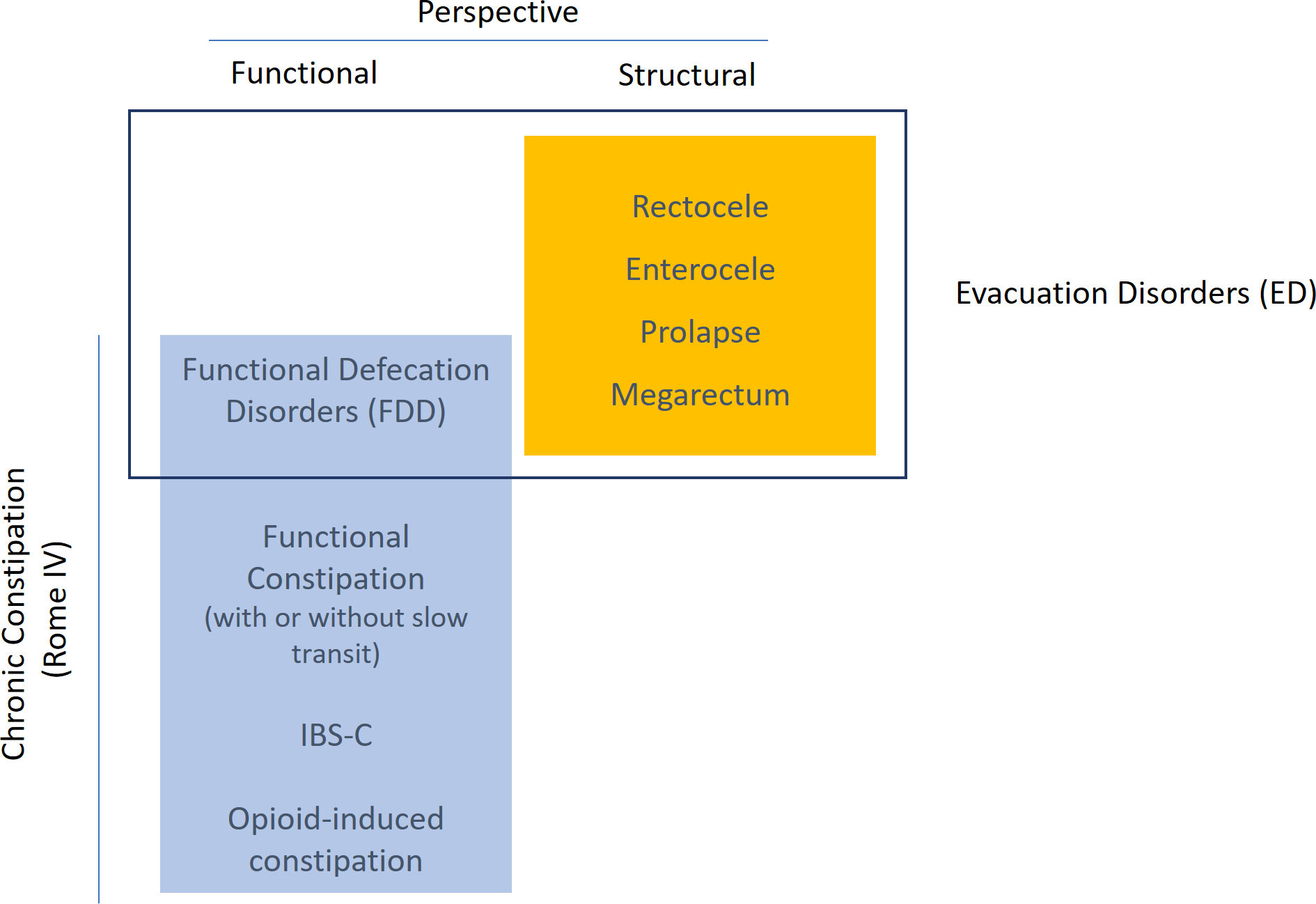
Defecation disorders can occur as a consequence of functional or structural anorectal dysfunctions during voiding. The aims of this study is to assess the prevalence of structural (SDD) vs functional (FDD) defecation disorders among patients with clinical complaints of obstructive defecation (OD) and their relationship with patients’ expulsive capacity.
Patients and methodsRetrospective study of 588 patients with OD studied between 2012 and 2020 with evacuation defecography (ED), and anorectal manometry (ARM) in a subgroup of 294.
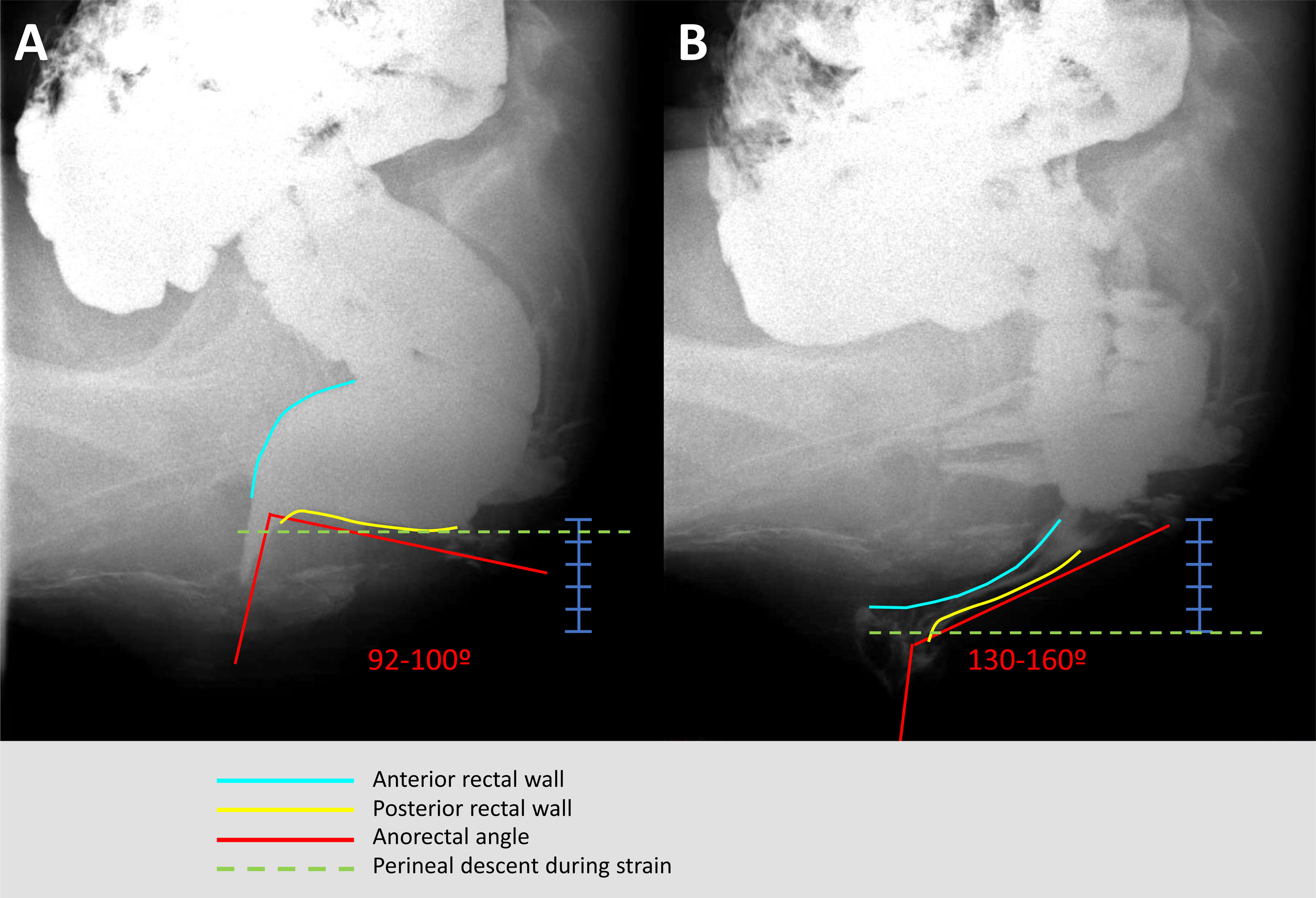
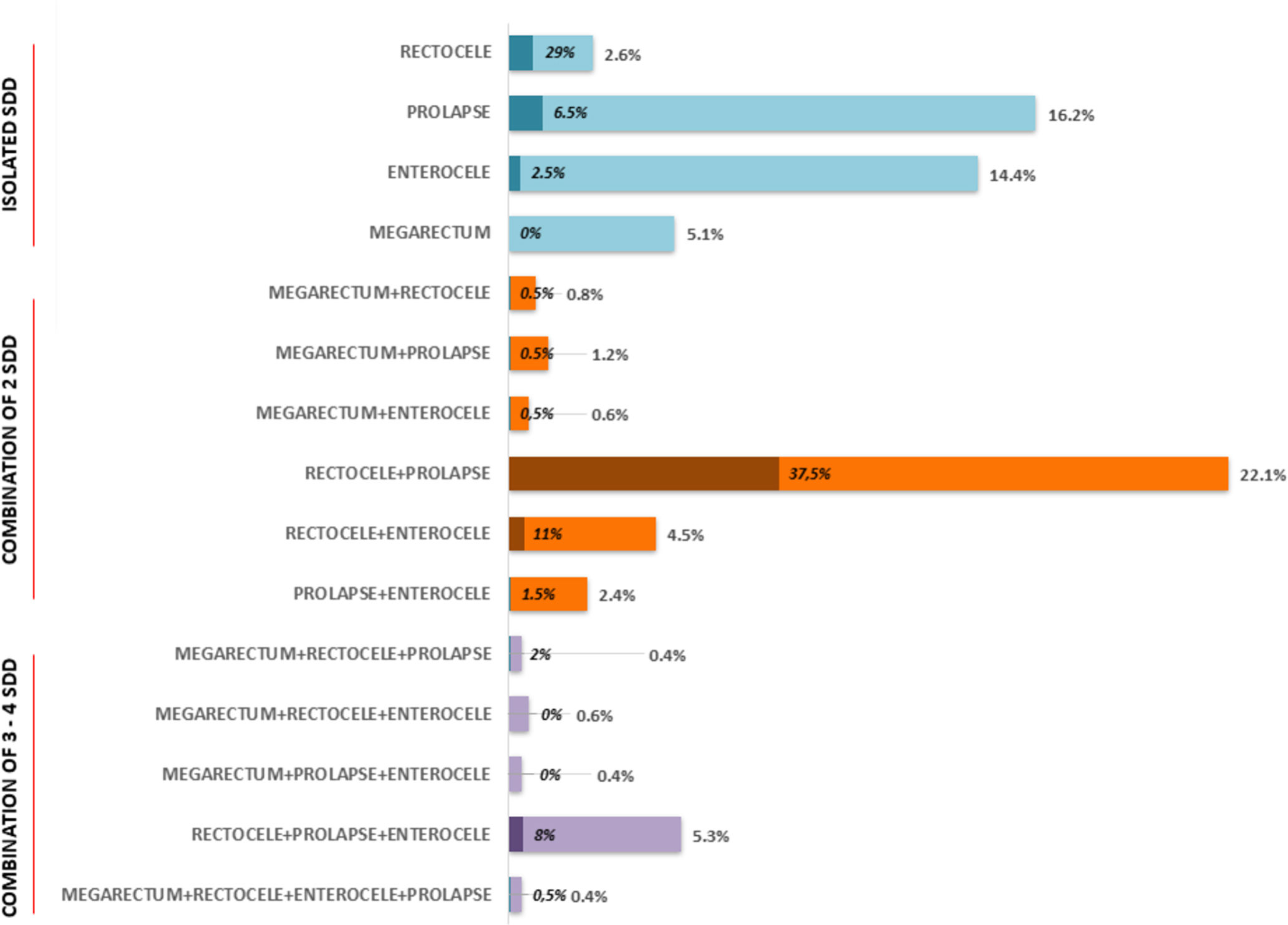
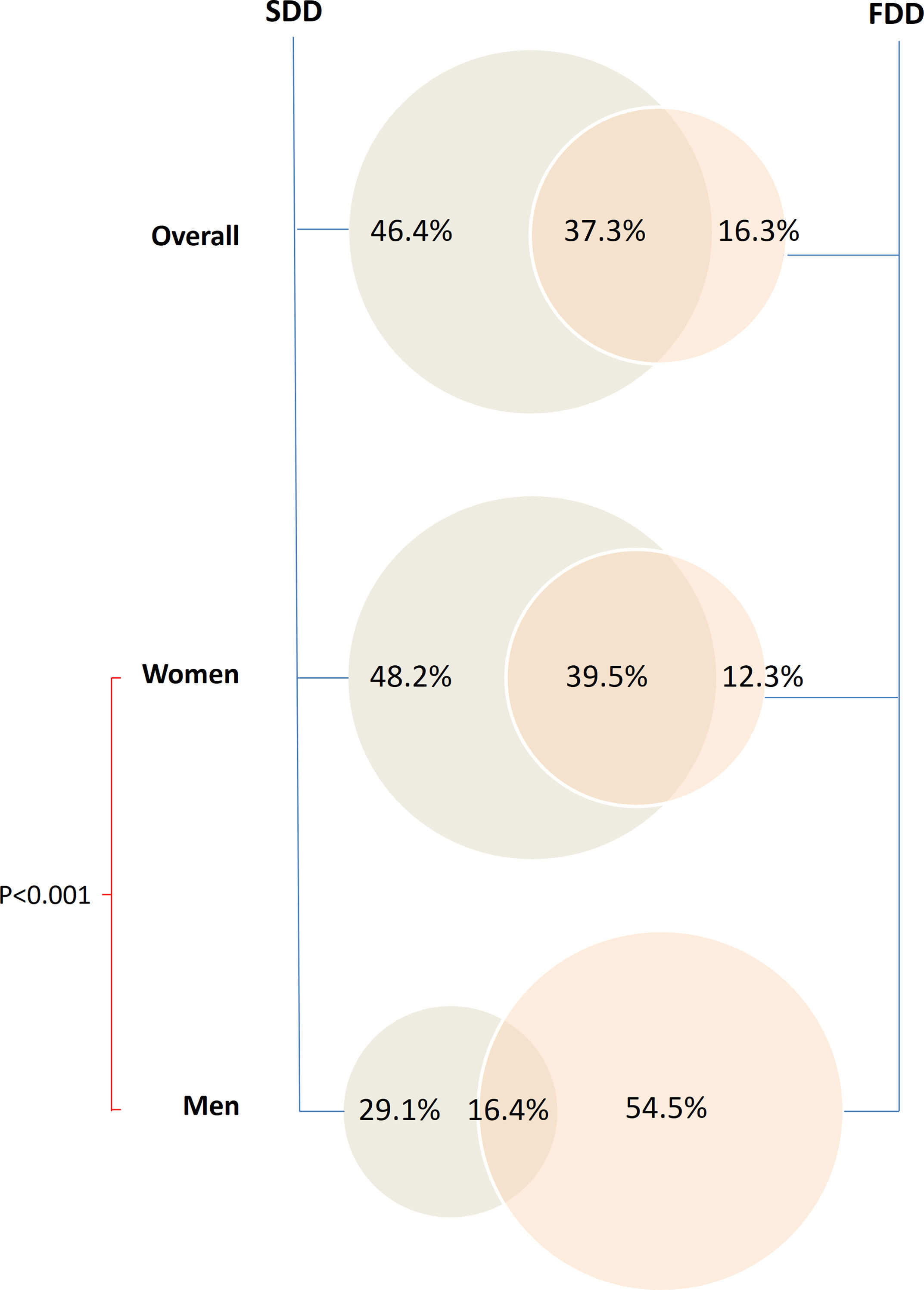
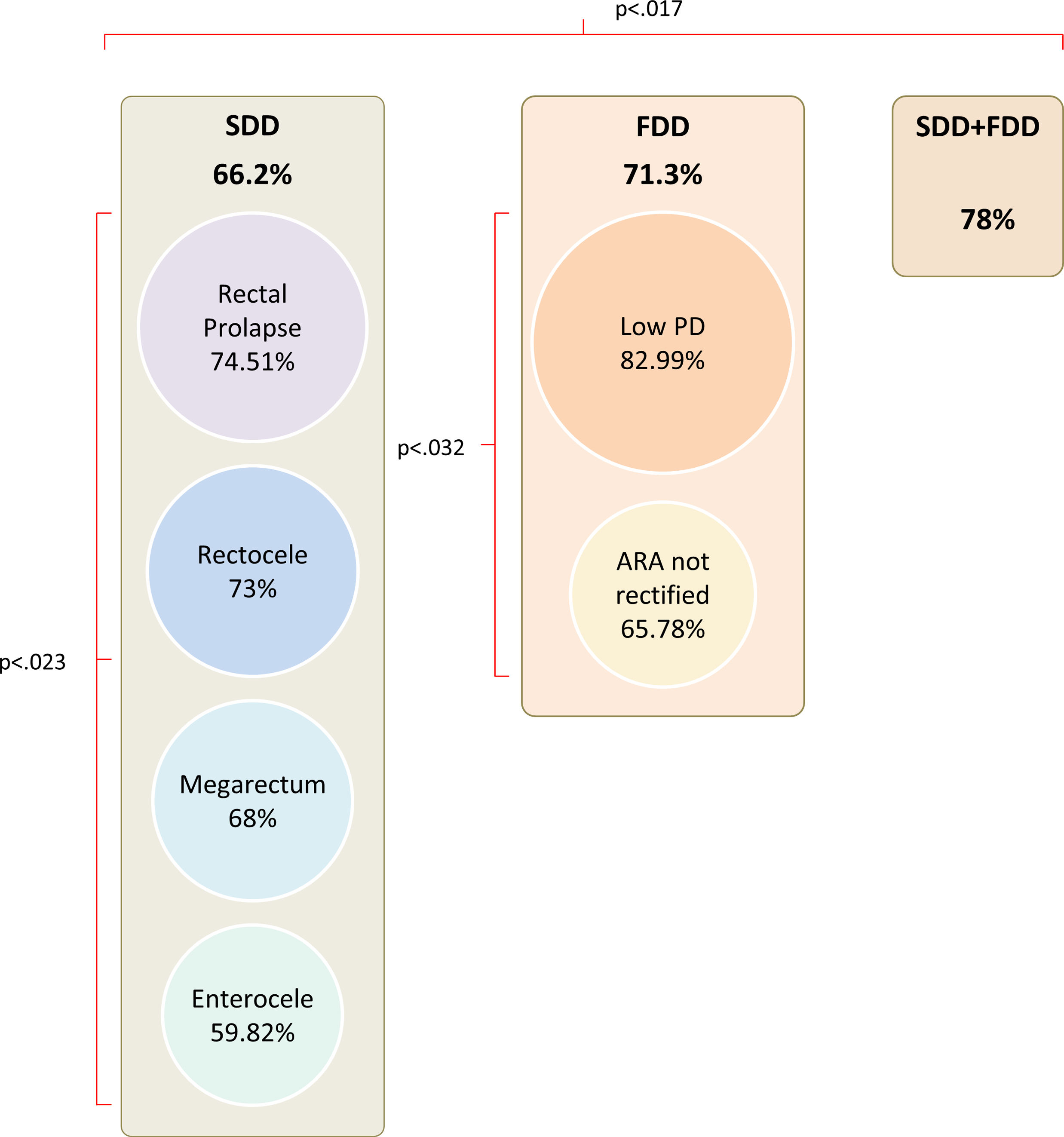
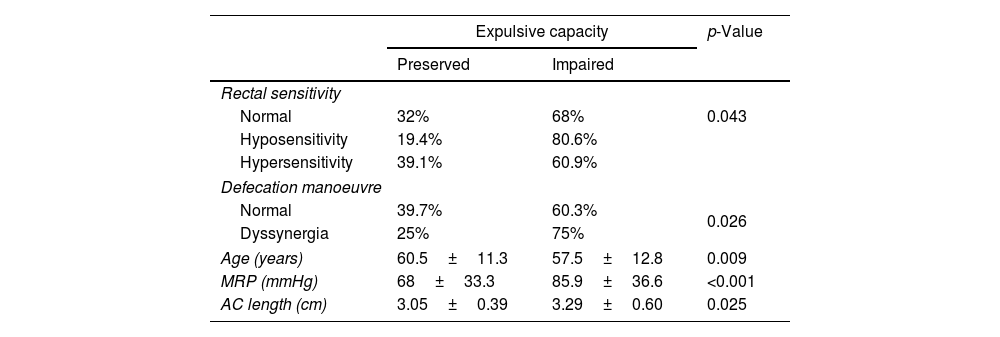
Results90.3% patients were women, age was 58.5±12.4 years. Most (83.7%) had SDD (43.7% rectocele, 45.3% prolapse, 19.3% enterocele, and 8.5% megarectum), all SDD being more prevalent in women except for megarectum. Functional assessments showed: (a) absence of rectification of anorectal angle in 51% of patients and poor pelvic descent in 31.6% at ED and (b) dyssynergic defecation in 89.9%, hypertonic IAS in 44%, and 33.3% rectal hyposensitivity, at ARM. Overall, 46.4% of patients were categorized as pure SDD, 37.3% a combination of SDD+FDD, and 16.3% as having pure FDD.
Rectal emptying was impaired in 66.2% of SDD, 71.3% of FDD and in 78% of patients with both (p=0.017).
ConclusionsThere was a high prevalence of SDD in middle-aged women with complaints of OD. Incomplete rectal emptying was more prevalent in FDD than in SDD although FDD and SDD frequently coexist. We recommend a stepwise therapeutic approach always starting with therapy directed to improve FDD and relaxation of striated pelvic floor muscles.
Los trastornos defecatorios ocurren como consecuencia de disfunciones anorrectales funcionales o estructurales. El objetivo del estudio es evaluar la prevalencia de trastornos estructurales defecatorios (TED) versus funcionales (TFD) entre pacientes con síntomas de defecación obstructiva (DO) y su relación con la capacidad expulsiva.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio retrospectivo con 588 pacientes con DO estudiados entre 2012 y 2020 con videodefecografía (VD), y manometría anorrectal (MAR) en un subgrupo de 294.
ResultadosEl 90,3% de los pacientes eran mujeres, con 58,5±12,4 años. La mayoría (83,7%) presentaban TED (43,7% rectocele, 45,3% prolapso, 19,3% enterocele y 8,5% megarrecto), siendo más prevalentes en mujeres excepto el megarrecto. Evaluación funcional: a) VD: ausencia de rectificación del ángulo anorrectal en el 51% de los pacientes y escaso o nulo descenso perineal en el 31,6; y b) MAR: defecación disinérgica en el 89,9%, EAI hipertónico en el 44% e hiposensibilidad rectal en el 33,3%. En conjunto, el 46,4% de los pacientes se clasificaron como SDD puro, el 37,3% TED+TFD y el 16,3% como TFD puro. La capacidad expulsiva estaba afectada en el 66,2% de los TED, el 71,3% de los TFD y en el 78% de los pacientes con ambos trastornos (p=0,017).
ConclusionesHubo una alta prevalencia de TED en mujeres con síntomas de DO. El vaciamiento rectal incompleto era más prevalente en los pacientes con TFD que en aquellos con TED, pero más cuando ambos coexistían. Recomendamos un enfoque terapéutico empezando siempre con terapia dirigida a mejorar el TFD y la relajación de los músculos estriados del suelo pélvico.