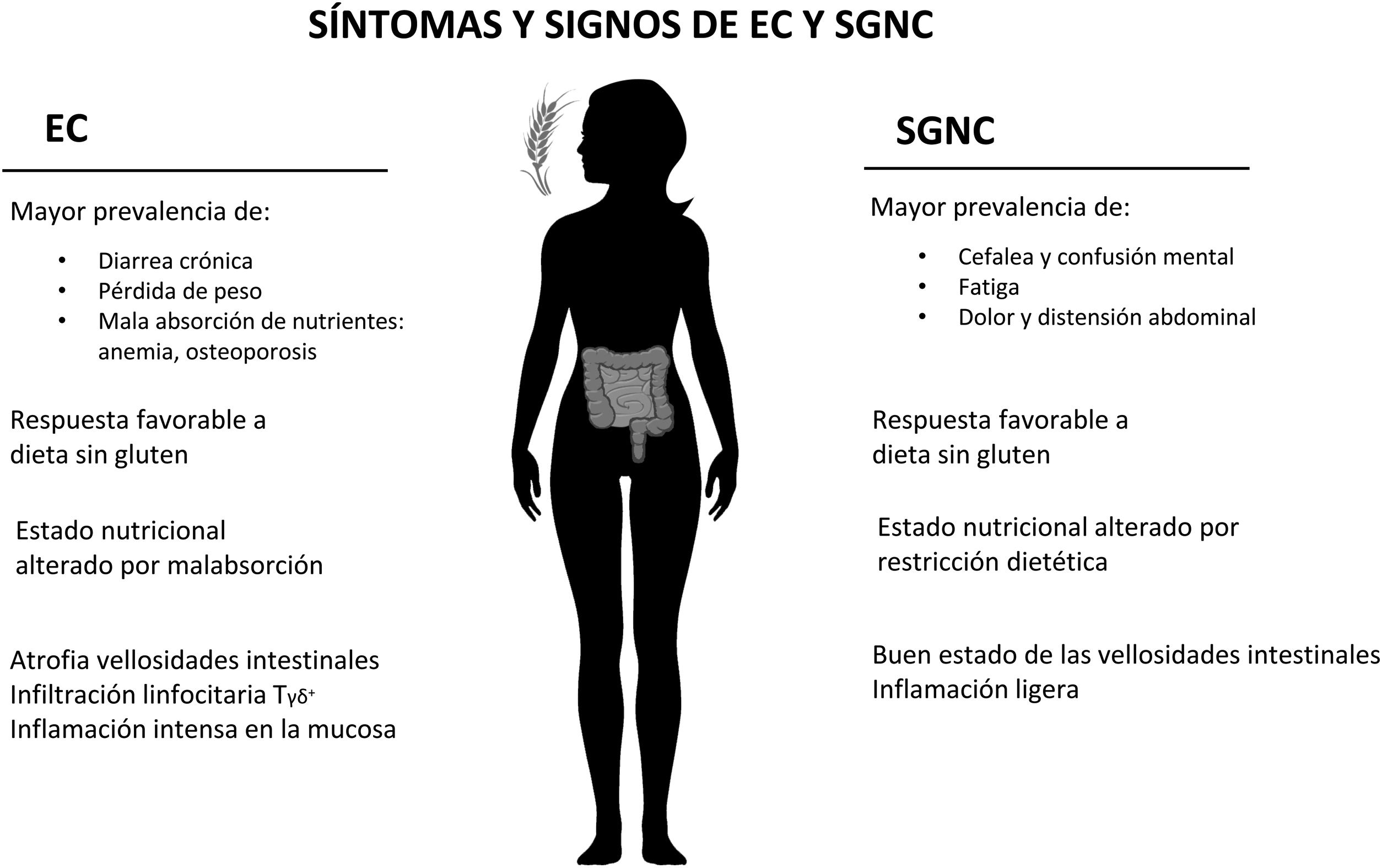
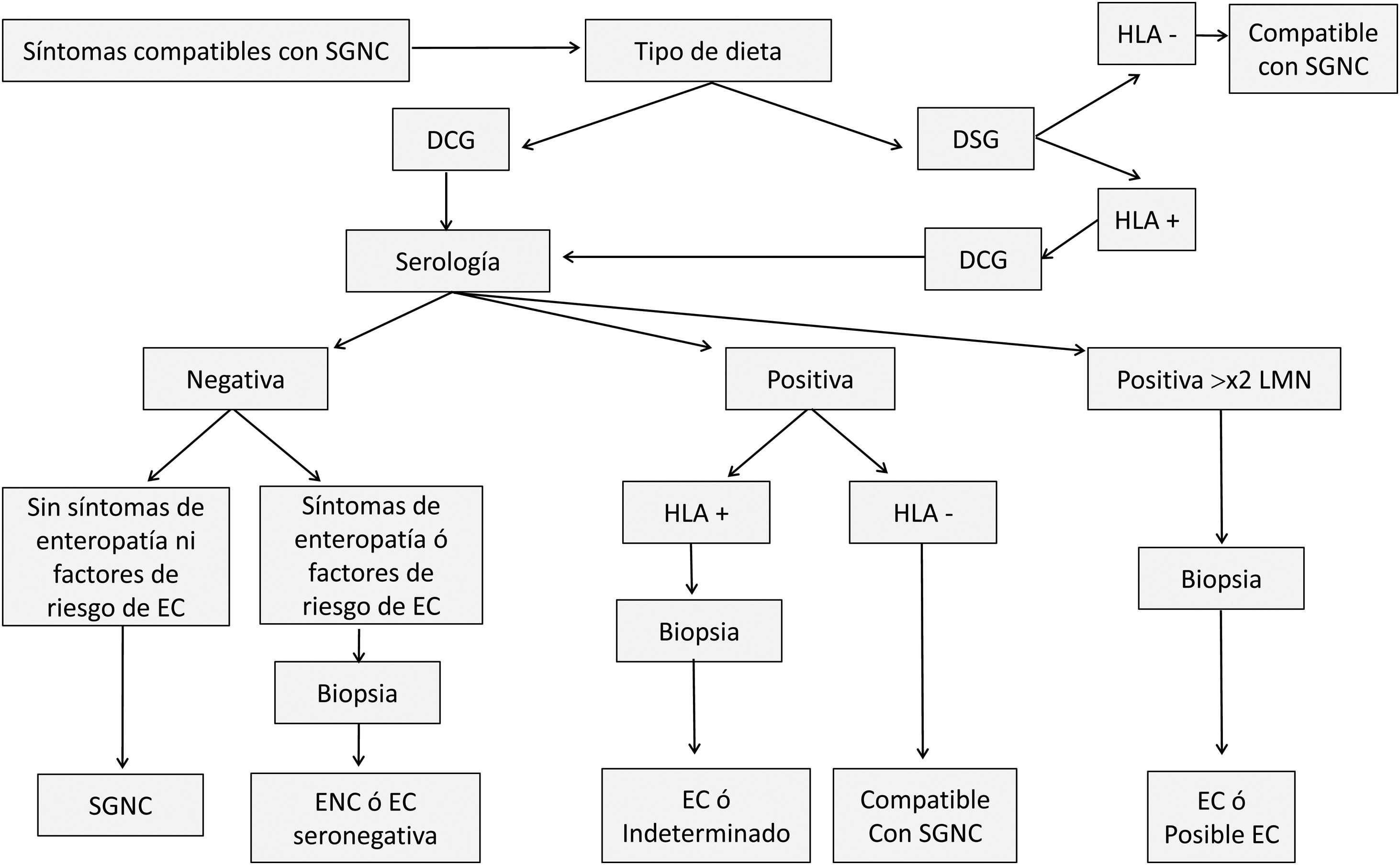
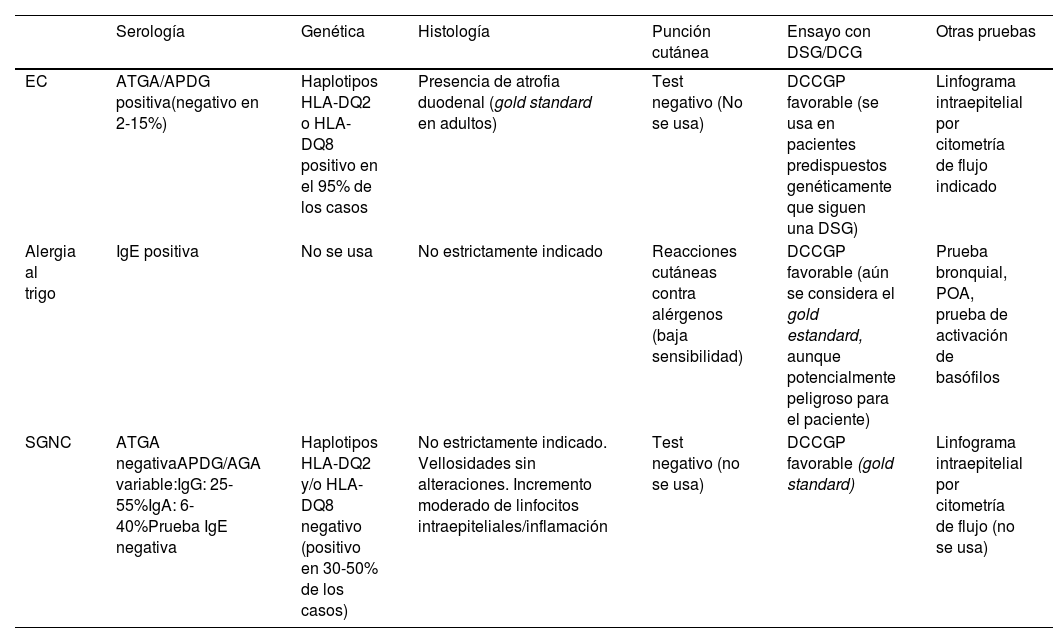
La sensibilidad al gluten no celiaca (SGNC) es la última enfermedad incorporada al grupo de trastornos relacionados con el gluten. Esta revisión aborda la evidencia sobre su etiología, diagnóstico diferencial y sintomatología. Aunque la SGNC se define por una reacción al gluten, se han descrito otros posibles mecanismos etiopatogénicos, como una respuesta inadecuada a otros componentes del trigo o a los FODMAP, extendiéndose últimamente el término sensibilidad al trigo no celiaca. Existen resultados contradictorios sobre la validez del protocolo diagnóstico de los expertos de Salerno. La evidencia sobre biomarcadores diagnóstico para la SGNC escasea, aunque algunos estudios señalan los siguientes: anticuerpos antigliadina, zonulina, prueba ALCAT, micro-ARN, incARN y ciertas citoquinas. En la SGNC, el dolor abdominal y la fatiga son los síntomas más comunes. Además, es frecuente la alteración del estado nutricional. En conclusión, se necesita más investigación sobre la SGNC para mejorar nuestro conocimiento de su etiopatogenia y clínica.
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) is the latest pathology incorporated into the group of gluten-related disorders. This review addresses the evidence on its etiology, differential diagnosis and symptomatology. Although NCGS is defined by a reaction to gluten, other possible etiopathogenic mechanisms have been described, such as an inadequate response to other components of wheat or to FODMAPs, with the term non-celiac sensitivity to wheat recently being extended. There are contradictory results on the validity of the diagnostic protocol of the Salerno experts. Evidence on diagnostic biomarkers for NCGS is scarce, although some studies indicate the following: antigliadin antibodies, zonulin, ALCAT test, micro-RNA, incRNA and certain cytokines. In NCGS, abdominal pain and fatigue are the most common symptoms. In addition, altered nutritional status is common. In conclusion, more research on NCGS is needed to improve understanding of its etiopathogenesis and clinical features.