En la actualidad hay información escasa en Latinoamérica sobre el resultado clínico y la evolución manométrica de los pacientes con acalasia sometidos a miotomía endoscópica peroral (POEM).
ObjetivoEvaluar los cambios manométricos y clínicos en pacientes adultos con acalasia posterior a la realización del POEM en un centro de referencia de Bogotá, Colombia.
MétodosEstudio observacional, analítico y longitudinal. Se incluyeron sujetos adultos con acalasia según los criterios Chicago 4,0. Se describieron las variables sociodemográficas, clínicas y manométricas. Para comparar las pre y posquirúrgicas se utilizó la prueba de t de Student o Wilcoxon para las cuantitativas de acuerdo con su normalidad, y X2 McNemar para las cualitativas.
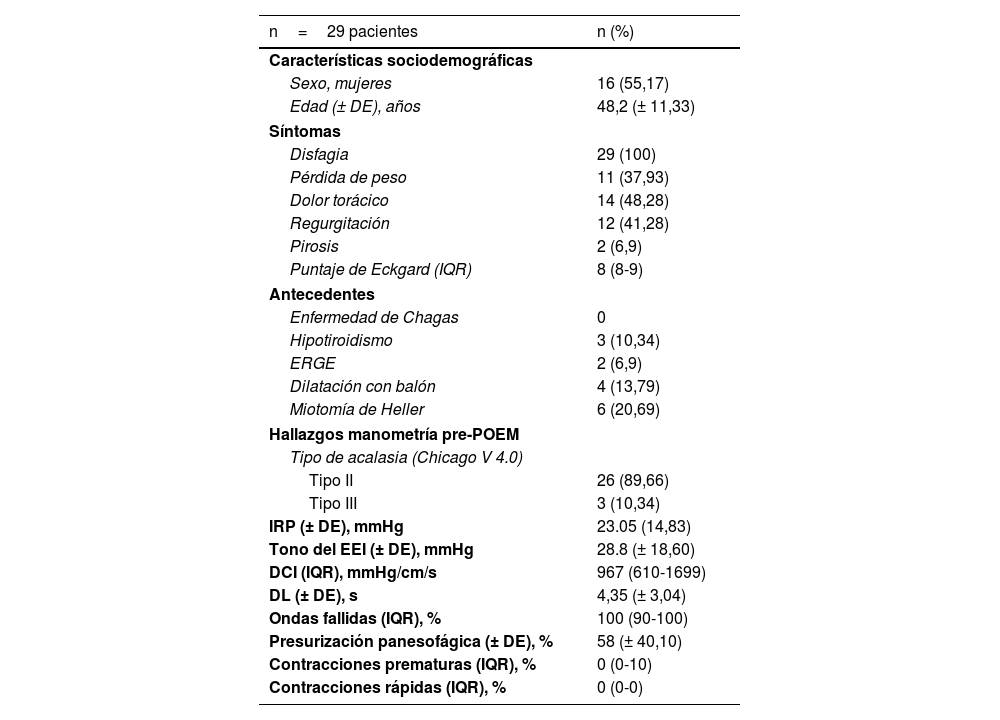
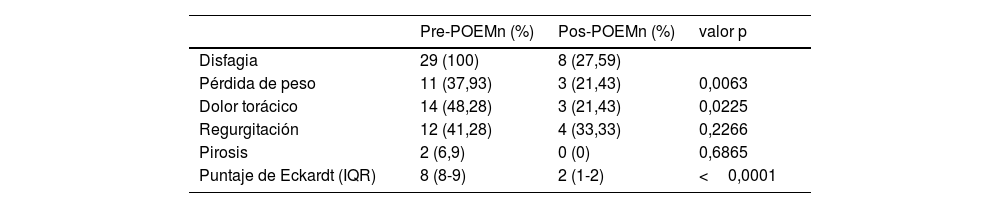
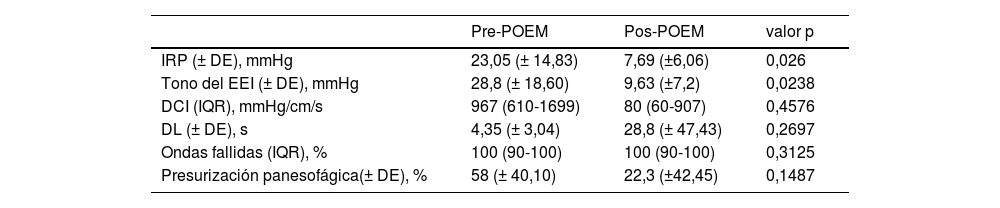
ResultadosSe incluyeron 29 pacientes, 55,17% (n=16) mujeres, con una media de edad al momento de cirugía de 48,2 años (± 11,33). El promedio de tiempo de evaluación posterior al procedimiento fue de 1,88± 0,81 años. Después de realizado este, se evidenció una disminución significativa en la proporción de sujetos con pérdida de peso (37,93 vs. 2,43% p = 0,0063), dolor torácico (48,28 vs. 21,43, p = 0,0225) y la mediana del puntaje de Eckardt: 8 (rango intercuartílico [IQR] 8-9 vs. 2 [IQR 1-2]), p <0,0001. Además, en 14 pacientes con manometría posquirúrgica se encontraron diferencias significativas entre los valores de presión integrada de relajación (IRP) (23,05±14,83mmHg vs. 7,69±6,06mmHg, p = 0,026) y en la media del tono del esfínter esofágico inferior (EEI) (9,63±7,2mmHg vs. 28,8±18,60mmHg, p = 0,0238).
ConclusiónLa POEM impacta positivamente en el mejoramiento de la sintomatología y de algunas variables manométricas (IRP y EEI) en los pacientes con acalasia.
Currently there is little information in Latin America on the clinical outcome and manometric evolution of patients with Achalasia undergoing peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM).
Primary outcomeEvaluate the manometric and clinical changes in adult patients with achalasia after peroral endoscopic myotomy at a referral center in Bogotá, Colombia.
MethodsObservational, analytical, longitudinal study. Adult patients with achalasia according to the Chicago 4.0 criteria were included. Sociodemographic, clinical and manometric variables were described. To compare the pre- and post-surgical variables, the Student's or Wilcoxon's t test was used for the quantitative variables according to their normality, and McNemar's chi-square for the qualitative variables.
Results29 patients were included, 55.17% (n=16) women, with a mean age at the time of surgery of 48.2 years (±11.33). The mean post-procedure evaluation time was 1.88±0.81 years. After the procedure, there was a significant decrease in the proportion of patients with weight loss (37.93% vs 21.43% p 0.0063), chest pain (48.28% vs 21.43, p 0.0225) and the median Eckardt score (8 (IQR 8 -9) vs 2(IQR 1-2), p <0.0001). In addition, in fourteen patients with post-surgical manometry, significant differences were found between IRP values (23.05±14.83mmHg vs 7.69±6.06mmHg, p 0.026) and in the mean lower esophageal sphincter tone (9.63±7.2mmHg vs 28.8±18.60mmHg, p 0.0238).
ConclusionPeroral endoscopic myotomy has a positive impact on the improvement of symptoms and of some manometric variables (IRP and LES tone) in patients with achalasia.