-brain axis describes a complex bidirectional association between neurological and gastrointestinal (GI) disorders. In patients with migraine, GI comorbidities are common. We aimed to evaluate the presence of migraine among patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) according to Migraine Screen-Questionnaire (MS-Q) and describe the headache characteristics compared to a control group. Additionally, we explored the relationship between migraine and IBD severities.
MethodsWe performed a cross-sectional study through an online survey including patients from the IBD Unit at our tertiary hospital. Clinical and demographic variables were collected. MS-Q was used for migraine evaluation. Headache disability scale HIT-6, anxiety-depression scale HADS, sleep scale ISI, and activity scale Harvey–Bradshaw and Partial Mayo scores were also included.
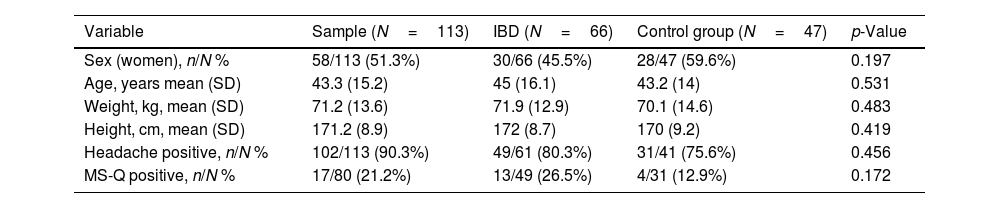
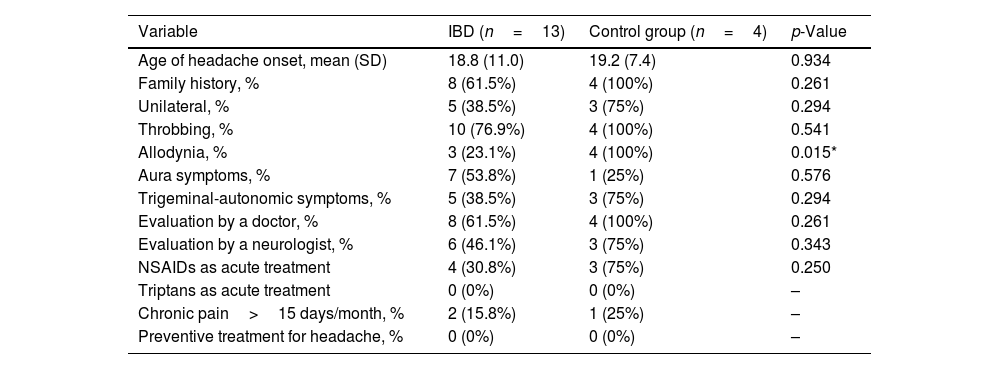
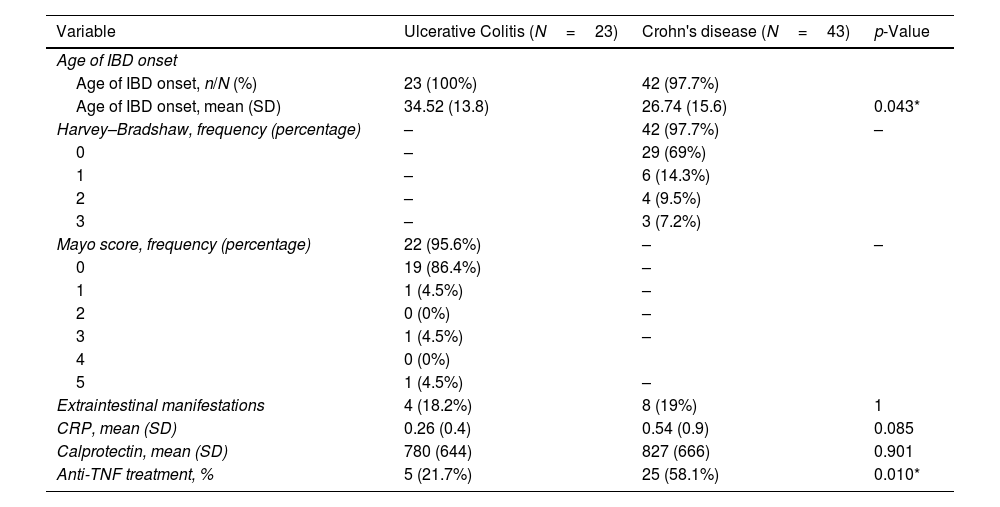
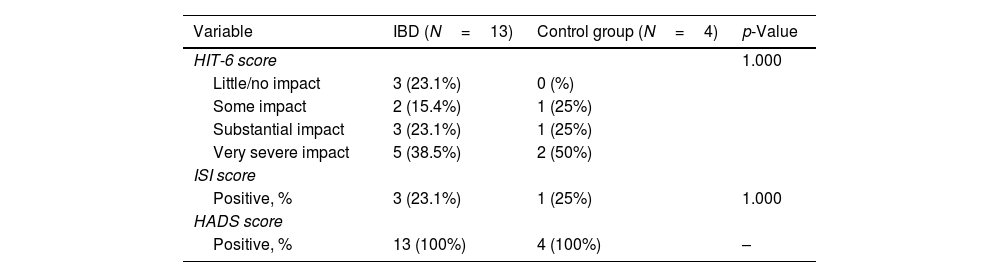
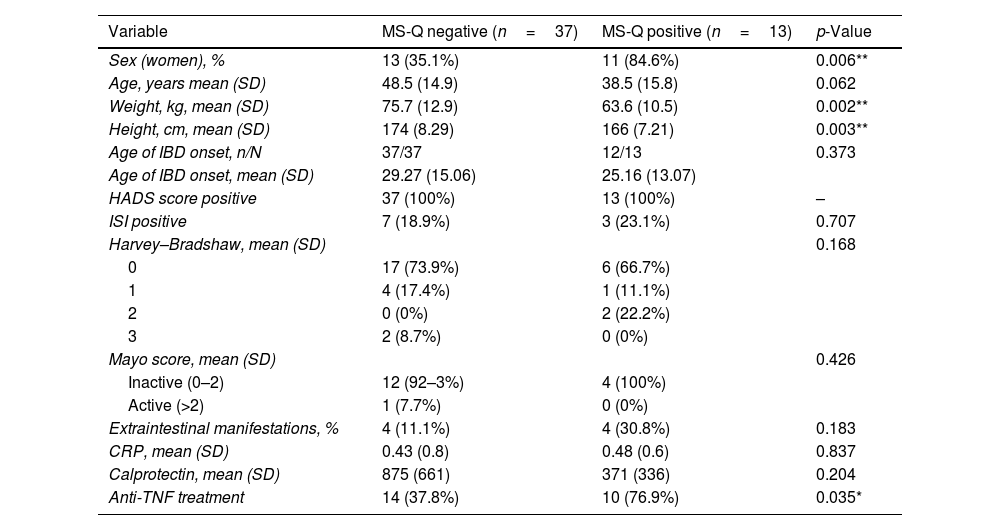
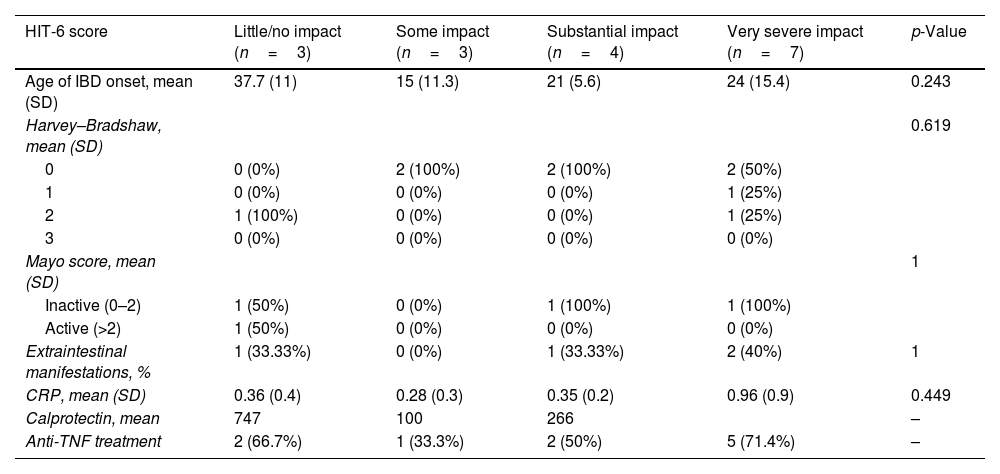
ResultsWe evaluated 66 IBD patients and 47 controls. Among IBD patients, 28/66 (42%) were women, mean age 42 years and 23/66 (34.84%) had ulcerative colitis. MS-Q was positive in 13/49 (26.5%) of IBD patients and 4/31 (12.91%) controls (p=0.172). Among IBD patients, headache was unilateral in 5/13 (38%) and throbbing in 10/13 (77%). Migraine was associated with female sex (p=0.006), lower height (p=0.003) and weight (p=0.002), anti-TNF treatment (p=0.035). We did not find any association between HIT-6 and IBD activity scales scores.
ConclusionsMigraine presence according to MS-Q could be higher in patients with IBD than controls. We recommend migraine screening in these patients, especially in female patients with lower height and weight and anti-TNF treatment.
El eje intestino-cerebro describe una asociación bidireccional compleja entre las enfermedades neurológicas y gastrointestinales (GI). Las comorbilidades GI son frecuentes en la migraña. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar la presencia de migraña en pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII) y describir las características de la cefalea. Además, analizamos la relación entre la gravedad de la migraña y la EII.
MétodosEstudio transversal a través de encuesta electrónica en pacientes con EII de un hospital terciario. Se recogieron variables clínicas y demográficas. Se usó MS-Q para presencia de migraña. Se incluyeron escala de discapacidad de cefalea HIT-6, ansiedad-depresión HADS, sueño ISI y actividad de EII Harvey-Bradshaw y Partial Mayo.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 66EII y 47controles. Entre los EII, 28/66 (42%) eran mujeres, con una edad media de 42años, y 23/66 (34,84%) tenían colitis ulcerosa. El MS-Q fue positivo en 13/49 (26,5%) de EII y en 4/31 (12,91%) controles (p=0,172). Entre los pacientes con EII, la cefalea fue unilateral en 5/13 (38%) y pulsátil en 10/13 (77%). El sexo femenino (p=0.006), la altura (p=0,003) y el peso más bajos (p=0,002) y el tratamiento con anti-TNF (p=0,035) se relacionaron con la probabilidad de migraña. No encontramos asociación entre el HIT-6 y las escalas de actividad de EII.
ConclusionesLa presencia de migraña de acuerdo al MS-Q podría ser más alta en los pacientes con EII que en controles. Recomendamos realizar un cribado de migraña en estos pacientes, especialmente en mujeres de menor peso y altura y tratamiento anti-TNF.